
How do you verify the first law of reflection of light with an experiment?
Answer
588k+ views
Hint:From the concept of the first law of reflection of light we can say that angle between the incident ray and normal to the mirror is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and normal to the mirror.
Complete step by step answer:
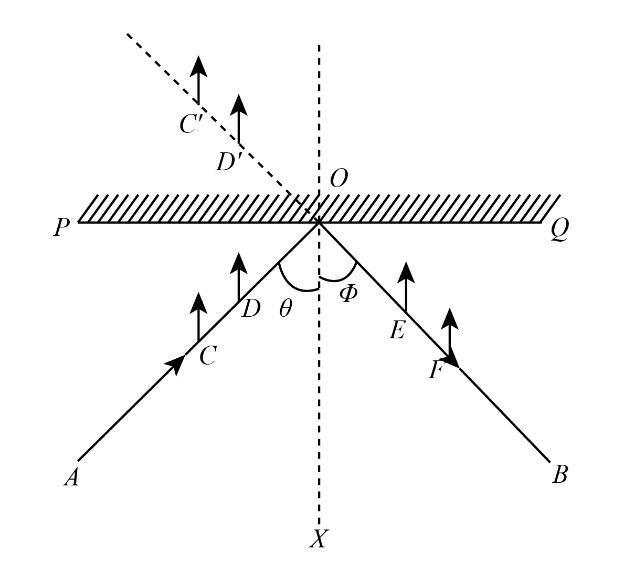
We will perform this experiment in a step by step manner as follows:
1. Let us take a white drawing sheet which is placed on a drawing board with the help of clamps.
2. We will draw a straight line PQ which is passing through the centre of the drawing sheet.
3. After this we will draw a perpendicular OX to PQ at the centre O.
4. Now we will draw a line OA making an angle \[\theta \] with normal OX, and this angle is known as angle of incidence.
6. After this, we will fix two pins at point C and D respectively in such a way that these points lie on OA.
7. We will place a mirror along the line PQ and observe that the image of pin C and pin D is represented as C’ and D’.
8. Now we will fix two more pins E and F in such a way that they lie on the line joining points C’ and D’.
9. If we measure the angle between the line joining the points E & F and normal OX, we will find that this angle is equal to the angle of incidence and called as the angle of reflection and denoted as \[\phi \].
10. We can also repeat this experiment for different values of angle of incidence, and again we will find that the angle of incidence is equal to angle on reflection.
Therefore, we can say that angle made by incident ray with the normal is equal to the angle made by reflected ray with the normal. Hence, the first law is verified.
Note: Fix pins C, D, E and F in such a way that pin C and pin D lie exactly on the line OA and pin E and pin F lie exactly on the line of image of pin C and D. Measure the angle of incidence and reflection carefully; however, human error can be neglected.
Complete step by step answer:

We will perform this experiment in a step by step manner as follows:
1. Let us take a white drawing sheet which is placed on a drawing board with the help of clamps.
2. We will draw a straight line PQ which is passing through the centre of the drawing sheet.
3. After this we will draw a perpendicular OX to PQ at the centre O.
4. Now we will draw a line OA making an angle \[\theta \] with normal OX, and this angle is known as angle of incidence.
6. After this, we will fix two pins at point C and D respectively in such a way that these points lie on OA.
7. We will place a mirror along the line PQ and observe that the image of pin C and pin D is represented as C’ and D’.
8. Now we will fix two more pins E and F in such a way that they lie on the line joining points C’ and D’.
9. If we measure the angle between the line joining the points E & F and normal OX, we will find that this angle is equal to the angle of incidence and called as the angle of reflection and denoted as \[\phi \].
10. We can also repeat this experiment for different values of angle of incidence, and again we will find that the angle of incidence is equal to angle on reflection.
Therefore, we can say that angle made by incident ray with the normal is equal to the angle made by reflected ray with the normal. Hence, the first law is verified.
Note: Fix pins C, D, E and F in such a way that pin C and pin D lie exactly on the line OA and pin E and pin F lie exactly on the line of image of pin C and D. Measure the angle of incidence and reflection carefully; however, human error can be neglected.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




