
What is dynamically induced emf?
Answer
507.6k+ views
Hint:The magnetic field system must be kept fixed while the conductor moves in order to generate a dynamically induced EMF (electromotive force). The magnetic field system can also be kept moving while the conductor remains stationary. The conductor cuts through the magnetic field and induces the emf in the coil if either of the preceding procedures is performed.
Complete answer:
Dynamically induced emf:
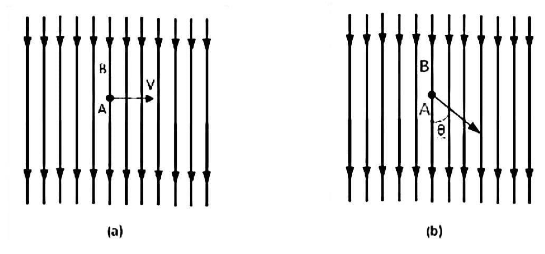
A conductor \[A\] lies within a uniform magnetic field whose flux density is a uniform magnetic field, as shown in the diagram. \[Bw{b^3}\] is the flux density. The movement of the conductor is depicted in this diagram by an arrow line. When conductor \[A\] cuts across the flux at a straight angle.
Let stand for the length of the conductor within the field. It also travels a distance of \[dx\] in time\[dt\] . As a result, the conductor's swept area is = \[ldx\] . As a result, flux cut by the conductor equals\[l.dx{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}B\] , Time = \[dt\] second Change in Flux = \[B.l.dx{\text{ }}weber\].
According to the laws of Faraday. The induced e.m.f in the conductor. Dynamically induced e.m.f. is the name given to this induced e.m.f.
The rate of change of flux linkages = $\dfrac{{Bldx}}{{dt}} = Bl\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = Blv\,volt$ [Where, $\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}$ is velocity]
If the conductor \[\left( A \right)\] moves at an angle to the flux direction (see diagram) \[\left( b \right)\] . Then the induced e.m.f is,
$e = Blv\sin \theta \\
\Rightarrow volts = \overrightarrow {lv} \times \overrightarrow B $
(i.e as cross product vector $\overrightarrow v $ and $\overrightarrow B $ )
The generator, for example, operates on producing dynamically induced e.m.f in conductors.
Note: It's worth noting that either the conductor or the field pole, or both, are moving about in space. Emf induced in the armature of a dc generator, and emf induced in the armature of an alternator with a static armature, for example.
Complete answer:
Dynamically induced emf:

A conductor \[A\] lies within a uniform magnetic field whose flux density is a uniform magnetic field, as shown in the diagram. \[Bw{b^3}\] is the flux density. The movement of the conductor is depicted in this diagram by an arrow line. When conductor \[A\] cuts across the flux at a straight angle.
Let stand for the length of the conductor within the field. It also travels a distance of \[dx\] in time\[dt\] . As a result, the conductor's swept area is = \[ldx\] . As a result, flux cut by the conductor equals\[l.dx{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}B\] , Time = \[dt\] second Change in Flux = \[B.l.dx{\text{ }}weber\].
According to the laws of Faraday. The induced e.m.f in the conductor. Dynamically induced e.m.f. is the name given to this induced e.m.f.
The rate of change of flux linkages = $\dfrac{{Bldx}}{{dt}} = Bl\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}} = Blv\,volt$ [Where, $\dfrac{{dx}}{{dt}}$ is velocity]
If the conductor \[\left( A \right)\] moves at an angle to the flux direction (see diagram) \[\left( b \right)\] . Then the induced e.m.f is,
$e = Blv\sin \theta \\
\Rightarrow volts = \overrightarrow {lv} \times \overrightarrow B $
(i.e as cross product vector $\overrightarrow v $ and $\overrightarrow B $ )
The generator, for example, operates on producing dynamically induced e.m.f in conductors.
Note: It's worth noting that either the conductor or the field pole, or both, are moving about in space. Emf induced in the armature of a dc generator, and emf induced in the armature of an alternator with a static armature, for example.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




