
Which d-orbital has a different shape from the rest of all d- orbitals?
A.${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ - }}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$
B.${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$
C.${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xz}}}}$
D.${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xy}}}}$
E.${{\text{d}}_{{\text{yz}}}}$
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint:The s shell has only 1 orbital. Therefore, it can hold only 2 electrons. It is spherical. P shell has 3 orbitals and holds a maximum of 6 electrons. Each P orbital has a pair of lobes on either side.
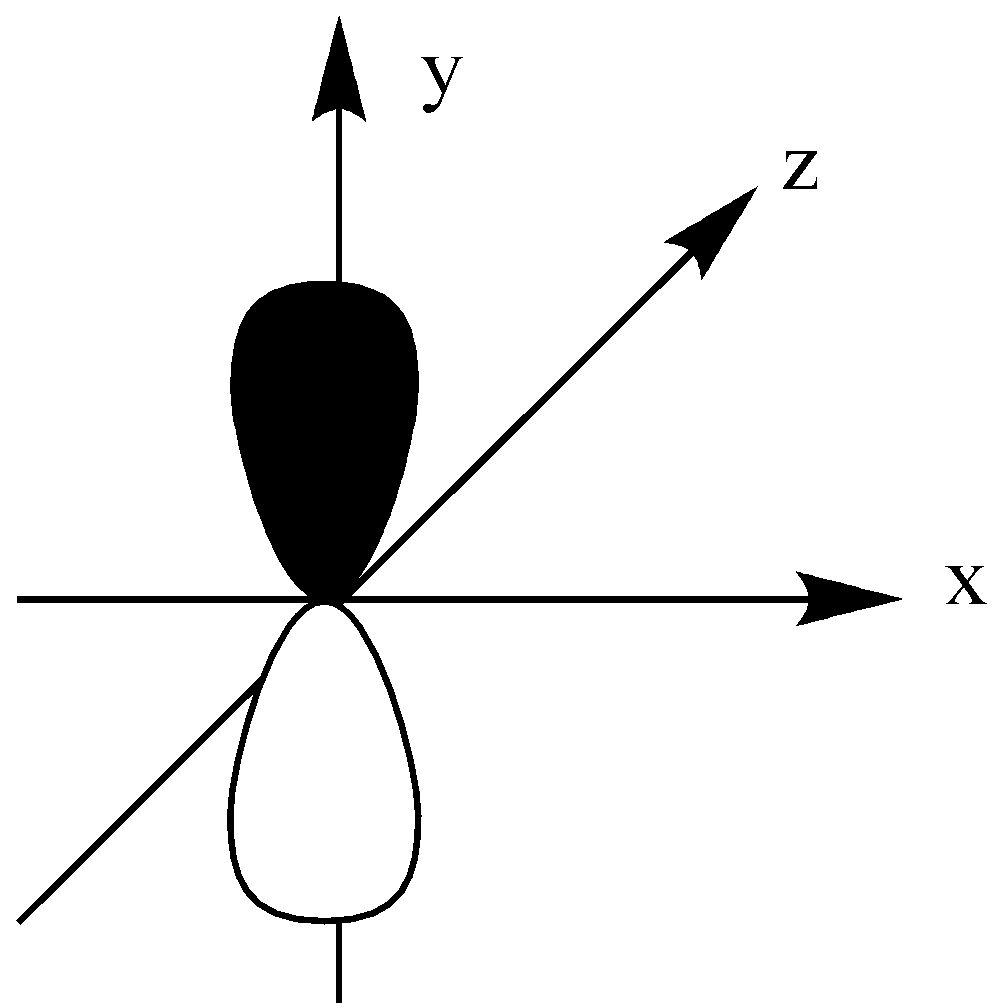
The d shell has 5 orbitals in which except 1 orbital, all others have 4 lobes.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us look at all the orbitals of d.
