
Using VSEPR theory, draw the shape of $PC{l_5}$and $Br{F_5}$
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint:
To answer this question, we must find the hybridisation of the central atom and the arrangement of the bond pairs and lone pairs on the central atom. To do that, you must recall the VSEPR (Valence shell electron pair repulsion) theory. It proposes that all valence shell electrons surrounding the central atom arrange themselves in such a manner so as to be as far away from each other as possible to avoid repulsion between the electron pairs.
Complete step by step solution:
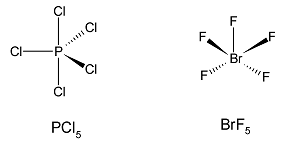
Considering $PC{l_5}$.
The atomic number of phosphorus is 15. It also has an empty $3d$ orbital and can thus use all the five electrons present for bonding. The ground state electron configuration for phosphorus is:
$P:\left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^3}3{d^0}$
One electron is excited to the $3d$orbital. The excited state configuration becomes:
$P:\left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^1}3{p^3}3{d^1}$
Phosphorus undergoes an $s{p^3}d$ hybridization. Now it has five hybrid orbitals available for bonding and no extra electrons. According to the VSEPR theory, three bonds are placed in an equatorial form and two remaining bonds are present axially perpendicular to the equatorial bonds. The shape of $PC{l_5}$is trigonal bipyramidal.
Considering $Br{F_5}$
Bromine is a group 17 element or a halogen. It has 7 valence electrons. It also has empty $d$ orbital and can increase its covalency to form five bonds. Two electrons from its valence $p$ orbital are excited to the $d$ orbital and the bromine atom undergoes a hybridisation of $s{p^3}{d^2}$. There are six electron pairs around the central bromine atom, out of which five are bond pairs and one is lone pair. According to VSEPR theory, the geometry of the molecule is octahedral but the shape is square pyramidal.
Note:
The atomic orbitals of an atom are mixed in order to produce equivalent orbitals during bond formation. This mixing of orbitals is known as hybridisation. The arrangement of these hybrid orbitals according to the VSEPR theory gives us the shape of the molecule.
To answer this question, we must find the hybridisation of the central atom and the arrangement of the bond pairs and lone pairs on the central atom. To do that, you must recall the VSEPR (Valence shell electron pair repulsion) theory. It proposes that all valence shell electrons surrounding the central atom arrange themselves in such a manner so as to be as far away from each other as possible to avoid repulsion between the electron pairs.
Complete step by step solution:
Considering $PC{l_5}$.
The atomic number of phosphorus is 15. It also has an empty $3d$ orbital and can thus use all the five electrons present for bonding. The ground state electron configuration for phosphorus is:
$P:\left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^2}3{p^3}3{d^0}$
One electron is excited to the $3d$orbital. The excited state configuration becomes:
$P:\left[ {Ne} \right]3{s^1}3{p^3}3{d^1}$
Phosphorus undergoes an $s{p^3}d$ hybridization. Now it has five hybrid orbitals available for bonding and no extra electrons. According to the VSEPR theory, three bonds are placed in an equatorial form and two remaining bonds are present axially perpendicular to the equatorial bonds. The shape of $PC{l_5}$is trigonal bipyramidal.
Considering $Br{F_5}$
Bromine is a group 17 element or a halogen. It has 7 valence electrons. It also has empty $d$ orbital and can increase its covalency to form five bonds. Two electrons from its valence $p$ orbital are excited to the $d$ orbital and the bromine atom undergoes a hybridisation of $s{p^3}{d^2}$. There are six electron pairs around the central bromine atom, out of which five are bond pairs and one is lone pair. According to VSEPR theory, the geometry of the molecule is octahedral but the shape is square pyramidal.

Note:
The atomic orbitals of an atom are mixed in order to produce equivalent orbitals during bond formation. This mixing of orbitals is known as hybridisation. The arrangement of these hybrid orbitals according to the VSEPR theory gives us the shape of the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




