
What is Apoenzyme?
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint It is often present in an inactive form. They are activated only when they are bound with the cofactor that may be organic or inorganic. They form a holoenzyme when they bind with the suitable cofactor and thus make them complete.
Complete answer:
Enzymes are biological molecules that help in decreasing the activation energy of the reaction, so that rate of reaction can be increased. The protein part of an enzyme is called an apoenzyme.
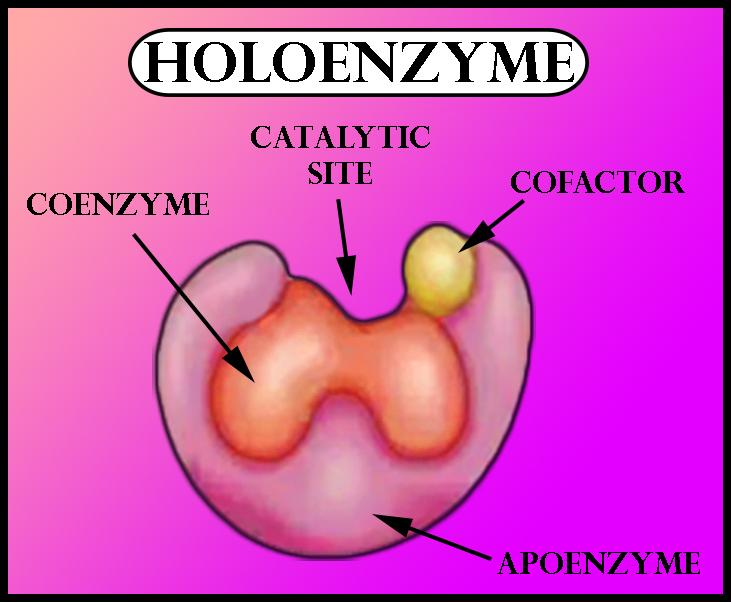
The non - protein part of an enzyme is a Cofactor. It is a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's activity. Apoenzyme and cofactor together form a holoenzyme. One such example is aminotransferase + pyridoxal phosphate.
Enzymes may be simple or complex depending upon their structure and function. Simple enzymes only have a protein part in them but complex enzymes have protein as well as no protein part associated. Examples of simple enzymes are pepsin, trypsin, etc. The other name of the complex enzyme is a Holoenzyme. Holoenzyme is composed of a protein part and a non-protein part. The protein part of the enzyme is called ‘apoenzyme’ while the non-protein part is called ‘prosthetic group’ or cofactor.
Some common examples of holoenzymes are DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase.
Some common examples of apoenzyme are trypsin, pepsin, and urease.
Cofactors may be organic or inorganic in nature. Examples of coenzymes are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and ascorbic acid.
Note:
Prosthetic groups are tightly bound, specific non-polypeptide units that are required for the biological functioning of some proteins. Apoenzymes lack prosthetic groups thus they are incomplete and are in inactive form.
Complete answer:
Enzymes are biological molecules that help in decreasing the activation energy of the reaction, so that rate of reaction can be increased. The protein part of an enzyme is called an apoenzyme.
The non - protein part of an enzyme is a Cofactor. It is a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's activity. Apoenzyme and cofactor together form a holoenzyme. One such example is aminotransferase + pyridoxal phosphate.
Enzymes may be simple or complex depending upon their structure and function. Simple enzymes only have a protein part in them but complex enzymes have protein as well as no protein part associated. Examples of simple enzymes are pepsin, trypsin, etc. The other name of the complex enzyme is a Holoenzyme. Holoenzyme is composed of a protein part and a non-protein part. The protein part of the enzyme is called ‘apoenzyme’ while the non-protein part is called ‘prosthetic group’ or cofactor.
Some common examples of holoenzymes are DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase.
Some common examples of apoenzyme are trypsin, pepsin, and urease.
Cofactors may be organic or inorganic in nature. Examples of coenzymes are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and ascorbic acid.

Note:
Prosthetic groups are tightly bound, specific non-polypeptide units that are required for the biological functioning of some proteins. Apoenzymes lack prosthetic groups thus they are incomplete and are in inactive form.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