We know that there are 5 lobes in the d orbital. They are ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xy}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xz}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{yz}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ - }}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$
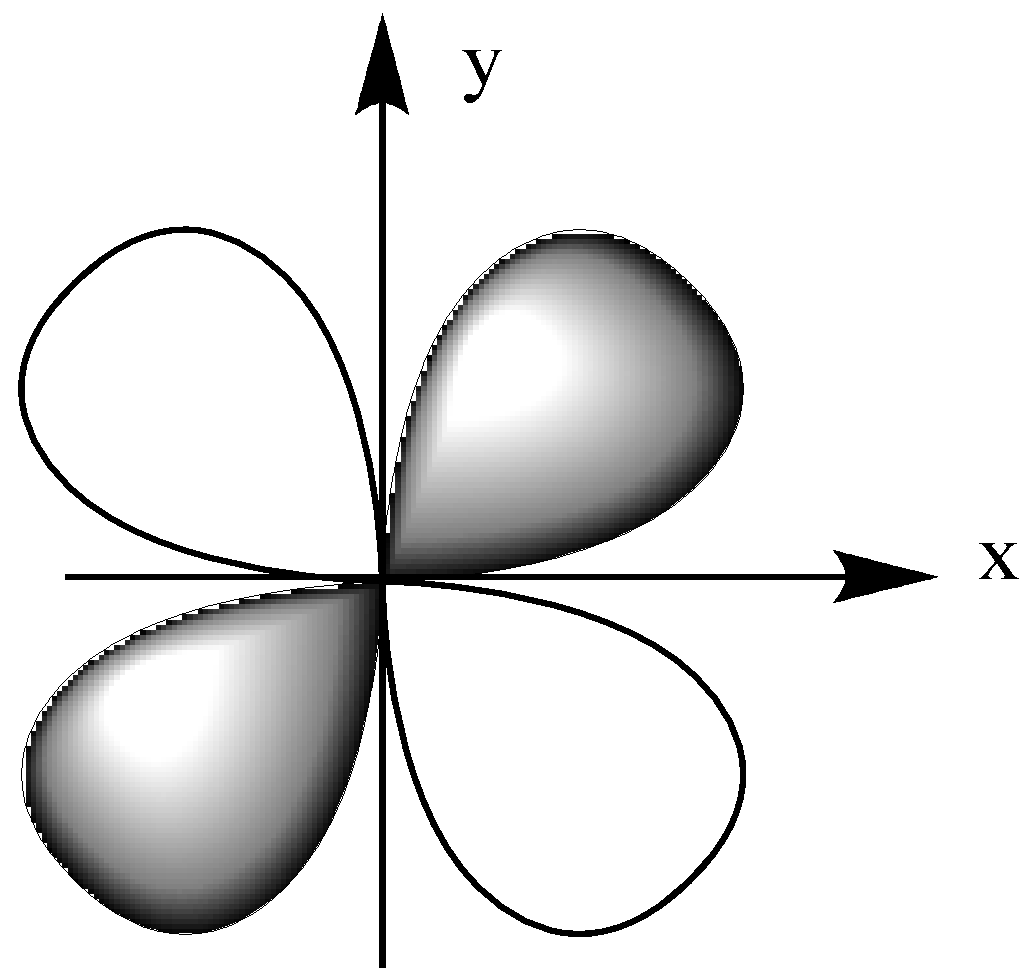
