
What is occlusion?
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: You should know that; occlusion is a type of adsorption and adsorption is a surface phenomenon. Adsorption is further characterized into two types i.e. chemisorption and physisorption
Complete answer:
Let us first understand about the adsorption phenomenon before proceeding to describe what is occlusion.
So, when there is attracting and retaining of the molecules of a particular substance on the surface of a liquid or a solid forming into a higher concentration of the molecules on the surface is called ‘adsorption’. The substance that is adsorbed on the surface is called the ‘adsorbate’ and the surface on which the substance is absorbed is called ‘adsorbent’. In short, we can say that the substance is called as “adsorbate” while the surface is called as “adsorbent”.
The reverse process of adsorption that is the removal of particles from the surface is known as ‘desorption’.
Occlusion is the term used to define the adsorption of gases on the surface of metals. So, we can say that it is a type of adsorption where the adsorbate is the gas and metal acts as the adsorbent where the gases are adsorbed. In chemistry, occlusion is the inclusion of one substance within another. This process can occur if precipitation or crystallization occurs rapidly. For example: Water molecules get packed into a pocket at the time of silver crystal formation due to rapid crystallization. The process is shown in the below diagram:
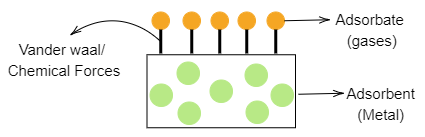
Note: There are two types of adsorption of gases on solids i.e. physisorption and chemisorption. In physisorption, weak Vander waals forces are present and this requires very small activation energy while chemisorption has chemical bond or ionic bond and requires high activation energy.
Complete answer:
Let us first understand about the adsorption phenomenon before proceeding to describe what is occlusion.
So, when there is attracting and retaining of the molecules of a particular substance on the surface of a liquid or a solid forming into a higher concentration of the molecules on the surface is called ‘adsorption’. The substance that is adsorbed on the surface is called the ‘adsorbate’ and the surface on which the substance is absorbed is called ‘adsorbent’. In short, we can say that the substance is called as “adsorbate” while the surface is called as “adsorbent”.
The reverse process of adsorption that is the removal of particles from the surface is known as ‘desorption’.
Occlusion is the term used to define the adsorption of gases on the surface of metals. So, we can say that it is a type of adsorption where the adsorbate is the gas and metal acts as the adsorbent where the gases are adsorbed. In chemistry, occlusion is the inclusion of one substance within another. This process can occur if precipitation or crystallization occurs rapidly. For example: Water molecules get packed into a pocket at the time of silver crystal formation due to rapid crystallization. The process is shown in the below diagram:

Note: There are two types of adsorption of gases on solids i.e. physisorption and chemisorption. In physisorption, weak Vander waals forces are present and this requires very small activation energy while chemisorption has chemical bond or ionic bond and requires high activation energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




