
What do you understand about food web? Describe a food web with the help of a diagrammatic representation.
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: The food web consists of all food chains in a single ecosystem. Multiple food chains connect all creatures in the ecosystem. Each food chain represents a potential path for energy and nutrients as they travel through the environment. The food web is made up of all of the ecosystem's interconnected and overlapping food chains.
Complete answer:
> The food web is a graphical representation of what consumes what and the inherent connection of food chains in an ecological community.
> A food web consists of a series of interlocking food chains. Each food chain is a description diagram, which includes a series of arrows.
> Each arrow points from one species to another, representing the flow of food energy of a group of organisms that feed on another organism.
> Basically, the food web represents the food relationships within the community. It also involves the transfer of dietary energy from plant sources through herbivores to carnivores.
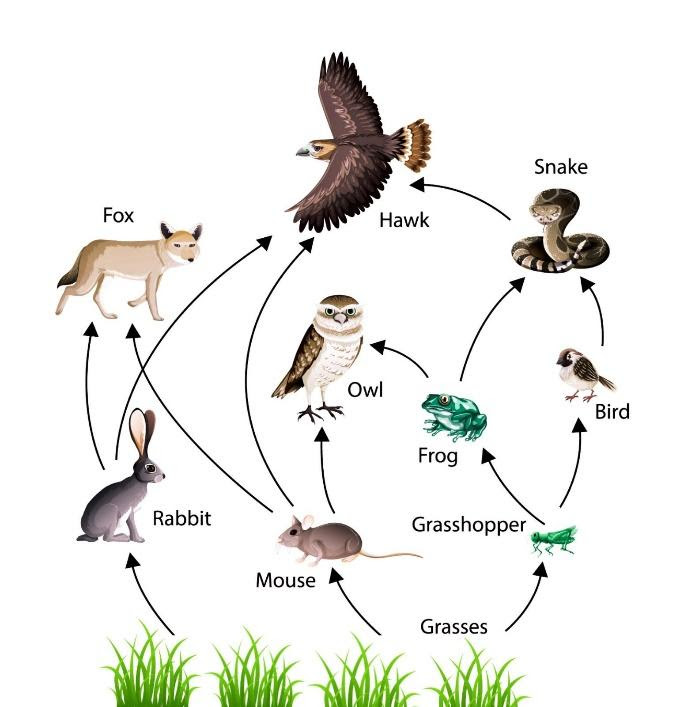
> The figure above shows the food web in an ecosystem. In this food web, grasshoppers, mice and rabbits feed on grass; birds and frogs feed on grasshoppers; snakes feed on both birds and frogs; owls feed on frogs and mice; foxes feed on rabbits and mice and finally hawks feed on snakes, rabbits and mice.
> Most food webs are complex and involve many species, with strong and weak interactions between them. For example, the natural enemies of scorpions in desert ecosystems may be golden eagles, owls, roadrunners or foxes.
Note:
Herbivory, carnivory, scavenging, and parasitism are some of the numerous forms of food relationships that exist. Some organic substances eaten by heterotrophs, such as sugar, provide energy. Autotrophs and heterotrophs appear in a wide range of sizes, ranging from microscopic to several tones, from cyanobacteria to massive redwoods, and from viruses and bdellovibrio to enormous blue whales.
Complete answer:
> The food web is a graphical representation of what consumes what and the inherent connection of food chains in an ecological community.
> A food web consists of a series of interlocking food chains. Each food chain is a description diagram, which includes a series of arrows.
> Each arrow points from one species to another, representing the flow of food energy of a group of organisms that feed on another organism.
> Basically, the food web represents the food relationships within the community. It also involves the transfer of dietary energy from plant sources through herbivores to carnivores.

> The figure above shows the food web in an ecosystem. In this food web, grasshoppers, mice and rabbits feed on grass; birds and frogs feed on grasshoppers; snakes feed on both birds and frogs; owls feed on frogs and mice; foxes feed on rabbits and mice and finally hawks feed on snakes, rabbits and mice.
> Most food webs are complex and involve many species, with strong and weak interactions between them. For example, the natural enemies of scorpions in desert ecosystems may be golden eagles, owls, roadrunners or foxes.
Note:
Herbivory, carnivory, scavenging, and parasitism are some of the numerous forms of food relationships that exist. Some organic substances eaten by heterotrophs, such as sugar, provide energy. Autotrophs and heterotrophs appear in a wide range of sizes, ranging from microscopic to several tones, from cyanobacteria to massive redwoods, and from viruses and bdellovibrio to enormous blue whales.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




