
What is the dipole moment of azulene?
Answer
525.9k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we first need to know what is azulene. Azulene is an isomer of naphthalene which is dark blue in color as opposed to colorless naphthalene. The structure of azulene is
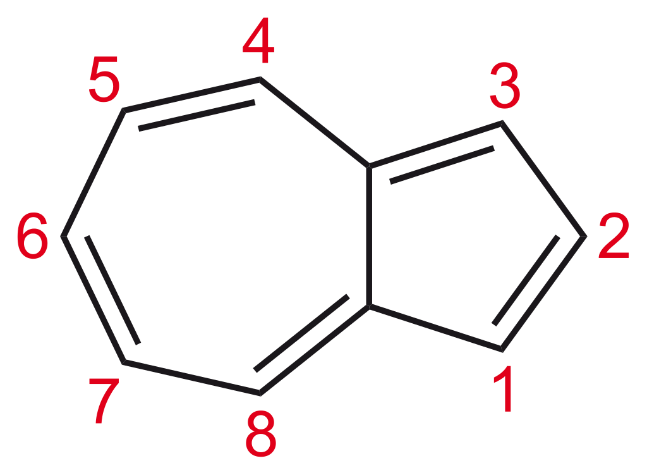
Complete answer:
Let us first understand what a dipole moment is by taking an example of hydrochloric acid (HCl).
In HCl, there is an electronegative difference between H atom and Cl atom, and the more electronegative Cl atom attracts the shared electrons towards itself.
Since there is a non-uniformity in the sharing of electrons between the bonded atoms of the molecule, the more electronegative atom forms a partial negative charge in polar compounds whereas the less electronegative atoms form a partial positive charge in polar compounds.
${{H}^{\delta +}}-C{{l}^{\delta -}}$
This leads to the formation of polar bonds and hence the molecule shows bond polarity and the molecule develops an electrical dipole moment.
The dipole moment in a molecule is measured as follows:
\[\mu =e\times d\]
Where $\mu $ is the bond dipole, e is the charge and d is the distance between the bonded atom's nuclei.
Now the dipole moment of azulene is 3.60 \[\times {{10}^{-30}}\] C.m or 1.08D.
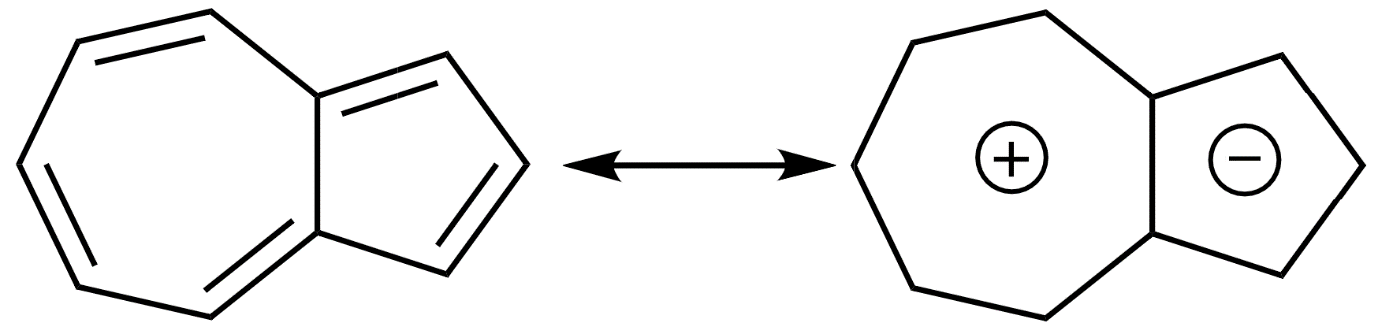
This is because, in the most stable resonance structure of azulene, there exists a positive charge in the 7 membered rings and a negative charge on the 5 membered rings.
Note:
Dipole moment is shown in both ionic compounds and polar covalent compounds, as the electron pairs are not shared equally between the two bonded atoms.
In ionic compounds like LiCl, the 2s orbital electrons of Li atom are included in the electronic structure of Cl atom to fulfill its outermost electron shell.
An example of a polar covalent compound is HCl.

Complete answer:
Let us first understand what a dipole moment is by taking an example of hydrochloric acid (HCl).
In HCl, there is an electronegative difference between H atom and Cl atom, and the more electronegative Cl atom attracts the shared electrons towards itself.
Since there is a non-uniformity in the sharing of electrons between the bonded atoms of the molecule, the more electronegative atom forms a partial negative charge in polar compounds whereas the less electronegative atoms form a partial positive charge in polar compounds.
${{H}^{\delta +}}-C{{l}^{\delta -}}$
This leads to the formation of polar bonds and hence the molecule shows bond polarity and the molecule develops an electrical dipole moment.
The dipole moment in a molecule is measured as follows:
\[\mu =e\times d\]
Where $\mu $ is the bond dipole, e is the charge and d is the distance between the bonded atom's nuclei.
Now the dipole moment of azulene is 3.60 \[\times {{10}^{-30}}\] C.m or 1.08D.
This is because, in the most stable resonance structure of azulene, there exists a positive charge in the 7 membered rings and a negative charge on the 5 membered rings.

Note:
Dipole moment is shown in both ionic compounds and polar covalent compounds, as the electron pairs are not shared equally between the two bonded atoms.
In ionic compounds like LiCl, the 2s orbital electrons of Li atom are included in the electronic structure of Cl atom to fulfill its outermost electron shell.
An example of a polar covalent compound is HCl.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




