
What is a codominant allele?
Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: In genetics, dominance refers to the phenomenon of one gene variant (allele) on one copy of a chromosome concealing or overcoming the influence of another gene variant on the other copy of the chromosome. The dominant version is dominant, while the recessive form is recessive. A mutation in one of the genes causes this situation of having two distinct forms of the same gene on each chromosome.
Complete answer:
When many alleles are expressed at the same time, this is known as codominance.
When many alleles are expressed at the same time, this is known as codominance.
Blood type is an example of codominance. Blood types A and B have glycoprotein antigens that can both be expressed without one "overpowering" the other. To put it another way, there is no recessive allele present. This blood type is known as AB because both the A and B alleles are expressed.
Compare this to a situation where there isn't complete domination. Rather of both features being fully displayed, the traits are blended here. If partial dominance is present, a flower heterozygous for colour with one red allele and one white allele will be pink rather than white or red.
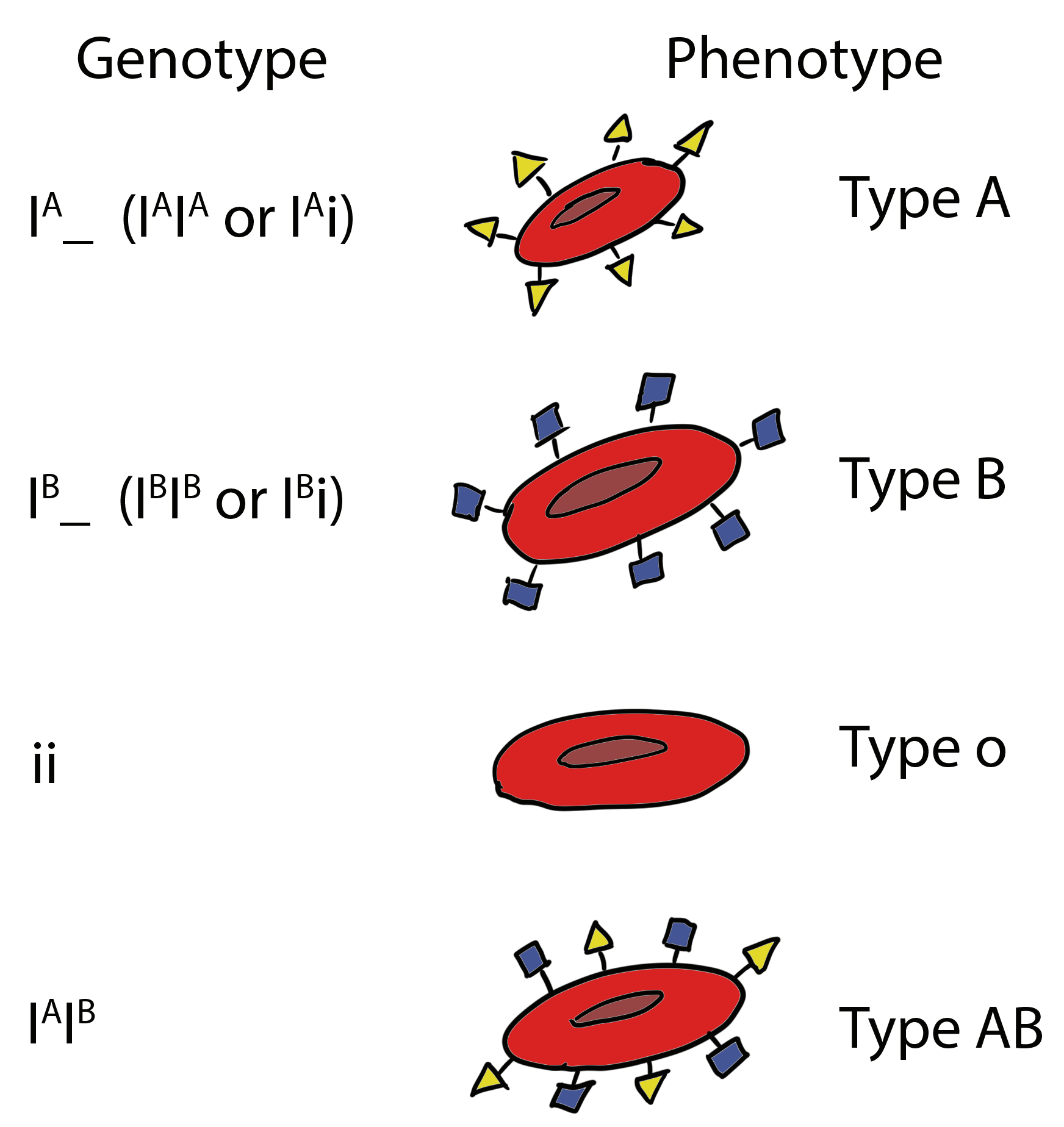
In a heterozygote, codominance is a type of inheritance in which both alleles of a gene pair are fully expressed. As a result, the offspring's phenotype is a blend of the parents' phenotypes. As a result, the trait isn't dominant or recessive. Individuals with type AB blood are an example of codominance in humans. Because IA and IB are codominant and hence expressed simultaneously, an individual inheriting both alleles will have type AB blood. The white-spotted red blossom in plants and black-and-white-coated mammals are two further instances of codominance.
A variant of a gene is known as an allele. Alleles are found in groups of two. Each pair controls the same trait and has its own spot (locus) in the chromosome. The expressed allele is referred to as dominant, whereas the masked allele is referred to as recessive.
Note:-
When a genotype is expressed, the phenotype of an individual is determined by the interaction between that genotype and the environment. The genotype is made up of alleles (gene forms), and the phenotype is the trait or enzyme that the genotype produces. The genotype influences the phenotype.
Complete answer:
When many alleles are expressed at the same time, this is known as codominance.
When many alleles are expressed at the same time, this is known as codominance.
Blood type is an example of codominance. Blood types A and B have glycoprotein antigens that can both be expressed without one "overpowering" the other. To put it another way, there is no recessive allele present. This blood type is known as AB because both the A and B alleles are expressed.
Compare this to a situation where there isn't complete domination. Rather of both features being fully displayed, the traits are blended here. If partial dominance is present, a flower heterozygous for colour with one red allele and one white allele will be pink rather than white or red.

In a heterozygote, codominance is a type of inheritance in which both alleles of a gene pair are fully expressed. As a result, the offspring's phenotype is a blend of the parents' phenotypes. As a result, the trait isn't dominant or recessive. Individuals with type AB blood are an example of codominance in humans. Because IA and IB are codominant and hence expressed simultaneously, an individual inheriting both alleles will have type AB blood. The white-spotted red blossom in plants and black-and-white-coated mammals are two further instances of codominance.
A variant of a gene is known as an allele. Alleles are found in groups of two. Each pair controls the same trait and has its own spot (locus) in the chromosome. The expressed allele is referred to as dominant, whereas the masked allele is referred to as recessive.
Note:-
When a genotype is expressed, the phenotype of an individual is determined by the interaction between that genotype and the environment. The genotype is made up of alleles (gene forms), and the phenotype is the trait or enzyme that the genotype produces. The genotype influences the phenotype.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




