
What type of image is formed by a plane mirror?
A. Upright
B. Magnified
C. Inverted
D. All of these
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: Plane mirror has a flat reflecting surface and the angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence. The image formed by a plane mirror is located in front of the mirror but appears to be formed behind the plane in which the mirror lies. To find the nature of the image formed by a plane mirror, we need to study the reflection through a plane mirror.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A plane mirror is a type of mirror with a flat or planar reflective surface. For the light rays striking a plane mirror, the angle of reflection always equals the angle of incidence. The angle of the incidence is defined as the angle between the incident ray and the surface normal, which is an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface. Thus, the angle of reflection is defined as the angle between the reflected ray and the normal. A collimated beam of incident light does not spread out after reflection from a plane mirror, except in case of diffraction effects.
A plane mirror makes an image of the object in front of the mirror and these images appear to be formed behind the plane in which the mirror lies. A straight line drawn from the part of an object to the corresponding part of its image makes a right angle with, and is bisected by, the surface of the plane mirror.
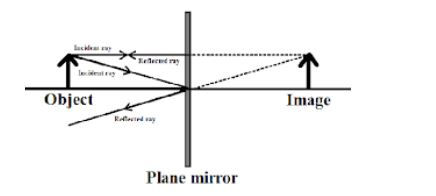
The image formed by a plane mirror is always virtual, meaning that the light rays do not actually come from the image but appear to do so, upright, and of the same shape and size as of the object it is reflecting. A virtual image is basically a copy of an object being formed at the location from which the light rays appear to come. However, the image is a laterally-inverted, called "mirror image" of the object. If a person is reflected in a plane mirror, the image of his left hand would appear to be the right hand of the image.
A plane mirror always forms a virtual, upright and the same sized image of the object.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Plane mirrors are the only type of optical mirrors for which a real object will always produce an image that is virtual, erect, and of the same size as the object. The virtual objects however, produce real images. The focal length of a plane mirror is defined as infinity, and its optical power is zero.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A plane mirror is a type of mirror with a flat or planar reflective surface. For the light rays striking a plane mirror, the angle of reflection always equals the angle of incidence. The angle of the incidence is defined as the angle between the incident ray and the surface normal, which is an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface. Thus, the angle of reflection is defined as the angle between the reflected ray and the normal. A collimated beam of incident light does not spread out after reflection from a plane mirror, except in case of diffraction effects.
A plane mirror makes an image of the object in front of the mirror and these images appear to be formed behind the plane in which the mirror lies. A straight line drawn from the part of an object to the corresponding part of its image makes a right angle with, and is bisected by, the surface of the plane mirror.

The image formed by a plane mirror is always virtual, meaning that the light rays do not actually come from the image but appear to do so, upright, and of the same shape and size as of the object it is reflecting. A virtual image is basically a copy of an object being formed at the location from which the light rays appear to come. However, the image is a laterally-inverted, called "mirror image" of the object. If a person is reflected in a plane mirror, the image of his left hand would appear to be the right hand of the image.
A plane mirror always forms a virtual, upright and the same sized image of the object.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Plane mirrors are the only type of optical mirrors for which a real object will always produce an image that is virtual, erect, and of the same size as the object. The virtual objects however, produce real images. The focal length of a plane mirror is defined as infinity, and its optical power is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




