
What is a cellular apparatus?
Answer
481.2k+ views
Hint: Cell biology is a discipline of biology that focuses on the cell, including its kinds, structure, functions, and interactions with other cells. Cell biology is also known as cytology, which comes from the Greek word kytos, which means vessel. All other biological sciences, such as genetics, molecular biology, and immunology, rely on cell biology. Because every living species is made up of cells, the cell is referred to as a fundamental unit of life. The word "cell" comes from the Latin word "cellus," which means "little room." Robert Hooke, an English philosopher and architect, was the first to discover it. The cell theory was later proposed by two German scientists, Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann.
Complete answer:
> The cellular apparatus refers to all of the organelles found inside each cell, such as the ribosome, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and golgi bodies.
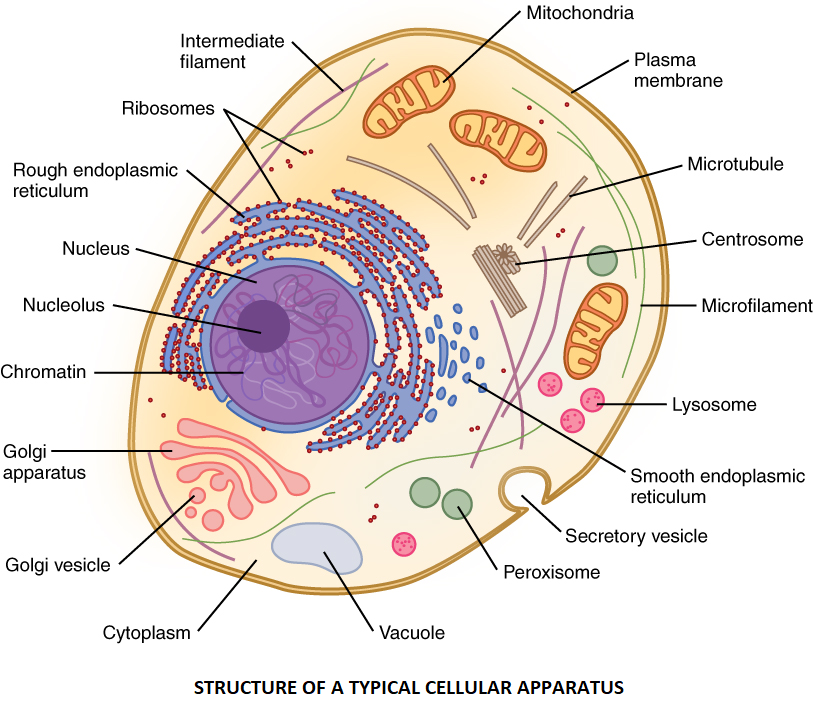
> Cell organelles are the cellular components. Membrane-bound and non-membrane-bound organelles exist within cells and have diverse structures and functions.
> They efficiently coordinate and operate for the cell's normal functioning. Others are involved in mobility and reproduction, while others offer shape and support.
> Cell organelles that are not membrane-bound include the cell wall, ribosomes, and cytoskeleton. They can be found in both bacterial and eukaryotic cells.
> Vacuole, Lysosome, Golgi Apparatus, and Endoplasmic Reticulum are single membrane-bound organelles. Only eukaryotic cells have reticulum, which are solitary membrane-bound organelles.
> The nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplast are double membrane-bound organelles that can only be found in eukaryotic cells.
Note:
Features of cell:
> The body of an organism is sustained and structured by cells.
> The cell's inside is divided into different organelles, each with its own membrane.
> The nucleus (major organelle) is where genetic information needed for cell reproduction and growth is stored.
> Each cell has a single nucleus and cytoplasm with membrane-bound organelles.
> Mitochondria, a double membrane-bound organelle, is responsible for the majority of the energy transactions required for cell survival.
Complete answer:
> The cellular apparatus refers to all of the organelles found inside each cell, such as the ribosome, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and golgi bodies.

> Cell organelles are the cellular components. Membrane-bound and non-membrane-bound organelles exist within cells and have diverse structures and functions.
> They efficiently coordinate and operate for the cell's normal functioning. Others are involved in mobility and reproduction, while others offer shape and support.
> Cell organelles that are not membrane-bound include the cell wall, ribosomes, and cytoskeleton. They can be found in both bacterial and eukaryotic cells.
> Vacuole, Lysosome, Golgi Apparatus, and Endoplasmic Reticulum are single membrane-bound organelles. Only eukaryotic cells have reticulum, which are solitary membrane-bound organelles.
> The nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplast are double membrane-bound organelles that can only be found in eukaryotic cells.
Note:
Features of cell:
> The body of an organism is sustained and structured by cells.
> The cell's inside is divided into different organelles, each with its own membrane.
> The nucleus (major organelle) is where genetic information needed for cell reproduction and growth is stored.
> Each cell has a single nucleus and cytoplasm with membrane-bound organelles.
> Mitochondria, a double membrane-bound organelle, is responsible for the majority of the energy transactions required for cell survival.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




