
Which dicarboxylic acid in presence of a dehydrating agent is least reactive to give an anhydride?
A.
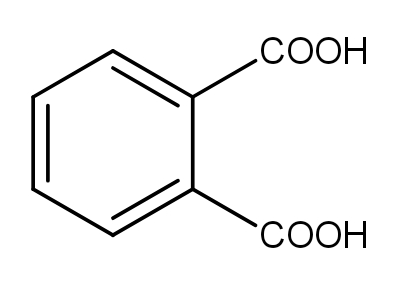
B.
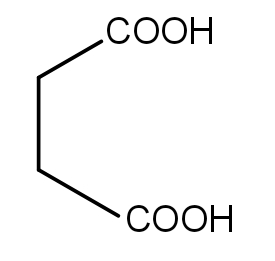
C.
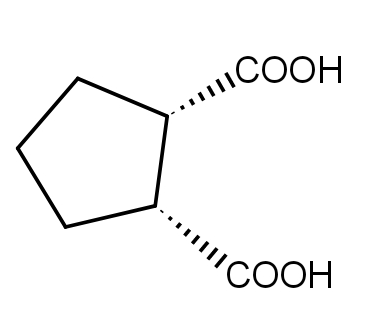
D.
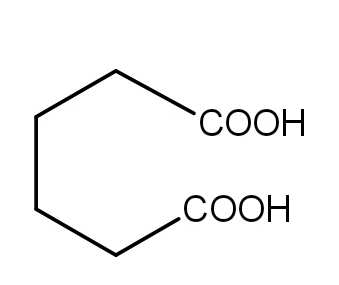




Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: The reaction that leads to an unstable product is always slow to occur i.e. the reaction in which substrate is more stable than the product will be least reactive. Dehydration involves removal of a molecule of water. The five and six-membered rings are more stable than seven-membered rings.
Complete Solution:
The dehydrating agent is used to remove water from the molecule. In the four given substrates, try to remove a molecule of water and see the products. The product which will be most stable will occur faster while the product with least stability will be least to give an anhydride.
Let us write the reaction which is happening and the product formed. This will give us an idea about the least reactive reaction.
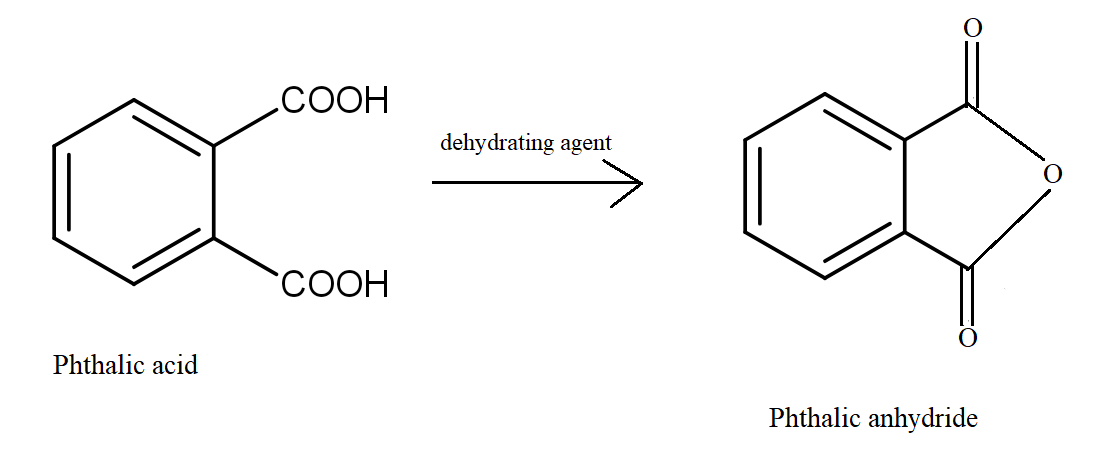
In the first option, Phthalic acid undergoes dehydration giving Phthalic anhydride, a five-membered cyclic anhydride. The delocalisation is increased with two Carbon atoms. It increases the stability of the product formed.
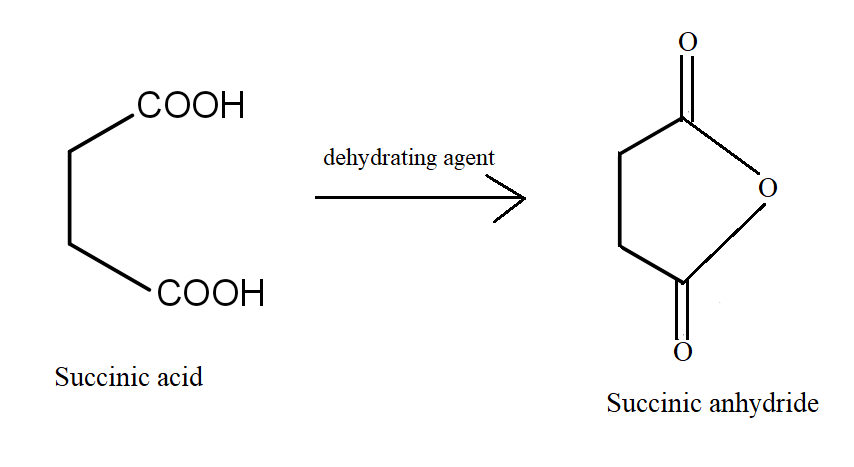
In the second reaction, Succinic acid undergoes dehydration giving Succinic anhydride, a five-membered cyclic anhydride which is stable.
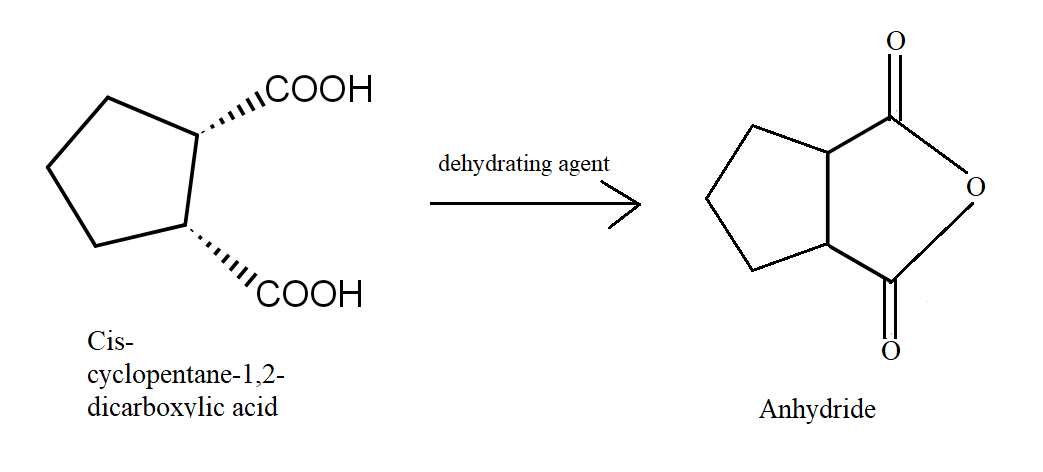
In the third reaction, Cis cyclopentane 1,2 dicarboxylic acid easily undergoes dehydration to give a five-membered cyclic anhydride which is stable.
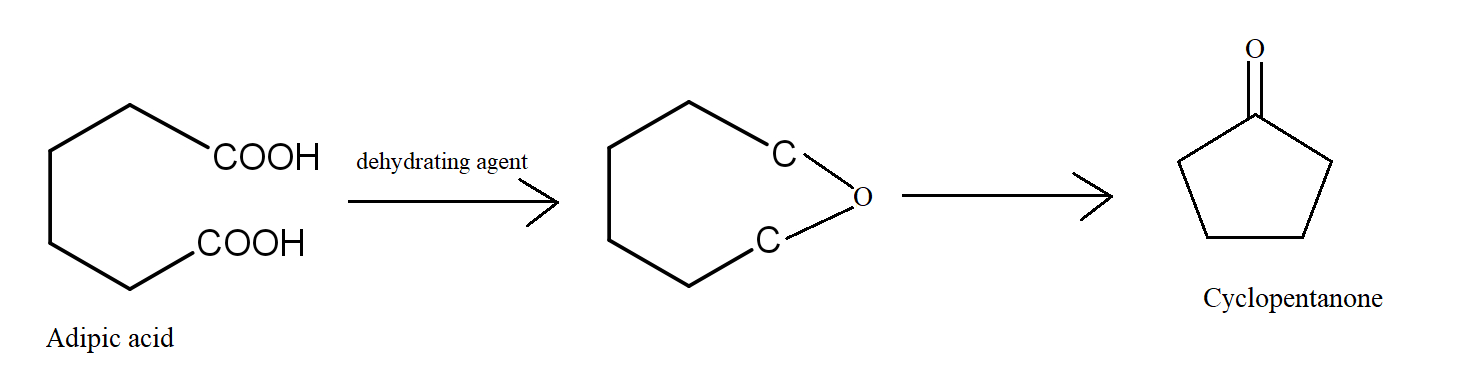
In the fourth reaction, Adipic acid undergoes a dehydration reaction giving a seven-membered cyclic anhydride which is unstable. It further degrades to form cyclopentanone which is stable. Because the seven-membered anhydride formed is unstable, so the reaction is least likely to occur.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Analysing the products formed in organic reactions give us a better idea about the kinetics of the reaction and we can find our answers easily.
Cis-cyclopentane-1,2-dicarboxylic acid can be easily dehydrated to form its anhydride. In contrast, the trans isomer is impossible to convert to its anhydride because carboxyl groups have large spatial distance which cannot be shortened by conformational changes.
Complete Solution:
The dehydrating agent is used to remove water from the molecule. In the four given substrates, try to remove a molecule of water and see the products. The product which will be most stable will occur faster while the product with least stability will be least to give an anhydride.
Let us write the reaction which is happening and the product formed. This will give us an idea about the least reactive reaction.

In the first option, Phthalic acid undergoes dehydration giving Phthalic anhydride, a five-membered cyclic anhydride. The delocalisation is increased with two Carbon atoms. It increases the stability of the product formed.

In the second reaction, Succinic acid undergoes dehydration giving Succinic anhydride, a five-membered cyclic anhydride which is stable.

In the third reaction, Cis cyclopentane 1,2 dicarboxylic acid easily undergoes dehydration to give a five-membered cyclic anhydride which is stable.

In the fourth reaction, Adipic acid undergoes a dehydration reaction giving a seven-membered cyclic anhydride which is unstable. It further degrades to form cyclopentanone which is stable. Because the seven-membered anhydride formed is unstable, so the reaction is least likely to occur.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Analysing the products formed in organic reactions give us a better idea about the kinetics of the reaction and we can find our answers easily.
Cis-cyclopentane-1,2-dicarboxylic acid can be easily dehydrated to form its anhydride. In contrast, the trans isomer is impossible to convert to its anhydride because carboxyl groups have large spatial distance which cannot be shortened by conformational changes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




