
What is the nerve cord?
Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint: Every organism’s perception is engineered by the brain. Certain nervous systems within animals assist the brain in receiving external stimuli and delivering their respective response. Apart from our sense organs, nerve cords play a significant role in the transmission and reception of stimuli.
Complete answer:
Nerve cord is a single hollow tract of nervous tissue which constitutes the central nervous system of chordates and develops into the spinal cord and brain in vertebrates, It is a solid double strand of nerve fibers running along the length of the body in elongate invertebrates, such as earthworms and insects, connecting with a pair of nerve ganglia at each body segment.
1. The dorsal nerve cord (DNC) is a unique feature to chordates and is mainly found in the Vertebrate chordate subphylum. The dorsal nerve cord is the only one embryonic feature that is unique to all chordates, among the other four chordate features- a notochord, a post-anal tail, an endostyle, and pharyngeal slits. The dorsal hollow nerve cord is a hollow cord that lies dorsal to the notochord. It is formed from a part of the ectoderm that rolls and forms the hollow tube. This feature distinguishes chordates from other animal phyla, such as Annelids and Arthropods, which have solid, ventral tubes.
2. The ventral nerve cord (VNC) is the major structure of the invertebrate central nervous system. It is also the functional equivalent of vertebrate spinal cord. The VNC coordinates neural signalling from the brain to the body and vice versa. Thus, it helps in integrating sensory input and locomotor output which is why decapitated insects can still walk, groom and mate. VNC is sufficient to perform complex motor programs without brain input.
Note:
The vertebrate spinal cord is the long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue. It extends from medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. The brain and the spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS).
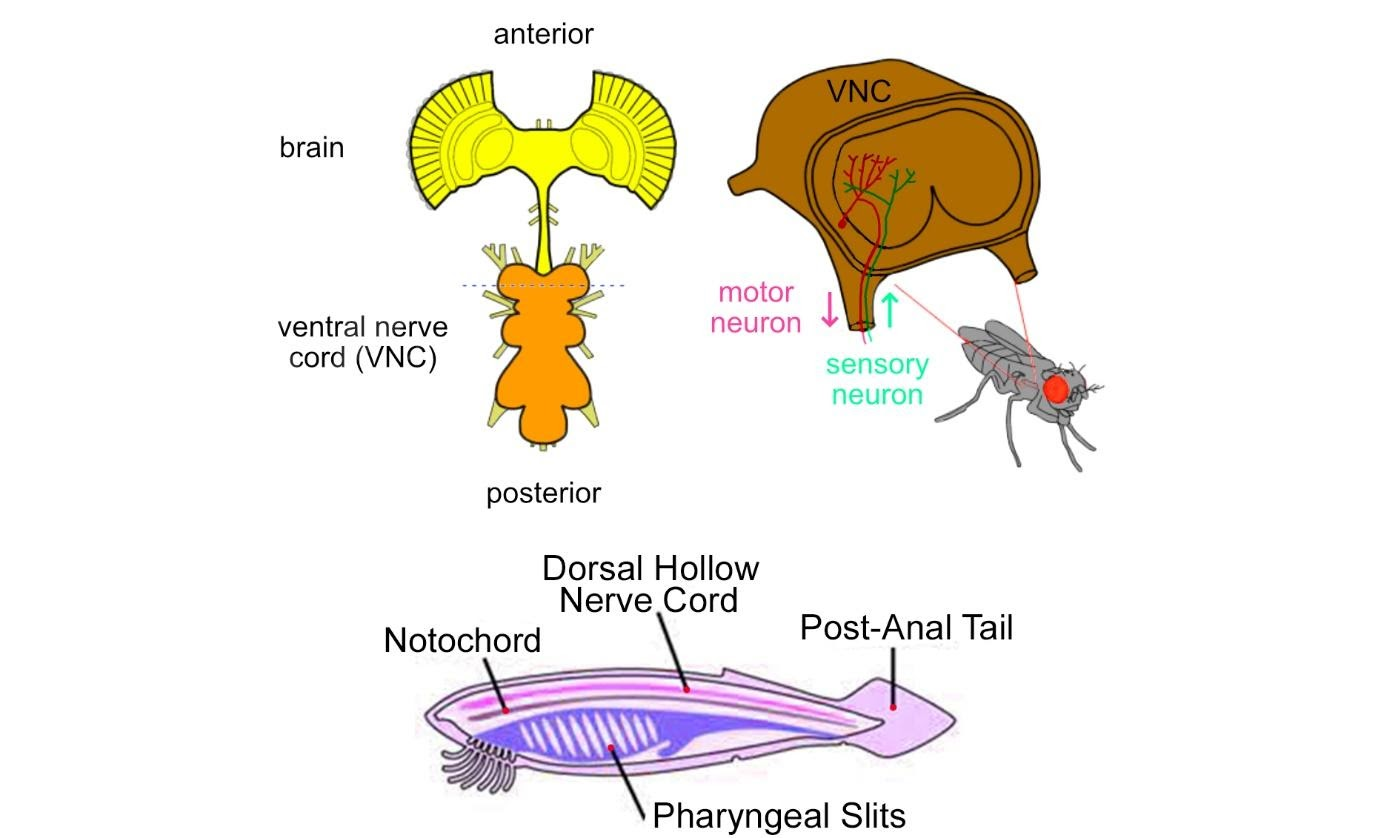
Figure: VNC and DNC
Complete answer:
Nerve cord is a single hollow tract of nervous tissue which constitutes the central nervous system of chordates and develops into the spinal cord and brain in vertebrates, It is a solid double strand of nerve fibers running along the length of the body in elongate invertebrates, such as earthworms and insects, connecting with a pair of nerve ganglia at each body segment.
1. The dorsal nerve cord (DNC) is a unique feature to chordates and is mainly found in the Vertebrate chordate subphylum. The dorsal nerve cord is the only one embryonic feature that is unique to all chordates, among the other four chordate features- a notochord, a post-anal tail, an endostyle, and pharyngeal slits. The dorsal hollow nerve cord is a hollow cord that lies dorsal to the notochord. It is formed from a part of the ectoderm that rolls and forms the hollow tube. This feature distinguishes chordates from other animal phyla, such as Annelids and Arthropods, which have solid, ventral tubes.
2. The ventral nerve cord (VNC) is the major structure of the invertebrate central nervous system. It is also the functional equivalent of vertebrate spinal cord. The VNC coordinates neural signalling from the brain to the body and vice versa. Thus, it helps in integrating sensory input and locomotor output which is why decapitated insects can still walk, groom and mate. VNC is sufficient to perform complex motor programs without brain input.
Note:
The vertebrate spinal cord is the long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue. It extends from medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. The brain and the spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS).

Figure: VNC and DNC
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




