
What do you understand by special type of inflorescence? Describe them with diagrams and examples.
Answer
582k+ views
Hint: The type of inflorescence which cannot be included in racemose type or cymose type. They have modified forms of cymose inflorescence. An axis bearing a bunch of flowers is known as inflorescence. Based on the nature of the peduncle and the arrangement of flowers, they are classified into racemose, cymose, and special.
Complete answer:
Special types of the inflorescence are strictly neither racemose nor cymose. At the same time, they have modified forms of the cymose type. They include hypanthodium, verticillaster, cyathium, and thyrsus. Hypanthodium is the condense type of cymose inflorescence, more precisely a modification of the capitulum, characteristic of Ficus. Here, the peduncle forms a hollow, fleshy, and flask-shaped receptacle. Verticillaster is a compound inflorescence, consisting of two axillary opposite cymose inflorescences developing one on either side and meeting around the stem. It is typically found in plants with opposite leaves and is characteristic of family Labiate. In this case, two clusters of sessile and opposite cymose inflorescences develop from the axils of opposite leaves as a dichasium. The subsequent development of a monochasial scorpioid nature. During this, they bend around the stem and meet together. So at each node, there is a cluster of flowers completely surrounding the stem.
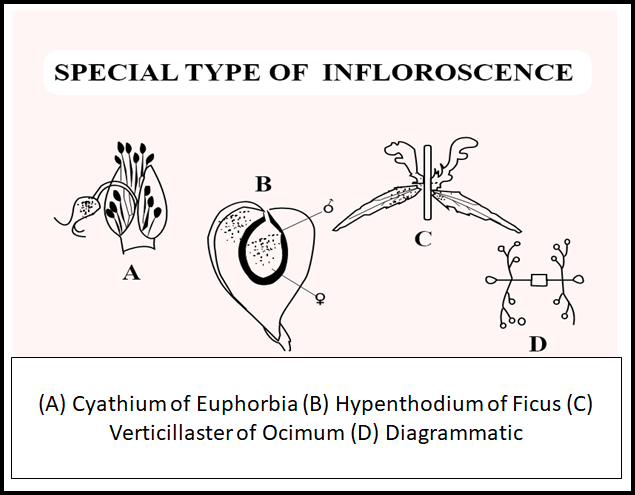
Cyathium is a highly condensed type of cymose inflorescence. It looks like a single flower, within an involucral cup, formed by the fusion of bracts. The peduncle is very much reduced. Thyrsus is a mixed inflorescence, composed of a number of simple cymes arranged in a racemose manner. There is a main peduncle giving rise to secondary inflorescences on the axils of bracts in acropetal succession. Each secondary peduncle has two bracteoles. From the axils of each Bracteole a single flower arises. Thus, each secondary peduncle forms a simple cyme of three flowers of which the central one is the oldest e.g. Ocimum.
Additional Information:
- In Hypanthodium the receptacle has a terminal opening, called the ostiole for the entry of insect pollinators. The ostiole is guarded by numerous incurved hairs. Many small, sessile, and unisexual flowers are arranged along the inner walls of the receptacle.
- The flowers include male, female, and sterile flowers. Male flowers are seen near the ostiole, the sterile flower in the middle, and the female flower towards the base.
- Cyathium terminally bears a single highly reduced and central female flower, surrounded by five scorpioid cymes of reduced male flowers.
- Female flowers are long- stalked and naked, and male flowers are short- stalked and naked and each of them is reduced to a stamen. Cyathium is often described as a “cyme of cymes”. It is the characteristic inflorescence of the genera Euphorbia. e.g., Acalypha, poinsettia,etc.
Note:
- Racemose is also called an indefinite or intermediate inflorescence. In it, the main axis does not end in a flower and is capable of unlimited growth.
- Flowers are arranged on either side of it in acropetal succession. The racemose inflorescence is of several kinds. The commonest ones among them are raceme, panicle, corymb, spike, spadix, umbel, capitulum, and catkin.
- Cymose inflorescence corresponds to the sympodial branching of the vegetative shoot. Here, the peduncle has only limited growth.
Complete answer:
Special types of the inflorescence are strictly neither racemose nor cymose. At the same time, they have modified forms of the cymose type. They include hypanthodium, verticillaster, cyathium, and thyrsus. Hypanthodium is the condense type of cymose inflorescence, more precisely a modification of the capitulum, characteristic of Ficus. Here, the peduncle forms a hollow, fleshy, and flask-shaped receptacle. Verticillaster is a compound inflorescence, consisting of two axillary opposite cymose inflorescences developing one on either side and meeting around the stem. It is typically found in plants with opposite leaves and is characteristic of family Labiate. In this case, two clusters of sessile and opposite cymose inflorescences develop from the axils of opposite leaves as a dichasium. The subsequent development of a monochasial scorpioid nature. During this, they bend around the stem and meet together. So at each node, there is a cluster of flowers completely surrounding the stem.

Cyathium is a highly condensed type of cymose inflorescence. It looks like a single flower, within an involucral cup, formed by the fusion of bracts. The peduncle is very much reduced. Thyrsus is a mixed inflorescence, composed of a number of simple cymes arranged in a racemose manner. There is a main peduncle giving rise to secondary inflorescences on the axils of bracts in acropetal succession. Each secondary peduncle has two bracteoles. From the axils of each Bracteole a single flower arises. Thus, each secondary peduncle forms a simple cyme of three flowers of which the central one is the oldest e.g. Ocimum.
Additional Information:
- In Hypanthodium the receptacle has a terminal opening, called the ostiole for the entry of insect pollinators. The ostiole is guarded by numerous incurved hairs. Many small, sessile, and unisexual flowers are arranged along the inner walls of the receptacle.
- The flowers include male, female, and sterile flowers. Male flowers are seen near the ostiole, the sterile flower in the middle, and the female flower towards the base.
- Cyathium terminally bears a single highly reduced and central female flower, surrounded by five scorpioid cymes of reduced male flowers.
- Female flowers are long- stalked and naked, and male flowers are short- stalked and naked and each of them is reduced to a stamen. Cyathium is often described as a “cyme of cymes”. It is the characteristic inflorescence of the genera Euphorbia. e.g., Acalypha, poinsettia,etc.
Note:
- Racemose is also called an indefinite or intermediate inflorescence. In it, the main axis does not end in a flower and is capable of unlimited growth.
- Flowers are arranged on either side of it in acropetal succession. The racemose inflorescence is of several kinds. The commonest ones among them are raceme, panicle, corymb, spike, spadix, umbel, capitulum, and catkin.
- Cymose inflorescence corresponds to the sympodial branching of the vegetative shoot. Here, the peduncle has only limited growth.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




