
What is an allosteric enzyme?
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: They are the enzymes that help in the change in the structure of the molecule when it is bound to the molecule. This also changes the affinity of the binding of the molecules. It helps in the process of metabolism.
Complete answer:
An allosteric enzyme is an enzyme that binds to the allosteric modulator that changes the conformational structure and when binds to the ligands then it results in the change in the structure of the ligand. This concept is called the allosteric concept which affects the binding of the ligand at one point and also affects the binding of the ligand at another point. This process helps in the functioning of the various metabolism regulation, cell signaling along with various other biological processes. In biochemistry, allostery is found to be the binding of the protein to an effector molecule instead of the active site of the enzyme.
The point at which the effector molecule binds is called the allosteric site. At this site, the protein binds to the effector molecule and may result in the conformational change and the change in the structure of the proteins. Those effectors that increase the activity of the proteins are called the allosteric activators, while those effectors that decrease the activity of the proteins are called the allosteric inhibitors. An example of allosteric regulation is the ability of the cell to adjust the active site. The example of allosteric enzymes are glycogen phosphorylase, aspartate transcarbamylase, phosphofructokinase, etc are used during the various metabolic pathways.
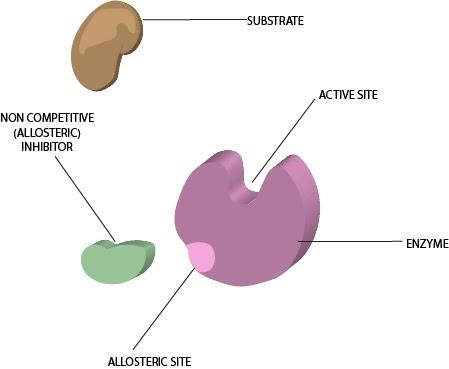
Allosteric Enzyme
Note:
The term allostery is derived from the Greek word allos, meaning ‘other’ and stereos, meaning ‘object’. This indicates that the active site and the regulatory site of an allosteric protein are different from each other. The first crystal structure of the allosteric enzyme was introduced by Max Perutz.
Complete answer:
An allosteric enzyme is an enzyme that binds to the allosteric modulator that changes the conformational structure and when binds to the ligands then it results in the change in the structure of the ligand. This concept is called the allosteric concept which affects the binding of the ligand at one point and also affects the binding of the ligand at another point. This process helps in the functioning of the various metabolism regulation, cell signaling along with various other biological processes. In biochemistry, allostery is found to be the binding of the protein to an effector molecule instead of the active site of the enzyme.
The point at which the effector molecule binds is called the allosteric site. At this site, the protein binds to the effector molecule and may result in the conformational change and the change in the structure of the proteins. Those effectors that increase the activity of the proteins are called the allosteric activators, while those effectors that decrease the activity of the proteins are called the allosteric inhibitors. An example of allosteric regulation is the ability of the cell to adjust the active site. The example of allosteric enzymes are glycogen phosphorylase, aspartate transcarbamylase, phosphofructokinase, etc are used during the various metabolic pathways.

Allosteric Enzyme
Note:
The term allostery is derived from the Greek word allos, meaning ‘other’ and stereos, meaning ‘object’. This indicates that the active site and the regulatory site of an allosteric protein are different from each other. The first crystal structure of the allosteric enzyme was introduced by Max Perutz.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




