
What is a glycosidic bond?
Answer
490.8k+ views
Hint: A carbohydrate is a biomolecule made up of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms, generally in a 2:1 hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio (as in water), and therefore having the empirical formula \[{{C}_{m}}{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{n}}\] (where m may or may not be different from n). However, not all carbohydrates meet this exact stoichiometric criteria, and not all compounds that do meet this description are automatically classed as carbs (e.g. formaldehyde and acetic acid).
Complete answer:
A glycosidic bond, also known as a glycosidic linkage, is a form of covalent connection that connects a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which might be another carbohydrate or not. The hemiacetal or hemiketal group of a saccharide (or a molecule generated from a saccharide) forms a glycosidic link with the hydroxyl group of a chemical such as an alcohol. A glycoside is a chemical that contains a glycosidic link.
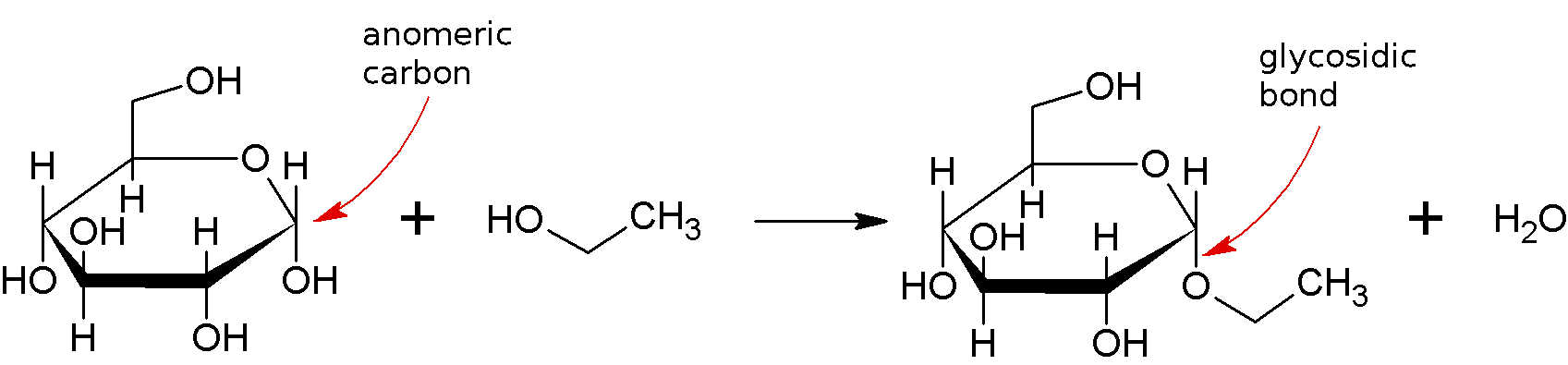
The chemical ROH from which the carbohydrate residue has been removed is frequently referred to as the aglycone, while the carbohydrate residue itself is sometimes referred to as the 'glycone', especially in naturally occurring glycosides.
The glycosidic oxygen that connects the glycoside to the aglycone or reducing end sugar is referred to as an O-glycosidic bond. S-glycosidic linkages (which create thioglycosides) are analogous in that the oxygen of the glycosidic bond is substituted with a sulphur atom. N-glycosidic bonds, on the other hand, have the glycosidic bond oxygen substituted with nitrogen. Glycosylamines are substances that have N-glycosidic linkages in them. The glycosidic oxygen is substituted by a carbon in C-glycosyl bonds; the name "C-glycoside" is considered a misnomer by IUPAC and is deprecated.
Note:
Carbohydrates have a variety of roles in living things. Polysaccharides are energy storage molecules (e.g., starch and glycogen) as well as structural elements (e.g. cellulose in plants and chitin in arthropods). Ribose, a 5-carbon monosaccharide, is a key component of coenzymes (such as ATP, FAD, and NAD) and the backbone of the genetic material RNA. Deoxyribose, which is related, is a component of DNA. Many other essential macromolecules are made up of saccharides and their derivatives, and they play vital roles in the immune system, fertilisation, pathogenesis prevention, blood coagulation, and development.
Complete answer:
A glycosidic bond, also known as a glycosidic linkage, is a form of covalent connection that connects a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which might be another carbohydrate or not. The hemiacetal or hemiketal group of a saccharide (or a molecule generated from a saccharide) forms a glycosidic link with the hydroxyl group of a chemical such as an alcohol. A glycoside is a chemical that contains a glycosidic link.

The chemical ROH from which the carbohydrate residue has been removed is frequently referred to as the aglycone, while the carbohydrate residue itself is sometimes referred to as the 'glycone', especially in naturally occurring glycosides.
The glycosidic oxygen that connects the glycoside to the aglycone or reducing end sugar is referred to as an O-glycosidic bond. S-glycosidic linkages (which create thioglycosides) are analogous in that the oxygen of the glycosidic bond is substituted with a sulphur atom. N-glycosidic bonds, on the other hand, have the glycosidic bond oxygen substituted with nitrogen. Glycosylamines are substances that have N-glycosidic linkages in them. The glycosidic oxygen is substituted by a carbon in C-glycosyl bonds; the name "C-glycoside" is considered a misnomer by IUPAC and is deprecated.
Note:
Carbohydrates have a variety of roles in living things. Polysaccharides are energy storage molecules (e.g., starch and glycogen) as well as structural elements (e.g. cellulose in plants and chitin in arthropods). Ribose, a 5-carbon monosaccharide, is a key component of coenzymes (such as ATP, FAD, and NAD) and the backbone of the genetic material RNA. Deoxyribose, which is related, is a component of DNA. Many other essential macromolecules are made up of saccharides and their derivatives, and they play vital roles in the immune system, fertilisation, pathogenesis prevention, blood coagulation, and development.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




