
What is Bakelite and melamine?
Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint: Polymers are macromolecules which consist of a large number of repeating units (called monomers). Thermosetting polymers are those which undergo extensive cross linking in moulds and become hard which cannot be reused. However, thermoplastic polymers are those which can be repeatedly softened on heating and hardened on cooling .
Complete answer:
Bakelite is a condensation polymer in which the repeating unit is formed by the reaction of formaldehyde with phenol. Electrophilic substitution reaction takes place between phenol and formaldehyde and leads to the formation of 2-hydroxymethyl phenol, 2,4-dihydroxy methyl phenol and 2,4,6-trihydroxy methyl phenol. These synthesized products undergo crosslinking to form Bakelite. This is illustrated in the following diagram.
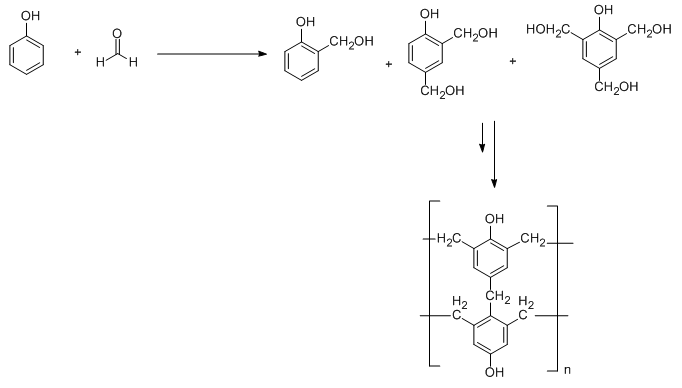
On the other hand, melamine resin polymer is a condensation polymer in which the repeating unit is formed by the reaction of melamine with formaldehyde. This is illustrated in the following diagram:
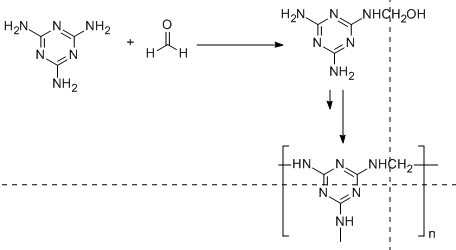
From the above two diagrams, we conclude that Bakelite is a heavily branched structure and thus cross-linked polymer in comparison to melamine. Because of this cross linking, Bakelite is a thermosetting polymer while melamine resin is a thermostatic polymer.
Additional information: The uses of Bakelite includes the making of combs and handles of kitchen utensils. However, melamine is used in the making of crockery.
Note:
It is important to note that the monomeric units in Bakelite are phenol and formaldehyde whereas melamine resin has melamine and formaldehyde as monomeric units. Bakelite is a heavily branched structure in comparison to melamine resin. Due to this heavy branching which is also called cross linkages is responsible to make Bakelite a thermosetting polymer.
Complete answer:
Bakelite is a condensation polymer in which the repeating unit is formed by the reaction of formaldehyde with phenol. Electrophilic substitution reaction takes place between phenol and formaldehyde and leads to the formation of 2-hydroxymethyl phenol, 2,4-dihydroxy methyl phenol and 2,4,6-trihydroxy methyl phenol. These synthesized products undergo crosslinking to form Bakelite. This is illustrated in the following diagram.

On the other hand, melamine resin polymer is a condensation polymer in which the repeating unit is formed by the reaction of melamine with formaldehyde. This is illustrated in the following diagram:

From the above two diagrams, we conclude that Bakelite is a heavily branched structure and thus cross-linked polymer in comparison to melamine. Because of this cross linking, Bakelite is a thermosetting polymer while melamine resin is a thermostatic polymer.
Additional information: The uses of Bakelite includes the making of combs and handles of kitchen utensils. However, melamine is used in the making of crockery.
Note:
It is important to note that the monomeric units in Bakelite are phenol and formaldehyde whereas melamine resin has melamine and formaldehyde as monomeric units. Bakelite is a heavily branched structure in comparison to melamine resin. Due to this heavy branching which is also called cross linkages is responsible to make Bakelite a thermosetting polymer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




