
Two tetrahedral dice with faces marked 1, 2, 3 and 4 are thrown. The score obtained is the sum of the numbers on the bottom face. Calculate the probability distribution for the score obtained and how?
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: A tetrahedral is a 3-Dimensional object which has four faces. So, we use this concept and concept of probability to solve this problem. A probability distribution table gives us the information about probabilities of happening of different possibilities of an event. So using probability distribution we will get the required solution.
Complete step by step answer:
In mathematics, probability is defined as the occurrence of a random event. It is also defined as the ratio of number of favorable outcomes to total number of outcomes.
So, \[P(E) = \dfrac{{{\text{number of favorable outcomes}}}}{{{\text{total number of outcomes}}{\text{.}}}}\] is the probability of an event E.
If the probability of an event is 0, then the event doesn’t happen.
If the probability of an event is 1, then it will happen for sure.
Now if two tetrahedral dice are rolled at a time, we get the possible outcomes as
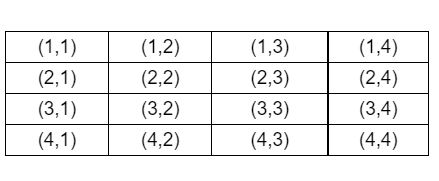
There are a total 16 possible outcomes.
So, if we add the numbers on the bottom faces of the tetrahedral, we get the scores.
And the least score possible is \[1 + 1 = 2\]
And the highest score is \[4 + 4 = 8\]
So, if we roll two tetrahedral dice, then the possible scores that we can get are
\[2,3,4,5,6,7{\text{ and }}8\]
So, the probability of getting score 2 is \[P(2)\] . So, the outcome in which the score is two is (1,1)
So, \[P(2) = \dfrac{1}{{16}}\]
Probability of getting score 3 is \[P(3)\] . And the outcomes in which the score is 3 are (1,2) and (2,1)
So, \[P(3) = \dfrac{2}{{16}}\] \[ = \dfrac{1}{8}\]
Probability of getting score 4 is \[P(4)\] . And the outcomes in which the score is 4 are (1,3), (2,2) and (3,1)
So, \[P(4) = \dfrac{3}{{16}}\]
Probability of getting a score 5 is \[P(5)\] . And the outcomes in which the score is 5 are (1,4), (2,3), (3,2) and (4,1)
So, \[P(5) = \dfrac{4}{{16}}\] \[ = \dfrac{1}{4}\]
Probability of getting a score 6 is \[P(6)\] . And the outcomes in which the score is 6 are (2,4), (3,3) and (4,2)
So, \[P(6) = \dfrac{3}{{16}}\]
Probability of getting a score 7 is \[P(7)\] . And the outcomes in which the score is 7 are (3,4) and (4,3)
So, \[P(7) = \dfrac{2}{{16}}\] \[ = \dfrac{1}{8}\]
Probability of getting score 8 is \[P(8)\] . And the outcome in which the score is 8 is (4,4)
So, \[P(8) = \dfrac{1}{{16}}\]
On tabulating these values, we get probability distribution table as
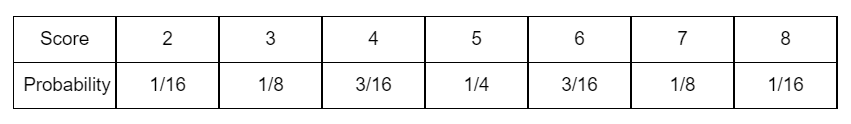
Note:
Make a note that the probability always lies in the range [0,1]. So, if you get a negative value or a value greater than 1, then you have made a mistake in your solution. And also remember that the sum of probabilities of random possibilities of an event is always equal to 1.
So, here,
\[ \Rightarrow P(2) + P(3) + P(4) + P(5) + P(6) + P(7) + P(8) = \dfrac{1}{{16}} + \dfrac{2}{{16}} + \dfrac{3}{{16}} + \dfrac{4}{{16}} + \dfrac{3}{{16}} + \dfrac{2}{{16}} + \dfrac{1}{{16}} = 1\]
Complete step by step answer:
In mathematics, probability is defined as the occurrence of a random event. It is also defined as the ratio of number of favorable outcomes to total number of outcomes.
So, \[P(E) = \dfrac{{{\text{number of favorable outcomes}}}}{{{\text{total number of outcomes}}{\text{.}}}}\] is the probability of an event E.
If the probability of an event is 0, then the event doesn’t happen.
If the probability of an event is 1, then it will happen for sure.
Now if two tetrahedral dice are rolled at a time, we get the possible outcomes as

There are a total 16 possible outcomes.
So, if we add the numbers on the bottom faces of the tetrahedral, we get the scores.
And the least score possible is \[1 + 1 = 2\]
And the highest score is \[4 + 4 = 8\]
So, if we roll two tetrahedral dice, then the possible scores that we can get are
\[2,3,4,5,6,7{\text{ and }}8\]
So, the probability of getting score 2 is \[P(2)\] . So, the outcome in which the score is two is (1,1)
So, \[P(2) = \dfrac{1}{{16}}\]
Probability of getting score 3 is \[P(3)\] . And the outcomes in which the score is 3 are (1,2) and (2,1)
So, \[P(3) = \dfrac{2}{{16}}\] \[ = \dfrac{1}{8}\]
Probability of getting score 4 is \[P(4)\] . And the outcomes in which the score is 4 are (1,3), (2,2) and (3,1)
So, \[P(4) = \dfrac{3}{{16}}\]
Probability of getting a score 5 is \[P(5)\] . And the outcomes in which the score is 5 are (1,4), (2,3), (3,2) and (4,1)
So, \[P(5) = \dfrac{4}{{16}}\] \[ = \dfrac{1}{4}\]
Probability of getting a score 6 is \[P(6)\] . And the outcomes in which the score is 6 are (2,4), (3,3) and (4,2)
So, \[P(6) = \dfrac{3}{{16}}\]
Probability of getting a score 7 is \[P(7)\] . And the outcomes in which the score is 7 are (3,4) and (4,3)
So, \[P(7) = \dfrac{2}{{16}}\] \[ = \dfrac{1}{8}\]
Probability of getting score 8 is \[P(8)\] . And the outcome in which the score is 8 is (4,4)
So, \[P(8) = \dfrac{1}{{16}}\]
On tabulating these values, we get probability distribution table as

Note:
Make a note that the probability always lies in the range [0,1]. So, if you get a negative value or a value greater than 1, then you have made a mistake in your solution. And also remember that the sum of probabilities of random possibilities of an event is always equal to 1.
So, here,
\[ \Rightarrow P(2) + P(3) + P(4) + P(5) + P(6) + P(7) + P(8) = \dfrac{1}{{16}} + \dfrac{2}{{16}} + \dfrac{3}{{16}} + \dfrac{4}{{16}} + \dfrac{3}{{16}} + \dfrac{2}{{16}} + \dfrac{1}{{16}} = 1\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




