
What is asymmetric carbon?
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Use tetravalency of Carbon atom to explain asymmetric carbon atom. Tetravalency of carbon means presence of 4 valence electrons in carbon atoms.
Complete answer:
Carbon forms covalent bonds with other atoms or groups of atoms.
Electronic configuration of carbon is 2, 4.
It has 4 electrons in the last orbit and hence can form four covalent bonds with other atoms.
If carbon is bonded with the same atoms, then it is said to be a symmetric carbon atom.
For example: Methane, $C{H_4}$.
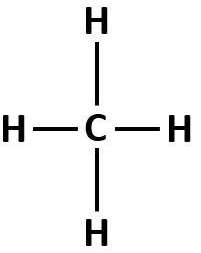
From the above diagram, we can observe that in methane, $C{H_4}$, all the four atoms that are attached to the carbon atom are hydrogen atoms. Hence, all the atoms attached to the carbon atom are the same. Thus, this carbon atom is called a symmetric carbon atom.
Now, if a carbon atom is bonded with all different atoms or groups of atoms. Then such a carbon atom is called an asymmetric carbon atom. Asymmetric carbon atoms are also called chiral carbon atoms.
Observe the diagram:
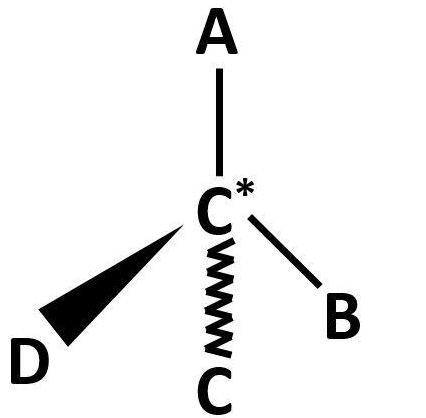
The above diagram is shown in the general sense, where the carbon atom is in the middle and A, B, C, D are four different atoms or groups of atoms attached to it.
One of the best examples of asymmetric carbon atoms are amino acids.
Observe the diagram:
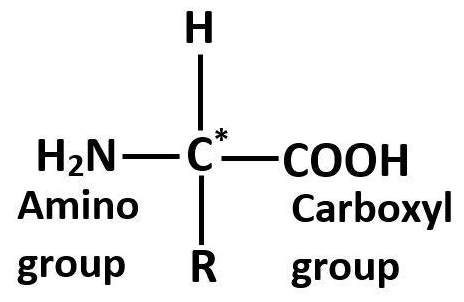
In the above diagram, the carbon atom is attached to four different atoms or groups. Namely, carboxyl group, hydrogen atom, amino group and R represents any alkyl chain that can be attached to the carbon atom.
Hence, this carbon atom is an asymmetric carbon atom.
Note: Asymmetric carbon atom is generally indicated by asterisk symbol as ${C^*}. $ A modern term for chiral carbon is stereogenic center or stereocenter. Organic compounds with chiral C-atoms form mirror images because they are highly superimposable. Such compounds are called isomers.
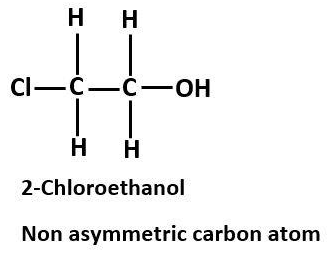
Asymmetric carbon atoms must be bonded to four different groups. If 2 out of four groups are the same, then the carbon atom is not asymmetric. For example, 2-Chloroethanol does not have a symmetric carbon atom as it does not contain all the same atoms attached to carbon atoms. But it is also not an asymmetric carbon atom at it contains two hydrogen atoms attached to it.
Complete answer:
Carbon forms covalent bonds with other atoms or groups of atoms.
Electronic configuration of carbon is 2, 4.
It has 4 electrons in the last orbit and hence can form four covalent bonds with other atoms.
If carbon is bonded with the same atoms, then it is said to be a symmetric carbon atom.
For example: Methane, $C{H_4}$.

From the above diagram, we can observe that in methane, $C{H_4}$, all the four atoms that are attached to the carbon atom are hydrogen atoms. Hence, all the atoms attached to the carbon atom are the same. Thus, this carbon atom is called a symmetric carbon atom.
Now, if a carbon atom is bonded with all different atoms or groups of atoms. Then such a carbon atom is called an asymmetric carbon atom. Asymmetric carbon atoms are also called chiral carbon atoms.
Observe the diagram:

The above diagram is shown in the general sense, where the carbon atom is in the middle and A, B, C, D are four different atoms or groups of atoms attached to it.
One of the best examples of asymmetric carbon atoms are amino acids.
Observe the diagram:

In the above diagram, the carbon atom is attached to four different atoms or groups. Namely, carboxyl group, hydrogen atom, amino group and R represents any alkyl chain that can be attached to the carbon atom.
Hence, this carbon atom is an asymmetric carbon atom.
Note: Asymmetric carbon atom is generally indicated by asterisk symbol as ${C^*}. $ A modern term for chiral carbon is stereogenic center or stereocenter. Organic compounds with chiral C-atoms form mirror images because they are highly superimposable. Such compounds are called isomers.
Asymmetric carbon atoms must be bonded to four different groups. If 2 out of four groups are the same, then the carbon atom is not asymmetric. For example, 2-Chloroethanol does not have a symmetric carbon atom as it does not contain all the same atoms attached to carbon atoms. But it is also not an asymmetric carbon atom at it contains two hydrogen atoms attached to it.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




