
What is meant by dentition?
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Dentition is derived from the Latin word dentitio which means teething. The members of class Mammalia have up to four distinct types of teeth except for monotremes, xenarthrans, the pangolins, and the cetaceans. Different types of teeth are modified to perform different functions.
Complete answer:
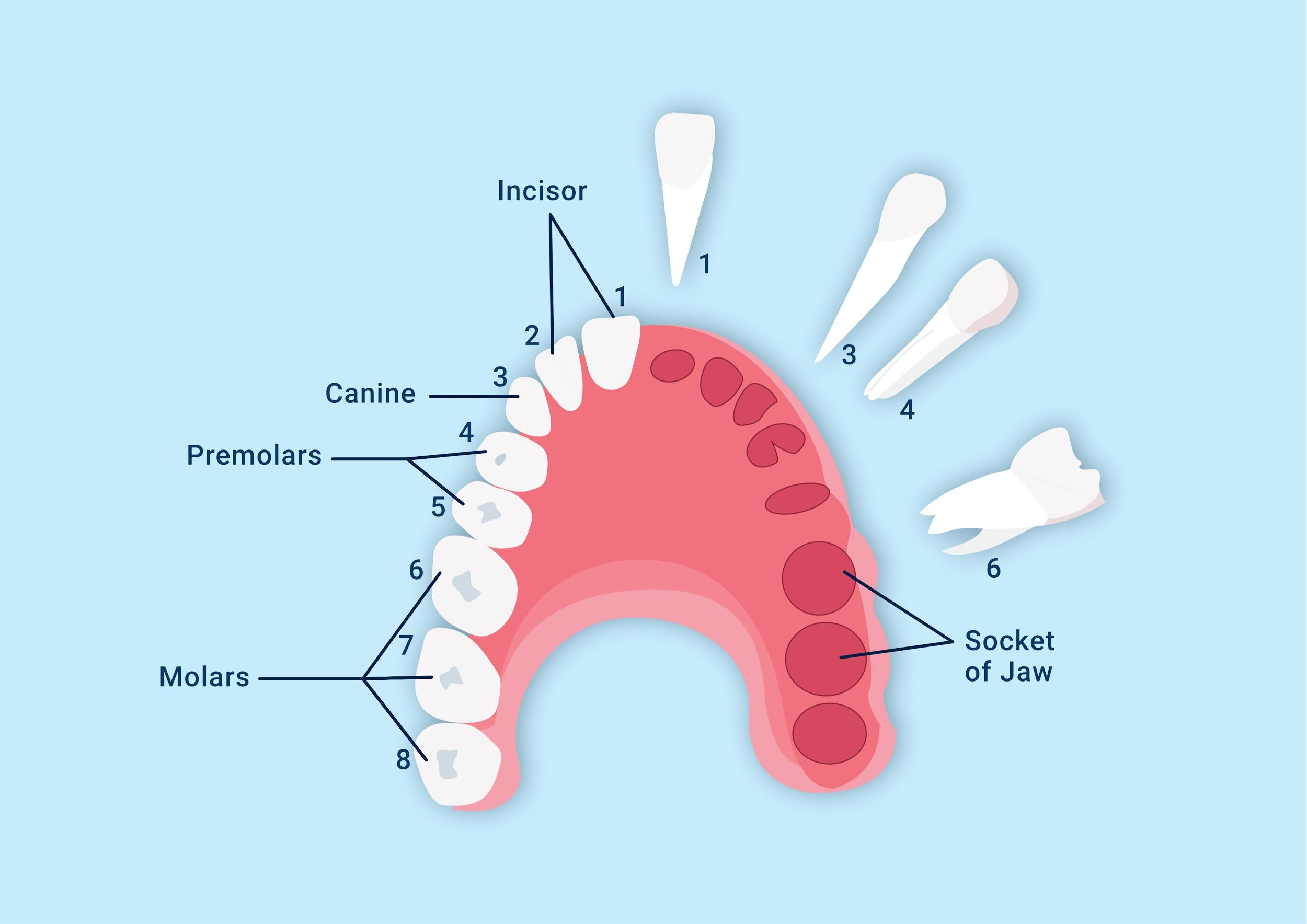
Dentition is the term used to define the arrangement of teeth in an individual. In humans, the dentition is defined as heterodont, thecodont, and diphyodont. Heterodont is the term used to define different types of teeth present. Thecodont is the term used to define that teeth are embedded in sockets of the jaw bone. Diphyodont is the term used to define that there occur two sets of teeth in human life- temporary or deciduous or milk teeth and permanent set of teeth. The dental formula for human adults is 2123/2123.
- The dental formula for the child is 212/212. The dental formula for a 17-year-old child is 2122/2122.
- Dental formula numbers the teeth in one half of the upper or lower jaw on either side. 2 in the dental formula for a human adult represents incisors, 1 represents canines, 2 represents premolars and 3 represents molars.
- Premolars are monophyodont because they occur only once in human life. And the third molar or the wisdom tooth is present only in adult humans.
- Incisors are the teeth present in front. They are used in biting. Canines are the teeth present next to incisors and are used to tear food. Premolars present next to canines and molars present next to premolars are used in grinding, crushing, and tearing food. Molars are the largest teeth.
Note: The tusks of elephants are modified incisors made of ivory. Enamel and dentine are the main components of the tooth. Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and is mainly composed of inorganic materials and is secreted by ameloblasts and dentine is secreted by odontoblasts.
Complete answer:
Dentition is the term used to define the arrangement of teeth in an individual. In humans, the dentition is defined as heterodont, thecodont, and diphyodont. Heterodont is the term used to define different types of teeth present. Thecodont is the term used to define that teeth are embedded in sockets of the jaw bone. Diphyodont is the term used to define that there occur two sets of teeth in human life- temporary or deciduous or milk teeth and permanent set of teeth. The dental formula for human adults is 2123/2123.
- The dental formula for the child is 212/212. The dental formula for a 17-year-old child is 2122/2122.
- Dental formula numbers the teeth in one half of the upper or lower jaw on either side. 2 in the dental formula for a human adult represents incisors, 1 represents canines, 2 represents premolars and 3 represents molars.
- Premolars are monophyodont because they occur only once in human life. And the third molar or the wisdom tooth is present only in adult humans.
- Incisors are the teeth present in front. They are used in biting. Canines are the teeth present next to incisors and are used to tear food. Premolars present next to canines and molars present next to premolars are used in grinding, crushing, and tearing food. Molars are the largest teeth.

Note: The tusks of elephants are modified incisors made of ivory. Enamel and dentine are the main components of the tooth. Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and is mainly composed of inorganic materials and is secreted by ameloblasts and dentine is secreted by odontoblasts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




