
What is knee voltage?
Answer
507.3k+ views
Hint: When a voltage is applied to the forward characteristics of a diode, the junction rapidly expands. The terms "knee voltage" and "cut in voltage" refer to the same thing.
Complete answer:
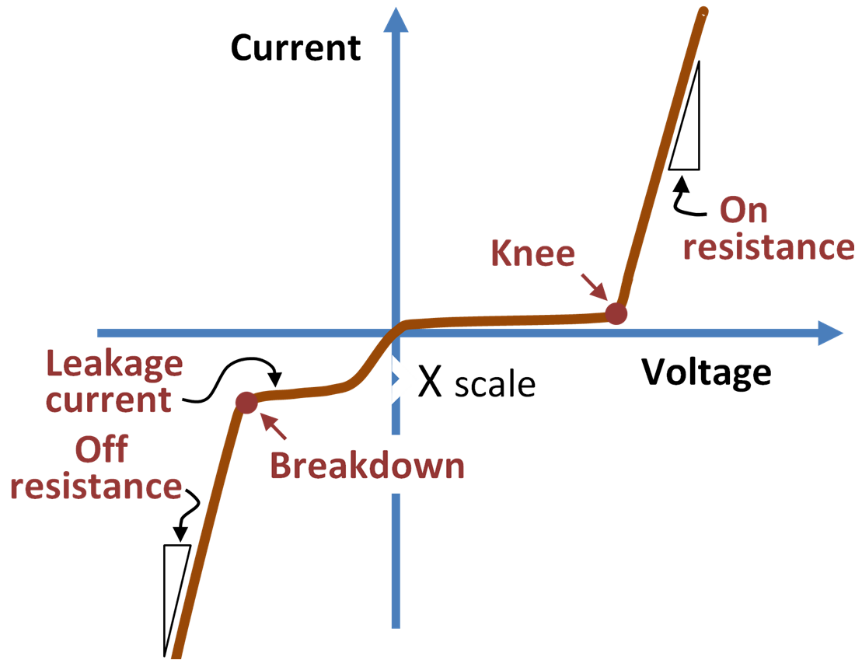
Knee voltage or cut-in voltage of PN junction diode is the voltage at which the forward-biased diode begins to conduct.
The barrier potential or built-in potential is created when the p- and n- junctions are linked. When the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the anode and the negative terminal is connected to the cathode, the diode is forward biased and will not conduct unless the battery voltage is greater than the barrier potential. The germanium and silicon diodes have barrier potentials of \[0.3\] and \[0.7\] , respectively. If the battery voltage is greater than \[0.7\], the silicon diode begins to conduct in forward biased mode.
Knee point voltage, also known as diode cut-in voltage, is the minimum voltage at which the diode begins to conduct heavily and current begins to increase rapidly in a forward biased state. The concept of the diode's knee point voltage can be further appreciated by looking at the diode's forwarding properties.
Note:
The diode is forward biased by applying a positive and negative voltage at the anode and cathode of the diode respectively. The applied voltage is increased gradually from zero voltage. The silicon diode does not conduct till voltage reaches \[0.7{\text{ }}volts\] . The germanium diode does not conduct till voltage reaches \[0.3{\text{ }}volts\] . The \[0.7{\text{ }}volts\] and \[0.3{\text{ }}volts\] are the cut-in or knee voltage of the silicon and germanium diodes respectively. When the applied voltage reaches cut-in or knee voltage the diode starts heavily conducting.
Complete answer:
Knee voltage or cut-in voltage of PN junction diode is the voltage at which the forward-biased diode begins to conduct.
The barrier potential or built-in potential is created when the p- and n- junctions are linked. When the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the anode and the negative terminal is connected to the cathode, the diode is forward biased and will not conduct unless the battery voltage is greater than the barrier potential. The germanium and silicon diodes have barrier potentials of \[0.3\] and \[0.7\] , respectively. If the battery voltage is greater than \[0.7\], the silicon diode begins to conduct in forward biased mode.
Knee point voltage, also known as diode cut-in voltage, is the minimum voltage at which the diode begins to conduct heavily and current begins to increase rapidly in a forward biased state. The concept of the diode's knee point voltage can be further appreciated by looking at the diode's forwarding properties.

Note:
The diode is forward biased by applying a positive and negative voltage at the anode and cathode of the diode respectively. The applied voltage is increased gradually from zero voltage. The silicon diode does not conduct till voltage reaches \[0.7{\text{ }}volts\] . The germanium diode does not conduct till voltage reaches \[0.3{\text{ }}volts\] . The \[0.7{\text{ }}volts\] and \[0.3{\text{ }}volts\] are the cut-in or knee voltage of the silicon and germanium diodes respectively. When the applied voltage reaches cut-in or knee voltage the diode starts heavily conducting.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




