
Uniform magnetic field B is acting vertically downwards as shown in the figure. A circuit of unthreaded wire with the resistance R is kept in the magnetic field. A conductor of the length l is placed on the circuit and is moving in x – direction.
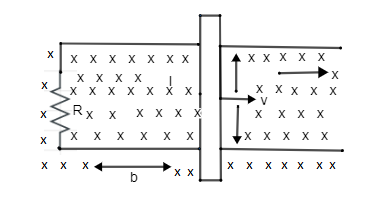
A. If the conductor is moving in the positive x – direction with velocity v what is the change in flux in one second.
B. What is the magnitude and the direction of the current in the circuit?
C. What is the power dissipation in the resistor?

Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: This question is similar to concept motional EMF in loop by generated we can solve this question by using formula $\left| e \right|=\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$ and right hand thumb rule and for section (C) we will use the formula of the power $P={{I}^{2}}R$ to solve the question.
Formula used:
$\phi =B.A$
$\phi $ = flux
B =magnetic field
A = area
$\left| e \right|=\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$
e = EMF
$\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$ = change in the flux
$P={{I}^{2}}R$
P = power dissipation across resistance
I = current in the circuit
R = resistance
Complete step by step solution:
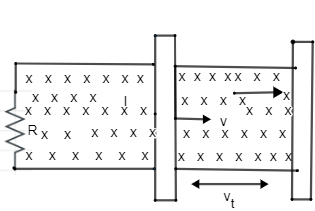
A).If the conductor is moving in positive x – direction with the velocity v what the change in the flux in one sec is.
$\to $ It is given that the time for displacement is
t = 1sec
We know that formula for the velocity
$v=\dfrac{displacement}{t}$
Hence
Displacement = $vt$
In time t distance travelled by the conductor is as shown in the figure
$vt......\left( 1 \right)$
Now change in the flux
$\left| e \right|=\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$
We know that the flux
$\phi =B.A$
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d\phi }{dt}=\dfrac{d(BA)}{dt} \\
& =A\times \dfrac{dB}{dt}.....(1) \\
\end{align}$
$\to $ Now for the area we will use the length l and distance travelled vt as shown in the figure.
$\to $So area,
$A=lvt.....\left( 2 \right)$
$\to $ Now substitute value of the equation (2) in equation (1)
$\left| e \right|=lvt\times \dfrac{dB}{dt}$
$\to $ Here magnetic field is constant across circuit
$\begin{align}
& \left| e \right|=l\times v\times 1\times B \\
& \left| e \right|=Bvl.....(3) \\
\end{align}$
B) Magnitude and the direction of the current
$\to $ We know that,
$I=\dfrac{\left| e \right|}{R}.....\left( 4 \right)$
$\to $ Now substitute value of the equation (3) in equation (4)
$I=\dfrac{Bvl}{R}....(5)$
$\to $ Now to know that direction of the current we will use thumb rule as magnetic field vertically downwards current direction will be
C) Power dissipation in the resistor:-
$\to $Power dissipation in resistor is given by below formula
$P={{I}^{2}}R.....(6)$
Now substitute value of the equation (5) in equation (6)
$\begin{align}
& P={{\left( \dfrac{Bvl}{R} \right)}^{2}}R \\
& P=\dfrac{{{B}^{2}}{{v}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}}{R} \\
\end{align}$
Note:
When we find direction of the current using the thumb rule we have to be careful of the direction of the magnetic field because in some cases it is vertically upwards.
Formula used:
$\phi =B.A$
$\phi $ = flux
B =magnetic field
A = area
$\left| e \right|=\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$
e = EMF
$\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$ = change in the flux
$P={{I}^{2}}R$
P = power dissipation across resistance
I = current in the circuit
R = resistance
Complete step by step solution:

A).If the conductor is moving in positive x – direction with the velocity v what the change in the flux in one sec is.
$\to $ It is given that the time for displacement is
t = 1sec
We know that formula for the velocity
$v=\dfrac{displacement}{t}$
Hence
Displacement = $vt$
In time t distance travelled by the conductor is as shown in the figure
$vt......\left( 1 \right)$
Now change in the flux
$\left| e \right|=\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}$
We know that the flux
$\phi =B.A$
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{d\phi }{dt}=\dfrac{d(BA)}{dt} \\
& =A\times \dfrac{dB}{dt}.....(1) \\
\end{align}$
$\to $ Now for the area we will use the length l and distance travelled vt as shown in the figure.
$\to $So area,
$A=lvt.....\left( 2 \right)$
$\to $ Now substitute value of the equation (2) in equation (1)
$\left| e \right|=lvt\times \dfrac{dB}{dt}$
$\to $ Here magnetic field is constant across circuit
$\begin{align}
& \left| e \right|=l\times v\times 1\times B \\
& \left| e \right|=Bvl.....(3) \\
\end{align}$
B) Magnitude and the direction of the current
$\to $ We know that,
$I=\dfrac{\left| e \right|}{R}.....\left( 4 \right)$
$\to $ Now substitute value of the equation (3) in equation (4)
$I=\dfrac{Bvl}{R}....(5)$
$\to $ Now to know that direction of the current we will use thumb rule as magnetic field vertically downwards current direction will be
C) Power dissipation in the resistor:-
$\to $Power dissipation in resistor is given by below formula
$P={{I}^{2}}R.....(6)$
Now substitute value of the equation (5) in equation (6)
$\begin{align}
& P={{\left( \dfrac{Bvl}{R} \right)}^{2}}R \\
& P=\dfrac{{{B}^{2}}{{v}^{2}}{{l}^{2}}}{R} \\
\end{align}$
Note:
When we find direction of the current using the thumb rule we have to be careful of the direction of the magnetic field because in some cases it is vertically upwards.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




