
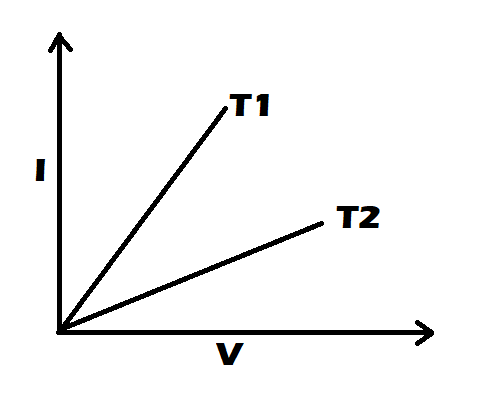
$V - I$ graph for a metallic wire at two different temperatures ${T_1}$ and ${T_2}$is shown in figure. Which of the two temperatures is higher and why?
A) ${T_1} > {T_2}$
B) ${T_1} < {T_2}$
C) ${T_1} = {T_2}$
D) ${T_1} = 2{T_2}$

Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: The main key to these solutions is observation of the graph. After deducing the relation if we just fix any one value then we can easily deduce by obtaining a specific quantity for both at the same point by simply a line passing through both points.
Complete step by step answer:
The slope of the lines will give the inverse relation of the resistance. Resistance of the material has the property of an increase in the resistance with increase in the temperature. This happens due to an increase in the collision of the molecules with the increase of the heat energy.
So as ${T_2}$has the smaller slope so it have high resistance and subsequently ${T_2} > {T_1}$
Now if V is constant then that makes ${R_1} < {R_2}$for a specific V
Thus, ${T_1} < {T_2}$due to inverse relation.
Note: Basically as the temperature increases there is an increase in collisions inside the matter(resistor) and hence there is more hindrance to the flow of electrons and charges, which in the end increases the resistivity of the material hence increasing the resistance. For the same voltage, increase in resistance decreases the current as we can see in the graph for a vertical line, for same voltage at T2 there is low current with respect to current at same voltage at T1.
Complete step by step answer:
The slope of the lines will give the inverse relation of the resistance. Resistance of the material has the property of an increase in the resistance with increase in the temperature. This happens due to an increase in the collision of the molecules with the increase of the heat energy.
So as ${T_2}$has the smaller slope so it have high resistance and subsequently ${T_2} > {T_1}$
Now if V is constant then that makes ${R_1} < {R_2}$for a specific V
Thus, ${T_1} < {T_2}$due to inverse relation.
Note: Basically as the temperature increases there is an increase in collisions inside the matter(resistor) and hence there is more hindrance to the flow of electrons and charges, which in the end increases the resistivity of the material hence increasing the resistance. For the same voltage, increase in resistance decreases the current as we can see in the graph for a vertical line, for same voltage at T2 there is low current with respect to current at same voltage at T1.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




