
What is a Finkelstein reaction?
Answer
506.4k+ views
Hint: We have to know that the Finkelstein response is a Substitution Nucleophilic Bimolecular response or $S{N_2}$ reaction includes the trading of halogen particles. It is named after Hans Finkelstein, a German scientist.
Complete answer:
We have to know that, it's anything but a natural response that utilizes an alkyl halide trade into another alkyl halide through a response wherein the metal halide salt is utilized. This response happens at a balance cycle by exploiting helpless acetone solvency in metal halide salt that is recently shaped. The component of the Finkelstein response is a single-step $S{N_2}$ response with stereochemistry reversal. The general reaction has to be given below.
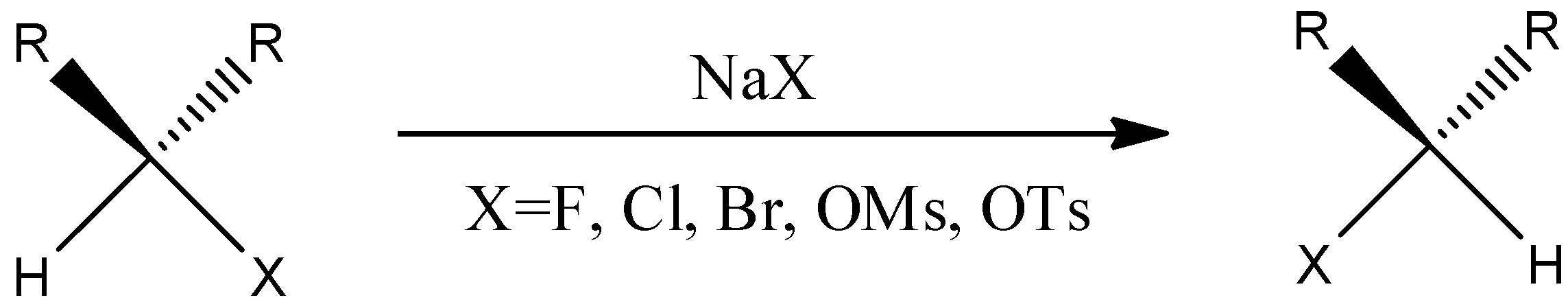
The exemplary Finkelstein response includes the interaction of an alkyl bromide or an alkyl chloride into an alkyl iodide, which is treated with a sodium iodide arrangement in acetone. As the sodium iodide is dissolvable in the acetone, however the sodium bromide and sodium chloride are not solvent in the acetone. The response works great with the essential halides however better with alpha-carbonyl halides and allyl benzyl.
For example, the bromoethane can be changed over to iodo ethane, that has to be given below,
$C{H_3}C{H_2}Br + NaI \to C{H_3}C{H_2}I + NaB{r_{(s)}}$
The accomplishment of this response relies upon the underneath conditions.
Nucleophilicity, Nature of gathering, Carbon-halogen bond, Alkyl Halide reactivity.
Note:
In the cutting edge use of Finkelstein response, it has extended remembering for the way toward changing alcohols to alkyl halides by changing the liquor over to a sulfonate ester in the main stage, and afterward the replacement changes. For Example, synthesis of chrysochlamic corrosive.
Complete answer:
We have to know that, it's anything but a natural response that utilizes an alkyl halide trade into another alkyl halide through a response wherein the metal halide salt is utilized. This response happens at a balance cycle by exploiting helpless acetone solvency in metal halide salt that is recently shaped. The component of the Finkelstein response is a single-step $S{N_2}$ response with stereochemistry reversal. The general reaction has to be given below.
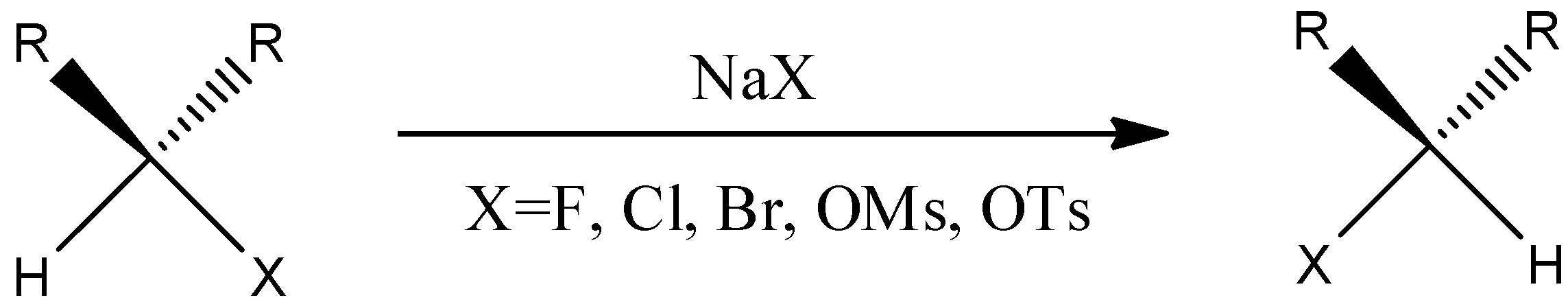
The exemplary Finkelstein response includes the interaction of an alkyl bromide or an alkyl chloride into an alkyl iodide, which is treated with a sodium iodide arrangement in acetone. As the sodium iodide is dissolvable in the acetone, however the sodium bromide and sodium chloride are not solvent in the acetone. The response works great with the essential halides however better with alpha-carbonyl halides and allyl benzyl.
For example, the bromoethane can be changed over to iodo ethane, that has to be given below,
$C{H_3}C{H_2}Br + NaI \to C{H_3}C{H_2}I + NaB{r_{(s)}}$
The accomplishment of this response relies upon the underneath conditions.
Nucleophilicity, Nature of gathering, Carbon-halogen bond, Alkyl Halide reactivity.
Note:
In the cutting edge use of Finkelstein response, it has extended remembering for the way toward changing alcohols to alkyl halides by changing the liquor over to a sulfonate ester in the main stage, and afterward the replacement changes. For Example, synthesis of chrysochlamic corrosive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




