
What is SONAR? How does it work?
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: SONAR are the devices which are used in multiple situations such as determining the depth of the sea bed. It uses the reflection property of the waves to calculate the distance from which they reflect back. It is inspired by the navigation system used by bats and dolphins.
Complete answer:
SONAR stands for Sound Navigation Ranging. It is sometimes also referred to as echo ranging. It sends pulses of sound waves down through the water and detects the reflected incoming waves. A SONAR device helps in determining the distance, speed and direction of objects underwater.
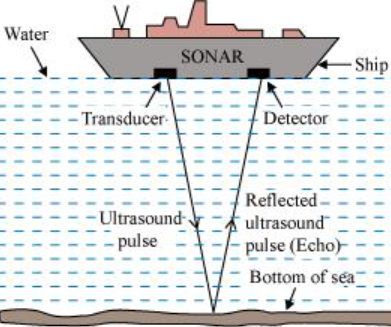
A SONAR device measures how long it takes for the sound wave to travel in water, reflect off a surface and travel back to the device. The working of a SONAR device was inspired by echo-location systems used by bats and dolphins to navigate and locate through a region. The device helps us to measure the depth of the surface from which it reflected off and also measures the strength of the reflected pulse. The strength of the reflected pulse can give us information about the nature of the reflecting surface. The stronger the reflected pulse, harder is the reflecting surface. A detector converts the received waves into electrical signals and are sent to further systems for interpretation. The time interval between transmission and reception is used to extract useful information.
Note:
SONAR scan in cones and not in a linear fashion. They are also used by the fisherman to detect the region where more fish are present. The SONAR detects the waves reflected by the fish and converts waves into electrical signals to give a visual representation of the surface.
Complete answer:
SONAR stands for Sound Navigation Ranging. It is sometimes also referred to as echo ranging. It sends pulses of sound waves down through the water and detects the reflected incoming waves. A SONAR device helps in determining the distance, speed and direction of objects underwater.

A SONAR device measures how long it takes for the sound wave to travel in water, reflect off a surface and travel back to the device. The working of a SONAR device was inspired by echo-location systems used by bats and dolphins to navigate and locate through a region. The device helps us to measure the depth of the surface from which it reflected off and also measures the strength of the reflected pulse. The strength of the reflected pulse can give us information about the nature of the reflecting surface. The stronger the reflected pulse, harder is the reflecting surface. A detector converts the received waves into electrical signals and are sent to further systems for interpretation. The time interval between transmission and reception is used to extract useful information.
Note:
SONAR scan in cones and not in a linear fashion. They are also used by the fisherman to detect the region where more fish are present. The SONAR detects the waves reflected by the fish and converts waves into electrical signals to give a visual representation of the surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




