
What is the chain isomer of ${C_4}{H_{10}}$?
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: If two or more compounds have the same molecular formula but different chemical and physical properties they are called isomers and the phenomena is known as isomerism.
Complete step by step answer:
Isomerism is of two types:
-Structural isomerism
-Stereoisomerism
If the compound has the same molecular formula but different structures i.e., different arrangements of atoms within the molecule are called structural isomers and the phenomena is known as structural isomerism. Whereas the compounds having the same structural formula but have a different relative arrangement of atoms or groups in space are called stereoisomers and the phenomena are known as stereoisomerism.
Structural isomers are of six types. Chain isomers are part of structural isomers and are defined as the compounds that have the same molecular formula but a different arrangement of the carbon chain within the molecule. They are also known as nuclear isomers and the phenomena is known as chain isomerism or nuclear isomerism.
The given compound is Butane and its chain isomer is isobutene, hence there are two chain isomers and the structures for them is given below:

The IUPAC name of isobutane is 2-methylpropane and the structure is given below:
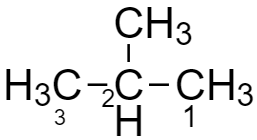
Here the first isomer i.e. n-butane is a straight-chain compound with four carbon atoms bonded with the single covalent compound. In another isomer i.e. isobutane there are three carbon atoms in the parent chain and one in the side-chain as a methyl group.
Note: Both compounds butane and isobutene occur in natural gas and crude oil. Both compounds are formed in large quantities in the refining of petroleum to produce gasoline. But in the terms of vapour pressure isobutane due to its structure far superior to n-butane.
Complete step by step answer:
Isomerism is of two types:
-Structural isomerism
-Stereoisomerism
If the compound has the same molecular formula but different structures i.e., different arrangements of atoms within the molecule are called structural isomers and the phenomena is known as structural isomerism. Whereas the compounds having the same structural formula but have a different relative arrangement of atoms or groups in space are called stereoisomers and the phenomena are known as stereoisomerism.
Structural isomers are of six types. Chain isomers are part of structural isomers and are defined as the compounds that have the same molecular formula but a different arrangement of the carbon chain within the molecule. They are also known as nuclear isomers and the phenomena is known as chain isomerism or nuclear isomerism.
The given compound is Butane and its chain isomer is isobutene, hence there are two chain isomers and the structures for them is given below:

The IUPAC name of isobutane is 2-methylpropane and the structure is given below:

Here the first isomer i.e. n-butane is a straight-chain compound with four carbon atoms bonded with the single covalent compound. In another isomer i.e. isobutane there are three carbon atoms in the parent chain and one in the side-chain as a methyl group.
Note: Both compounds butane and isobutene occur in natural gas and crude oil. Both compounds are formed in large quantities in the refining of petroleum to produce gasoline. But in the terms of vapour pressure isobutane due to its structure far superior to n-butane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




