
What is the N-glycosidic linkage?
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: Glycosidic bond is found in DNA that helps in the formation of the nucleoside which is made up of two molecules only. When a hemiacetal reacts with an amine, a mixed acetal is formed in which the anomeric carbon in the hemiacetal is bonded to one oxygen atom and one nitrogen atom.
Complete answer:
Glycosidic is a covalent bond that is formed between a carbohydrate and another molecule. Here, another molecule can either be a carbohydrate or some molecule other than carbohydrates. A typical glycosidic bond is shown here –
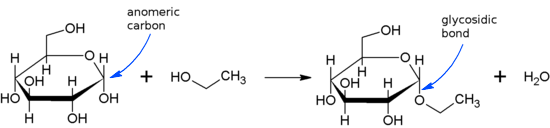
If the anomeric carbon present in the carbohydrate molecule bonds to nitrogen atom another molecule, the glycosidic bond is termed as N-glycosidic bond or N-glycosidic linkage that can be as given below –
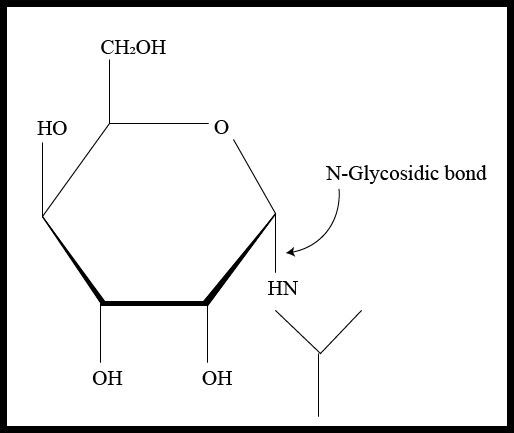
This type of linkage can be seen in nucleosides and nucleotides found in nucleic acids because the nitrogenous bases contain nitrogen atoms that form bonds with the anomeric carbon of the sugar molecule releasing a molecule of water. The formation of N-glycosidic linkage follows the ${ S }_{ N }$ 1 type of reaction mechanism that occurs through a resonance stabilized carbocation intermediate. The mechanism can be understood by the illustration given below –
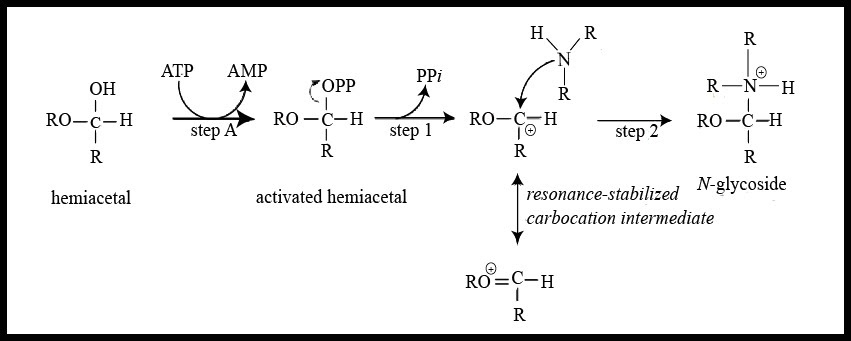
Note:
These linkages serve as an important type of bond in the biological world because formations of the disaccharides, oligosaccharides, or polysaccharides occur just because the monosaccharides or longer chains of other sugar molecules join together by the glycosidic linkages.
These bonds enable monosaccharides to join not only other sugars but also amines and alcohol-like compounds that result in the formation of a wide variety of molecules serving as a key to various biological reactions.
Complete answer:
Glycosidic is a covalent bond that is formed between a carbohydrate and another molecule. Here, another molecule can either be a carbohydrate or some molecule other than carbohydrates. A typical glycosidic bond is shown here –

If the anomeric carbon present in the carbohydrate molecule bonds to nitrogen atom another molecule, the glycosidic bond is termed as N-glycosidic bond or N-glycosidic linkage that can be as given below –

This type of linkage can be seen in nucleosides and nucleotides found in nucleic acids because the nitrogenous bases contain nitrogen atoms that form bonds with the anomeric carbon of the sugar molecule releasing a molecule of water. The formation of N-glycosidic linkage follows the ${ S }_{ N }$ 1 type of reaction mechanism that occurs through a resonance stabilized carbocation intermediate. The mechanism can be understood by the illustration given below –

Note:
These linkages serve as an important type of bond in the biological world because formations of the disaccharides, oligosaccharides, or polysaccharides occur just because the monosaccharides or longer chains of other sugar molecules join together by the glycosidic linkages.
These bonds enable monosaccharides to join not only other sugars but also amines and alcohol-like compounds that result in the formation of a wide variety of molecules serving as a key to various biological reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




