
What is denticity?
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint:
Denticity is a term related to the constituent molecules present in a coordination compound, otherwise known as ligands. The word is derived from the Latin word ‘dentist’, meaning tooth. Thus, we can understand that it describes the tooth-like behaviour of ligands.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know, ligands are molecules/atoms/ions attached to the central atom in coordination compounds. These ligands are attached to the central atom by means of chemical bonds created between one atoms of the ligand and the central atom. Ligands attach to the central atom in a similar way as to how teeth grasp onto food/objects.
Denticity refers to this, and is defined as the number of donor atoms through which a ligand is attached to the central atom. Accordingly, ligands are classified as:
Monodentate ligands, which are attached to the central atom through only one atom. A common example is the ammonia molecule, which attaches itself through the lone pair present on nitrogen.
Bidentate ligands, which are attached to the central atom through two atoms. A common example is the ethylenediamine molecule.
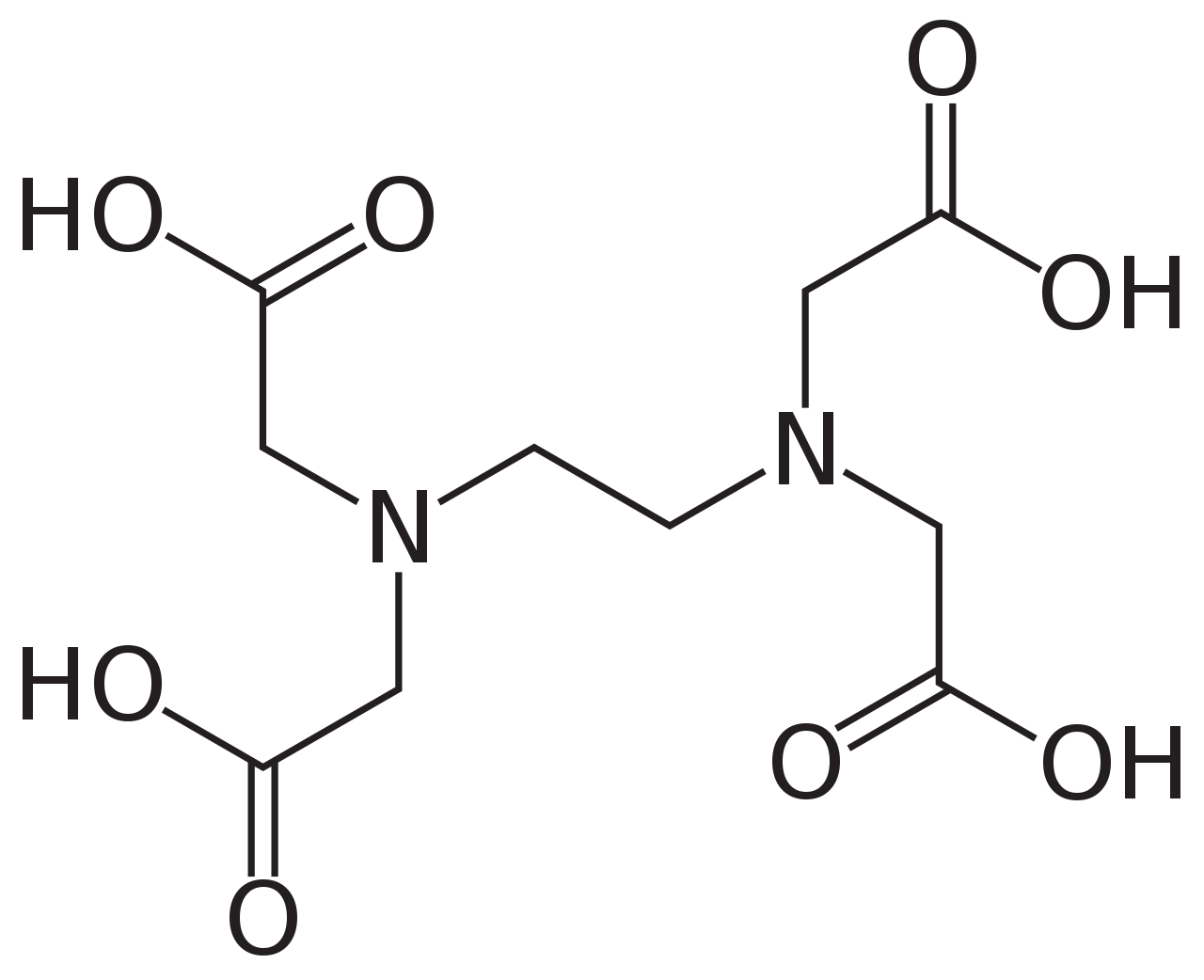
Polydentate ligands, which are attached to the central atom through more than two atoms. A common example is the molecule EDTA (ethylenediamine tetraacetate), which has six points of attachment. Its structure is shown below:
The points of attachment of this molecule with the metal ion is shown in the image below:
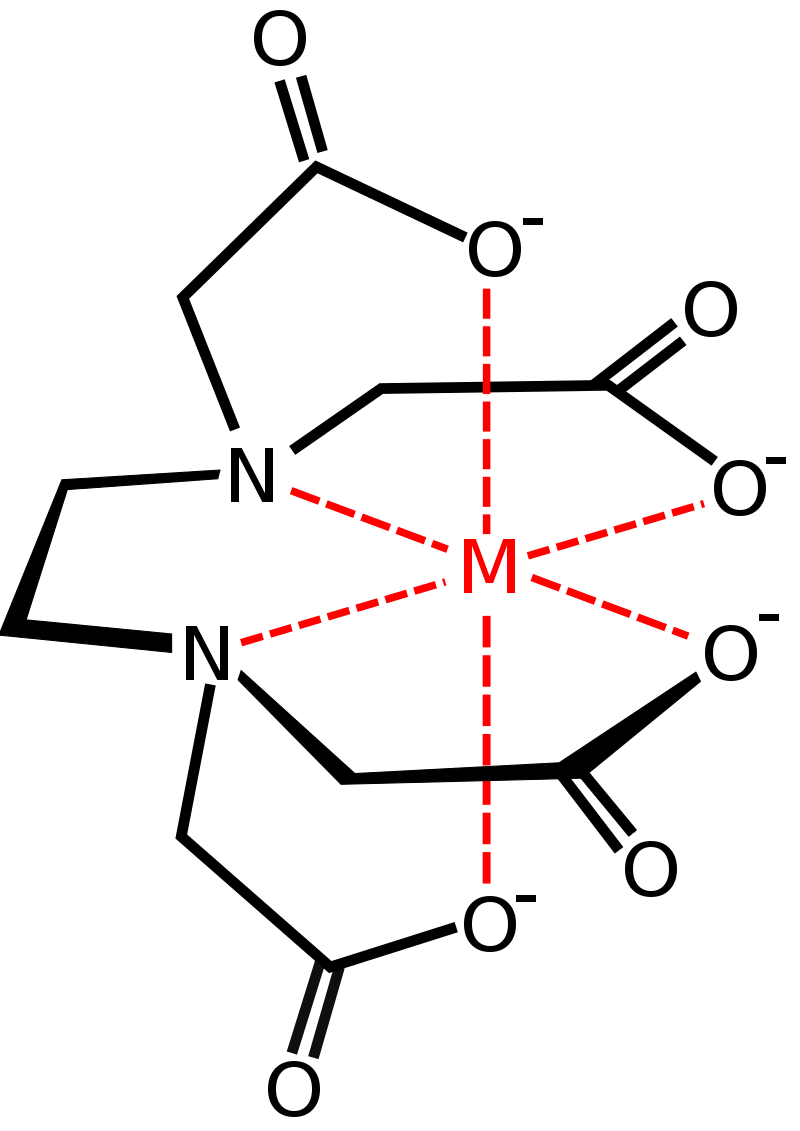
As we can see, the lone pairs present on the two nitrogen atoms contribute to two points of attachment. When in aqueous solution, the oxygen atoms present on the four acetate ions too grab on to the metal ion, by releasing the hydrogen ions attached to them into the solution. Thus, a total of six points of attachment are made, making EDTA a hexadentate ligand.
Note:Denticity of the ligands present can directly affect the stability of a metal ion complex. Ligands with higher denticity form more stable compounds than ones with lower denticity, and this phenomenon is known as the chelate effect. The stability of chelating compounds can be attributed to better changes in entropy, as most chelating compounds are able to form stable ring structures.
