
What is a meta-director?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: As we know that ortho, meta and para directors are the substituents attached to the benzene ring or other rings which guide the mechanism of reaction and make the other substituents attack at the particular sites in organic chemistry. So here we have to explain about meta directors.
Complete answer:
Let us understand the concept of meta directors in organic chemistry as follows:-
Meta directors: It is a substituent that favors electrophilic attack at meta position with respect to the substituent in electrophilic substitution reactions. The reaction takes place as meta position because these meta directors deactivate the ortho and para position by taking the electron cloud from them through electron displacement effects which ultimately result in more electron density or cloud at meta position that make the coming electrophile attached to it during electrophilic substitution reaction.
Few examples of meta directors are given below:-
$-C\equiv N$, $-COOH$, $-CHO$, $-COOR$, $-C{{F}_{3}}$, $-N{{O}_{2}}$, $-N{{R}_{3}}^{+}$, etc.
The meta directing reaction is given below:-
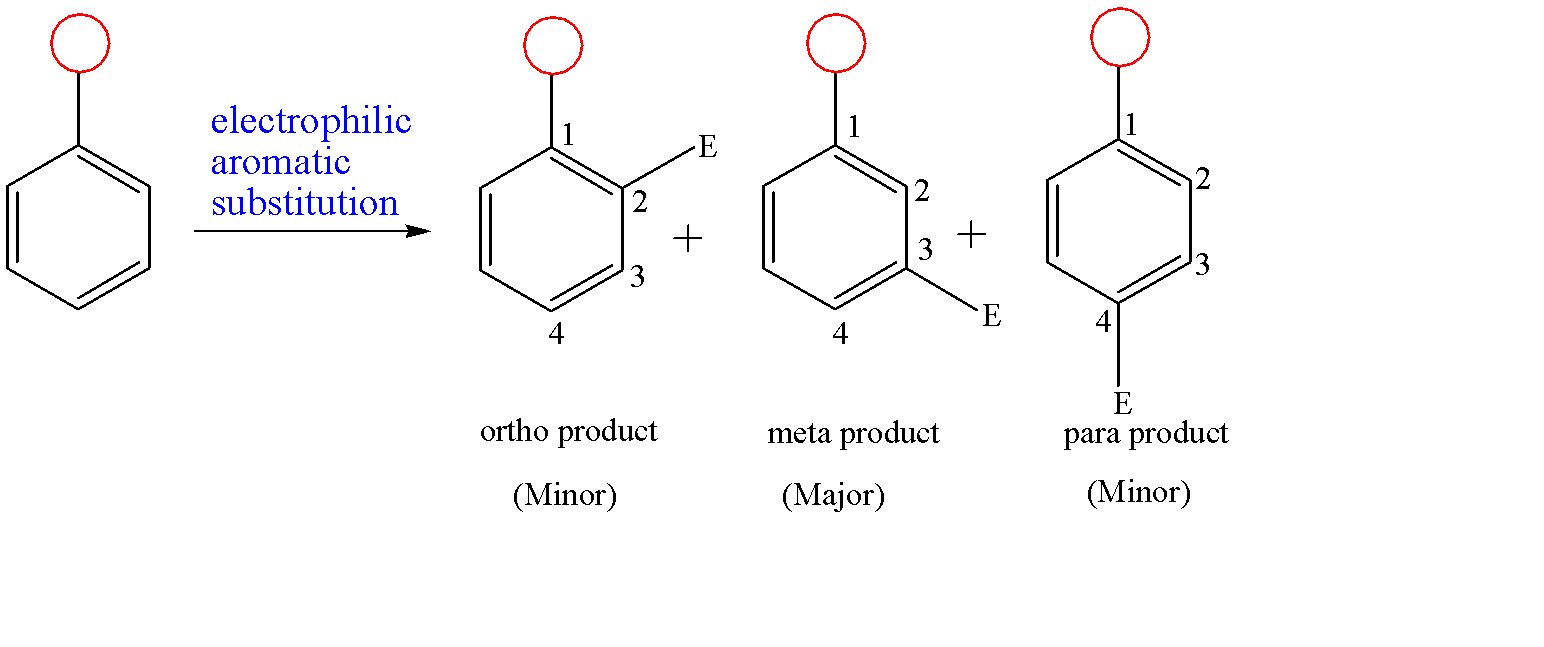
Here the red circular substituent is a meta director. This substituent decreases the electron density at ortho and para positions through mesomeric effect or resonance effect and hence there is more electron density at meta site with respect to the substituent. Now, when the electrophile arrives, it interacts with more electron density sites and gets attached to it. As a result of this, we get a meta product as a major product and rest as minor products.
Note:
-Remember that these meta directors are also known as deactivating groups. Deactivating groups or substituents are those which decrease the rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction with respect to hydrogen as a substituent attached to the ring.
Complete answer:
Let us understand the concept of meta directors in organic chemistry as follows:-
Meta directors: It is a substituent that favors electrophilic attack at meta position with respect to the substituent in electrophilic substitution reactions. The reaction takes place as meta position because these meta directors deactivate the ortho and para position by taking the electron cloud from them through electron displacement effects which ultimately result in more electron density or cloud at meta position that make the coming electrophile attached to it during electrophilic substitution reaction.
Few examples of meta directors are given below:-
$-C\equiv N$, $-COOH$, $-CHO$, $-COOR$, $-C{{F}_{3}}$, $-N{{O}_{2}}$, $-N{{R}_{3}}^{+}$, etc.
The meta directing reaction is given below:-

Here the red circular substituent is a meta director. This substituent decreases the electron density at ortho and para positions through mesomeric effect or resonance effect and hence there is more electron density at meta site with respect to the substituent. Now, when the electrophile arrives, it interacts with more electron density sites and gets attached to it. As a result of this, we get a meta product as a major product and rest as minor products.
Note:
-Remember that these meta directors are also known as deactivating groups. Deactivating groups or substituents are those which decrease the rate of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction with respect to hydrogen as a substituent attached to the ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




