
What is the greenhouse effect?
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: Whenever any substance gets in contact with any type of radiation or any radiation gets reflected from any substance, there is an increase in surface temperature observed in that substance.
Complete answer:
Similarly, when radiations from the planet’s atmosphere come into the earth's surface and get reflected, it increases the temperature of the planet’s surface above than the temperature it would be in absence of an atmosphere. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, etc.
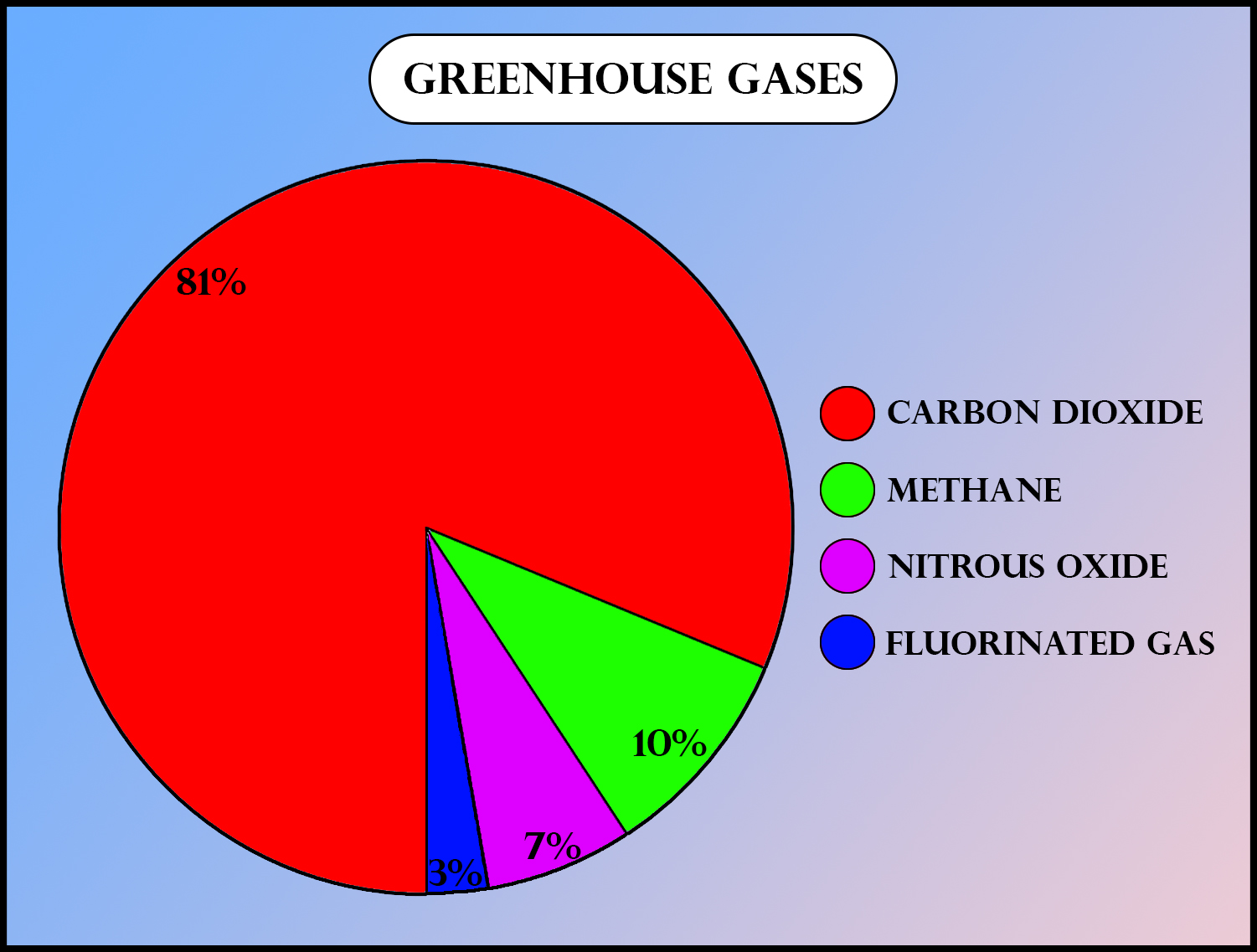
- Increase in greenhouse gases leads to an increase in global warming. The steps of the greenhouse effect are explained below:
- The radiation from the sun reaches the atmosphere of the earth.
- Only some of the radiations are reflected space, while others are absorbed by the lands and oceans present on Earth.
- This absorbance works in heating the Earth.
- Some of the heat is radiated towards space but others are trapped by greenhouse gases present in Earth.
- This absorbed heat by greenhouse gases makes the Earth Warm.
Global warming also increases heat- trapping greenhouse gas levels in Earth's atmosphere. which is harmful to live beings. Harmful effects of global warming are – melting of glaciers, an increase in sea level, even variations in season is the most commonly seen effect of greenhouse gases. Many living beings such as birds have to migrate to different places as they cannot survive those unfavorable conditions.
Note: Humans are also responsible for the increase in global warming. Many human activities are also leading to global warming. Some of them are deforestation, burning fossil fuels, man- made fertilizers used in agriculture, etc.
Complete answer:
Similarly, when radiations from the planet’s atmosphere come into the earth's surface and get reflected, it increases the temperature of the planet’s surface above than the temperature it would be in absence of an atmosphere. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, etc.

- Increase in greenhouse gases leads to an increase in global warming. The steps of the greenhouse effect are explained below:
- The radiation from the sun reaches the atmosphere of the earth.
- Only some of the radiations are reflected space, while others are absorbed by the lands and oceans present on Earth.
- This absorbance works in heating the Earth.
- Some of the heat is radiated towards space but others are trapped by greenhouse gases present in Earth.
- This absorbed heat by greenhouse gases makes the Earth Warm.
Global warming also increases heat- trapping greenhouse gas levels in Earth's atmosphere. which is harmful to live beings. Harmful effects of global warming are – melting of glaciers, an increase in sea level, even variations in season is the most commonly seen effect of greenhouse gases. Many living beings such as birds have to migrate to different places as they cannot survive those unfavorable conditions.
Note: Humans are also responsible for the increase in global warming. Many human activities are also leading to global warming. Some of them are deforestation, burning fossil fuels, man- made fertilizers used in agriculture, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




