
What Is Sclerenchyma?
Answer
526.8k+ views
Hint: Sclerenchyma is one of the three types of ground, or fundamental, tissue in plants; the other two types are parenchyma (living thin-walled tissue) and collenchyma (living support tissue with irregular walls).
Complete answer:
Sclerenchyma is a simple permanent tissue that is composed of dead cells. The walls (that is outer layer) of sclerenchyma consist of the deposition of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin.
The characteristics of sclerenchyma are:
a) Cells of sclerenchyma are known as sclerenchyma cells. They are typically dead cells. During maturation, the cells lose their protoplasm and come to be dead.
b) Cells are elongated and narrow without intercellular space and have thickened cell walls. They are made up of resources like cellulose, hemicellulose and a specialised organic material called lignin which imparts mechanical power to the plant and its parts. Lignin deposition is so thick that the cell walls tend to become strong, inflexible and impermeable to water.
c) Walls of the sclerenchyma cells possess few to several pits.
Sclerenchyma is made up of two different types of cells:
a. Sclerenchymatous fibres: These are the enormously elongated cells which have pointed or oblique ends. Their elongated and narrow structure makes them seem to be like fibres. These are the thick-walled cells and, in some cases, the cell wall is highly lignified as a result of which the lumen (inner space or cavity) is greatly reduced. These fibres typically appear in bundles in several plant parts like stems. They are commonly found along with xylem and phloem of the vascular bundles. These furnish the mechanical strength to the organs that possess them.
b. Sclereids: These are spherical, oval or cylindrical cells with highly thickened cell walls. Sclereids are responsible for the grittiness of pulp of fruits.
The figure below represents the sclerenchyma tissue:
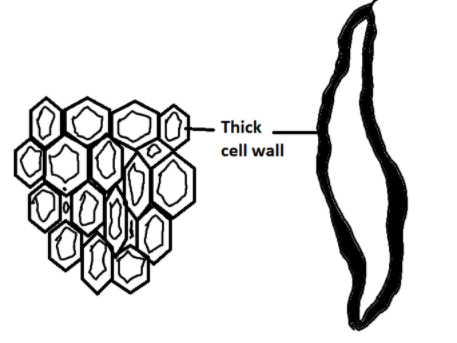
Note: Sclerenchyma is a type of permanent tissue which provides stiffness to the plants. Sclereids are present in: Fruit partitions of nuts like walnut, almond, etc. Pulp of fruits like guava, pear and sapota (cheeku) etc. The 'gritty' (crisp) texture of these fruits is due to sclerenchyma.
Complete answer:
Sclerenchyma is a simple permanent tissue that is composed of dead cells. The walls (that is outer layer) of sclerenchyma consist of the deposition of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin.
The characteristics of sclerenchyma are:
a) Cells of sclerenchyma are known as sclerenchyma cells. They are typically dead cells. During maturation, the cells lose their protoplasm and come to be dead.
b) Cells are elongated and narrow without intercellular space and have thickened cell walls. They are made up of resources like cellulose, hemicellulose and a specialised organic material called lignin which imparts mechanical power to the plant and its parts. Lignin deposition is so thick that the cell walls tend to become strong, inflexible and impermeable to water.
c) Walls of the sclerenchyma cells possess few to several pits.
Sclerenchyma is made up of two different types of cells:
a. Sclerenchymatous fibres: These are the enormously elongated cells which have pointed or oblique ends. Their elongated and narrow structure makes them seem to be like fibres. These are the thick-walled cells and, in some cases, the cell wall is highly lignified as a result of which the lumen (inner space or cavity) is greatly reduced. These fibres typically appear in bundles in several plant parts like stems. They are commonly found along with xylem and phloem of the vascular bundles. These furnish the mechanical strength to the organs that possess them.
b. Sclereids: These are spherical, oval or cylindrical cells with highly thickened cell walls. Sclereids are responsible for the grittiness of pulp of fruits.
The figure below represents the sclerenchyma tissue:

Note: Sclerenchyma is a type of permanent tissue which provides stiffness to the plants. Sclereids are present in: Fruit partitions of nuts like walnut, almond, etc. Pulp of fruits like guava, pear and sapota (cheeku) etc. The 'gritty' (crisp) texture of these fruits is due to sclerenchyma.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