Denticity is a term related to the constituent molecules present in a coordination compound, otherwise known as ligands. The word is derived from the Latin word ‘dentist’, meaning tooth. Thus, we can understand that it describes the tooth-like behaviour of ligands.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know, ligands are molecules/atoms/ions attached to the central atom in coordination compounds. These ligands are attached to the central atom by means of chemical bonds created between one atoms of the ligand and the central atom. Ligands attach to the central atom in a similar way as to how teeth grasp onto food/objects.
Denticity refers to this, and is defined as the number of donor atoms through which a ligand is attached to the central atom. Accordingly, ligands are classified as:
Monodentate ligands, which are attached to the central atom through only one atom. A common example is the ammonia molecule, which attaches itself through the lone pair present on nitrogen.
Bidentate ligands, which are attached to the central atom through two atoms. A common example is the ethylenediamine molecule.
Polydentate ligands, which are attached to the central atom through more than two atoms. A common example is the molecule EDTA (ethylenediamine tetraacetate), which has six points of attachment. Its structure is shown below:

The points of attachment of this molecule with the metal ion is shown in the image below:

As we can see, the lone pairs present on the two nitrogen atoms contribute to two points of attachment. When in aqueous solution, the oxygen atoms present on the four acetate ions too grab on to the metal ion, by releasing the hydrogen ions attached to them into the solution. Thus, a total of six points of attachment are made, making EDTA a hexadentate ligand.
Note:Denticity of the ligands present can directly affect the stability of a metal ion complex. Ligands with higher denticity form more stable compounds than ones with lower denticity, and this phenomenon is known as the chelate effect. The stability of chelating compounds can be attributed to better changes in entropy, as most chelating compounds are able to form stable ring structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




