
Two small balls having equal positive charges Q on each are suspended by two insulating strings of equal length L from a hook fixed to a stand. The whole set up is taken in a satellite into space where there is no gravity (state of weightlessness). The angle between the two strings is… and the tension in each string is….. Newton.
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: We know that the like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. When charges are at rest, the force between them is given by Coulomb's law.
Formula used:
According to coulomb’s law, the magnitude of electrostatic force between the charges is given by,
$F \propto \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
$F = k\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$ …………. (1)
Where $k$ is a constant of proportionality called electrostatic force constant. $F$ is the force, ${q_1}{q_2}$ charges, $d$ is the distance
We have $k = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}$
Substituting the value of $k$ is equation 1 we get,
From equation (1), $F = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$ ……………(2)
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider two positive charges $ + Q$ is suspended by a two insulating string and charges are separated.
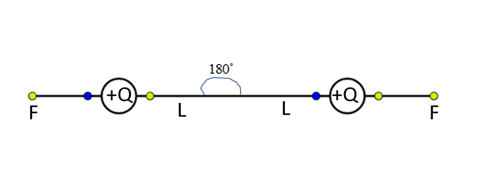
By a distance $L$ from the fixed-point O. Now we can observe the force of repulsion between the charges and they are trying to move away from each other by applying force F.
Now the whole set up is taken in a satellite into space where there is no gravity (state of weightlessness), then \[mg = 0\]
In the absence of gravitational force, they stand horizontal and opposite to each other at an angle ${180^ \circ }$.
Therefore, the angle between the two strings is ${180^ \circ }$.
The Force of repulsion between the positive charges is $F$, which equal to the tension in the string
Thus electrostatic force=tension in the string
Since there is no gravity.
We are aware of the coulomb’s law; it states that the electrostatic force between two stationary point charges is directly proportional to the product of their magnitudes and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
Electrostatic force, $F = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Then, using the equation, where, ${q_1} = Q$, ${q_2} = Q$ and $r = 2L = $ distance between two charges.
We get,
$F = T$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{{{{\left( {2L} \right)}^2}}}$
$\therefore $ Tension in each string $T = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{{\left( {4{L^2}} \right)}}$
Note:
Coulomb’s force will be repulsive or attractive depending upon whether the charges are like or unlike charges. Further, the force always acts along the line joining the centers of the two charges.
The electrostatic force is strongest compare to gravitational force. The weight of a body is measured by the reaction of the surface which supports the body. The absence of a reaction on a body produces weightlessness.
Formula used:
According to coulomb’s law, the magnitude of electrostatic force between the charges is given by,
$F \propto \dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
$F = k\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$ …………. (1)
Where $k$ is a constant of proportionality called electrostatic force constant. $F$ is the force, ${q_1}{q_2}$ charges, $d$ is the distance
We have $k = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}$
Substituting the value of $k$ is equation 1 we get,
From equation (1), $F = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$ ……………(2)
Complete step by step answer:
Let us consider two positive charges $ + Q$ is suspended by a two insulating string and charges are separated.

By a distance $L$ from the fixed-point O. Now we can observe the force of repulsion between the charges and they are trying to move away from each other by applying force F.
Now the whole set up is taken in a satellite into space where there is no gravity (state of weightlessness), then \[mg = 0\]
In the absence of gravitational force, they stand horizontal and opposite to each other at an angle ${180^ \circ }$.
Therefore, the angle between the two strings is ${180^ \circ }$.
The Force of repulsion between the positive charges is $F$, which equal to the tension in the string
Thus electrostatic force=tension in the string
Since there is no gravity.
We are aware of the coulomb’s law; it states that the electrostatic force between two stationary point charges is directly proportional to the product of their magnitudes and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
Electrostatic force, $F = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{{q_1}{q_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$
Then, using the equation, where, ${q_1} = Q$, ${q_2} = Q$ and $r = 2L = $ distance between two charges.
We get,
$F = T$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{{{{\left( {2L} \right)}^2}}}$
$\therefore $ Tension in each string $T = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{{Q^2}}}{{\left( {4{L^2}} \right)}}$
Note:
Coulomb’s force will be repulsive or attractive depending upon whether the charges are like or unlike charges. Further, the force always acts along the line joining the centers of the two charges.
The electrostatic force is strongest compare to gravitational force. The weight of a body is measured by the reaction of the surface which supports the body. The absence of a reaction on a body produces weightlessness.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




