
What are the 22 skull bones?
Answer
480.3k+ views
Hint: The skull is a bony structure,it forms the head in vertebrates. It supports the structures of the face and it creates a protective cavity for the brain. Our 22 Skull bones are divided into two parts, the first one is Cranial Bones and the second part is Facial Bones.
Complete answer:
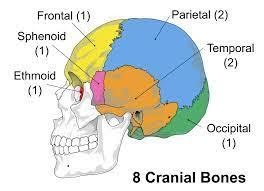
Cranial Bones (Total 8 bones):-
Frontal (1 bone) - The frontal bone is a bowl-shaped bone in the frontal or forehead region of the skull. It is located superior to the nasal bones and anterior to the parietal bones. It creates the forehead and upper wall of Orbit (eye cavity).
Parietal (2 bones) -These bones are usually present in the posterior of the frontal bone and in the both side near to the midline. They form the skull roof, which is a pair of bones that cover the brain, eyes and nostrils. The parietal bones are connected with several other bones in the skull through sutures.
Occipital (1 Bone) –Occipital bone forms the base of the skull posteriorly. There is a large oval foramen or opening in the occipital bone that is called the foramen magnum. This opening is for passage of the spinal cord. This bone is the only cranial bone that connects with the cervical spine.
Temporal (2 bones) - The temporal bones are laterally situated at both sides and base of the skull. These bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples and create the structures of the ears.
Sphenoid (1 bone) – This is a part of the neurocranium. It is situated medially towards the front of the skull and anteriorly to the basilar part of the occipital bone. This bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit of the eye cavity.
Ethmoid (1 bone) - It is situated between the two orbital cavities and at the roof of the nasal cavity. It forms the medial wall of the orbital fossa and also forms part of the anterior cranial fossa, where it separates the nasal cavity inferiorly and from the cranial cavity superiorly.
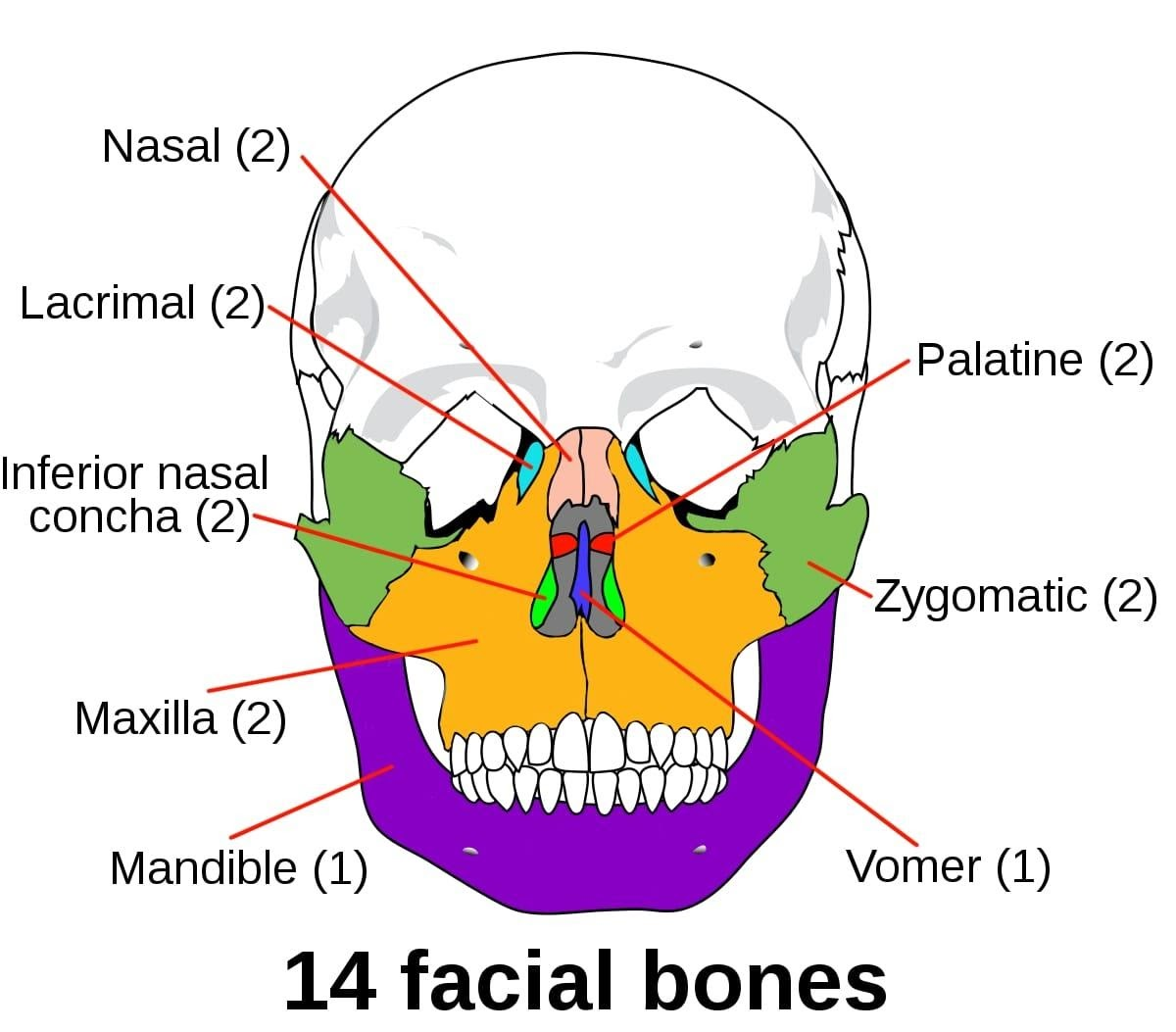
Facial Bones (14 bones):-
Maxilla (2 bones)– These bones help to make up the skull. It is specifically located medially on our skull and forms the upper jaw. These bones separate the nasal and oral cavities and contain the maxillary sinuses that are located on each side of the nose.
