
What is demodulation?
Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: Low frequency waves cannot be transmitted to long distances. There are multiple reasons for this, like if low frequency waves are used in transmission an antenna almost the size of moon would be needed to receive the signal and a lot more energy would be required. Thus they undergo modulation for transmission and then we recover the low frequency back from the modulated signal.
Complete step by step answer:
A high frequency carrier wave is used to carry the audio signal, or better known as the message to larger distances. This is done with the help of modulation. Modulation is the process by which some characteristic like amplitude, phase angle or frequency commonly, of a high frequency carrier wave is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the low frequency audio signal.
The following factors are responsible for the need of modulation:
(i)Practical antenna length
(ii)Effective power radiated by the antenna
(iii)Frequency multiplexing
(iv)Narrow banding
Now, once this signal has been transmitted it is received by an antenna. This obtained signal is now needed to be used to recover the original message or data from the modulated signal. The task of recovering an original data or message from the modulated signal after its propagation through a communication channel is done by the receiver. Receiver performs this with the help of the process of demodulation.
This process of recovering the audio signal from the modulated wave is known as demodulation or detection. It is the reverse process of modulation, and thus the name. The following diagram shows a schematic representation of a receiver.
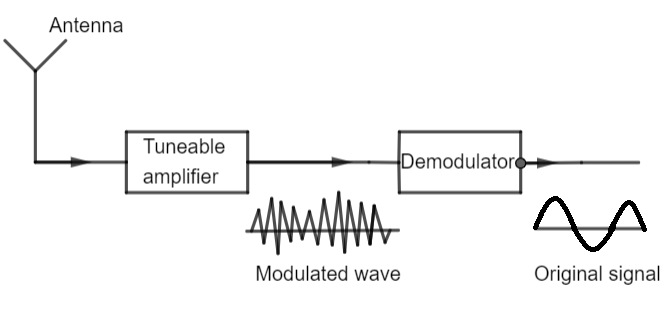
Note: There are multiple ways in which demodulation can be applied to different modulated signals depending upon which of their parameters were transmitted in the carrier signal. These parameters can be anything between frequency, phase angle or amplitude. Different types of electrical circuits are used to perform this function.
Complete step by step answer:
A high frequency carrier wave is used to carry the audio signal, or better known as the message to larger distances. This is done with the help of modulation. Modulation is the process by which some characteristic like amplitude, phase angle or frequency commonly, of a high frequency carrier wave is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the low frequency audio signal.
The following factors are responsible for the need of modulation:
(i)Practical antenna length
(ii)Effective power radiated by the antenna
(iii)Frequency multiplexing
(iv)Narrow banding
Now, once this signal has been transmitted it is received by an antenna. This obtained signal is now needed to be used to recover the original message or data from the modulated signal. The task of recovering an original data or message from the modulated signal after its propagation through a communication channel is done by the receiver. Receiver performs this with the help of the process of demodulation.
This process of recovering the audio signal from the modulated wave is known as demodulation or detection. It is the reverse process of modulation, and thus the name. The following diagram shows a schematic representation of a receiver.

Note: There are multiple ways in which demodulation can be applied to different modulated signals depending upon which of their parameters were transmitted in the carrier signal. These parameters can be anything between frequency, phase angle or amplitude. Different types of electrical circuits are used to perform this function.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