Zygomatic (2 bones) - Zygomatic bones are also called ass cheekbones or malar bones. These bones are diamond-shaped bones. Situated at the bottom and lateral to the orbitat the widest part of the cheek. It articulates with the frontal bone at the outer edge of the orbital facet and the sphenoid and maxilla within the orbit.
Mandible (1 bone) - The mandible is the largest and strongest bone of the face. It is located anterior-inferiorly in the facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and acts as a receptacle or holder for the lower teeth. It also articulates on either side with the temporal bone and forms the temporomandibular joint.
Nasal (2 bones)–Nasal bones are two small bones that are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and their junction forms the bridge of the superior one third of our nose.
Platine (2 bones) - These bones are situated posteriorly to the nasal cavity between the maxilla and the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone. They take part to create the walls of three cavities: the lateral walls and the floor of the nasal cavity, the floor of the orbits and the roof of the mouth.
Inferior nasal concha (2 bones) - the inferior nasal concha is a bony structure. It forms the nasal septum, which separates the nasal cavity into two symmetrical and bilateral anatomical caves.
Lacrimal (2 bones) - The lacrimal bones are small and fragile bones of the facial skeleton.One lacrimal bone is roughly the size of the little finger’s nail. It is anatomically situated at the anterior part of the medial wall of the orbit.
Vomer (1 bone)–It is a small and thin bone. This trapezoidal bone is the part of the nasal septum.
Note:
Except Mandible, all the skull bones are joined together by the sutures. These sutures or joints are immovable joints formed by bony ossification with Sharpey's fibres, which gives them some flexibility. These joints are also called synarthrodial joints. Sometimesthere can be extra bone pieces within the suture, they are known as sutural bones. These bony parts are also known as wormian bones.Generally these bones are found in the course of the lambdoid suture.
Complete answer:
Cranial Bones (Total 8 bones):-
Frontal (1 bone) - The frontal bone is a bowl-shaped bone in the frontal or forehead region of the skull. It is located superior to the nasal bones and anterior to the parietal bones. It creates the forehead and upper wall of Orbit (eye cavity).
Parietal (2 bones) -These bones are usually present in the posterior of the frontal bone and in the both side near to the midline. They form the skull roof, which is a pair of bones that cover the brain, eyes and nostrils. The parietal bones are connected with several other bones in the skull through sutures.
Occipital (1 Bone) –Occipital bone forms the base of the skull posteriorly. There is a large oval foramen or opening in the occipital bone that is called the foramen magnum. This opening is for passage of the spinal cord. This bone is the only cranial bone that connects with the cervical spine.
Temporal (2 bones) - The temporal bones are laterally situated at both sides and base of the skull. These bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples and create the structures of the ears.
Sphenoid (1 bone) – This is a part of the neurocranium. It is situated medially towards the front of the skull and anteriorly to the basilar part of the occipital bone. This bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit of the eye cavity.
Ethmoid (1 bone) - It is situated between the two orbital cavities and at the roof of the nasal cavity. It forms the medial wall of the orbital fossa and also forms part of the anterior cranial fossa, where it separates the nasal cavity inferiorly and from the cranial cavity superiorly.

Facial Bones (14 bones):-
Maxilla (2 bones)– These bones help to make up the skull. It is specifically located medially on our skull and forms the upper jaw. These bones separate the nasal and oral cavities and contain the maxillary sinuses that are located on each side of the nose.
Zygomatic (2 bones) - Zygomatic bones are also called ass cheekbones or malar bones. These bones are diamond-shaped bones. Situated at the bottom and lateral to the orbitat the widest part of the cheek. It articulates with the frontal bone at the outer edge of the orbital facet and the sphenoid and maxilla within the orbit.
Mandible (1 bone) - The mandible is the largest and strongest bone of the face. It is located anterior-inferiorly in the facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and acts as a receptacle or holder for the lower teeth. It also articulates on either side with the temporal bone and forms the temporomandibular joint.
Nasal (2 bones)–Nasal bones are two small bones that are placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and their junction forms the bridge of the superior one third of our nose.
Platine (2 bones) - These bones are situated posteriorly to the nasal cavity between the maxilla and the pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone. They take part to create the walls of three cavities: the lateral walls and the floor of the nasal cavity, the floor of the orbits and the roof of the mouth.
Inferior nasal concha (2 bones) - the inferior nasal concha is a bony structure. It forms the nasal septum, which separates the nasal cavity into two symmetrical and bilateral anatomical caves.
Lacrimal (2 bones) - The lacrimal bones are small and fragile bones of the facial skeleton.One lacrimal bone is roughly the size of the little finger’s nail. It is anatomically situated at the anterior part of the medial wall of the orbit.
Vomer (1 bone)–It is a small and thin bone. This trapezoidal bone is the part of the nasal septum.

Note:
Except Mandible, all the skull bones are joined together by the sutures. These sutures or joints are immovable joints formed by bony ossification with Sharpey's fibres, which gives them some flexibility. These joints are also called synarthrodial joints. Sometimesthere can be extra bone pieces within the suture, they are known as sutural bones. These bony parts are also known as wormian bones.Generally these bones are found in the course of the lambdoid suture.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