First, let us have a look at the orientation of the ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xy}}}}$ orbital. It is in the x-y plane.
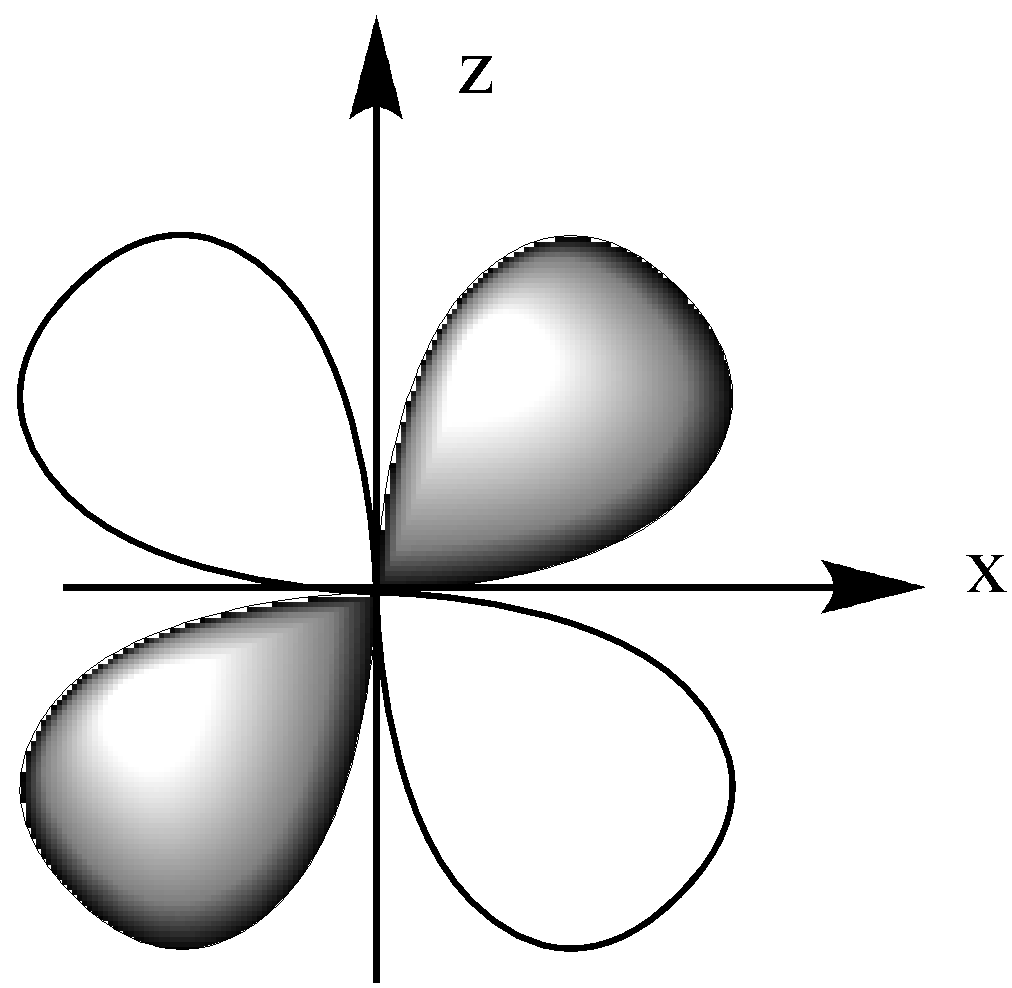
The ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xz}}}}$ orbital is in the x-z plane, which means the lobe lies between the x and y-axis.
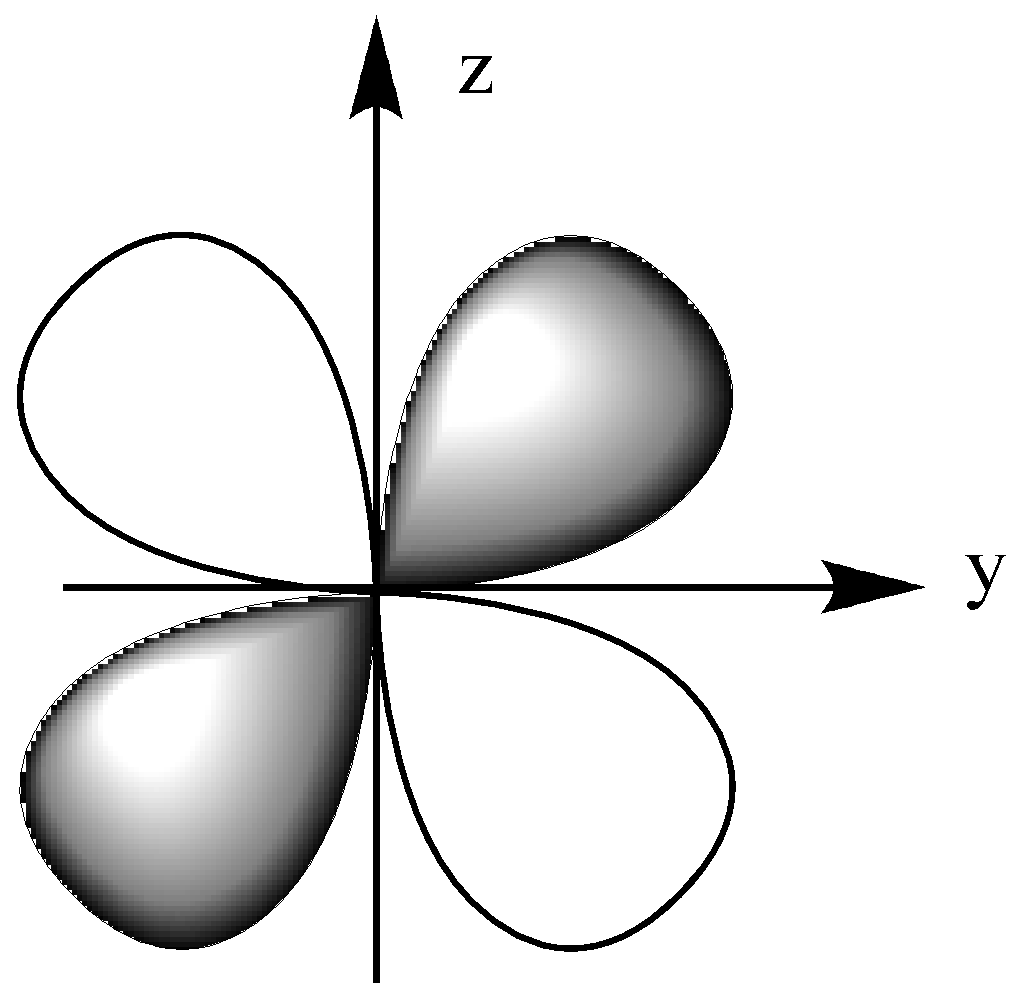
The ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{yz}}}}$ orbital lies in the y-z plane, which is between the z and y-axis.
The ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ - }}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ orbital lies on the x and y-axis.
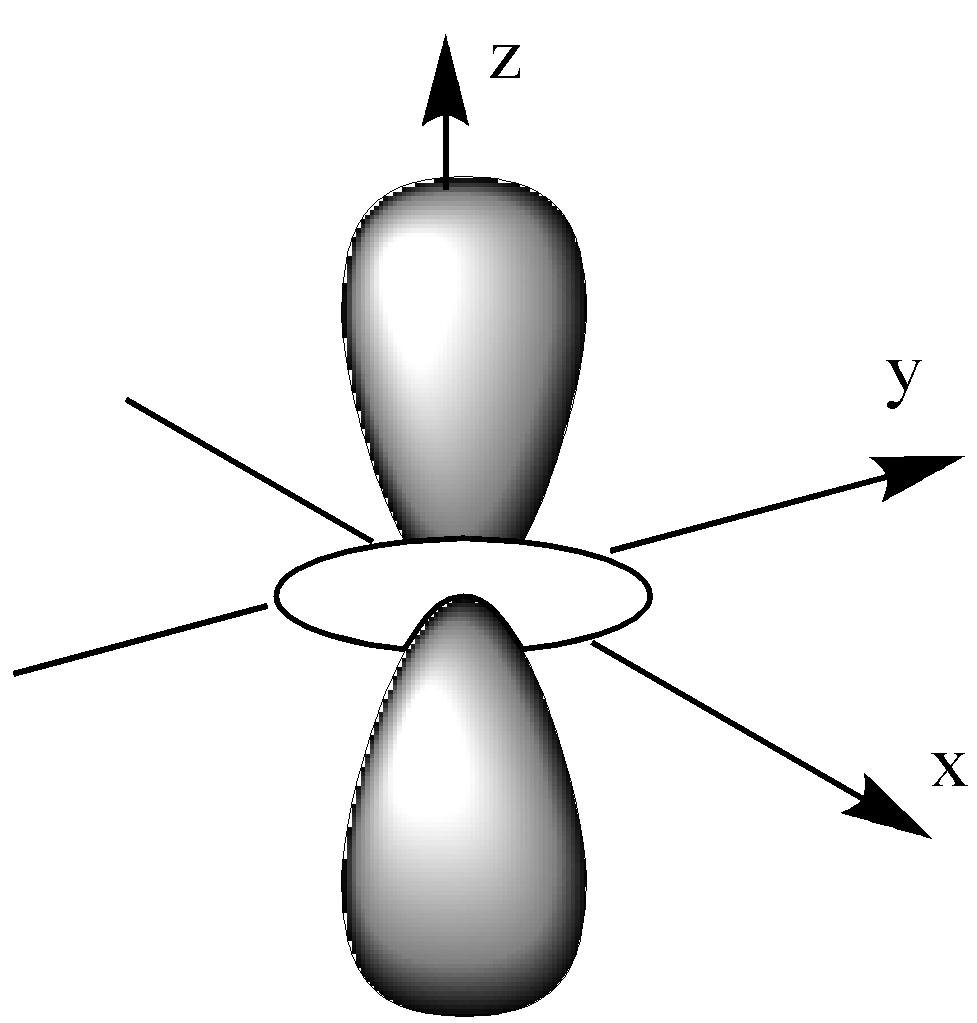
The ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ orbital is like a single dumbbell along the z-axis and a ring around the nucleus on the XY plane. It has only 2 lobes and 1 ring.
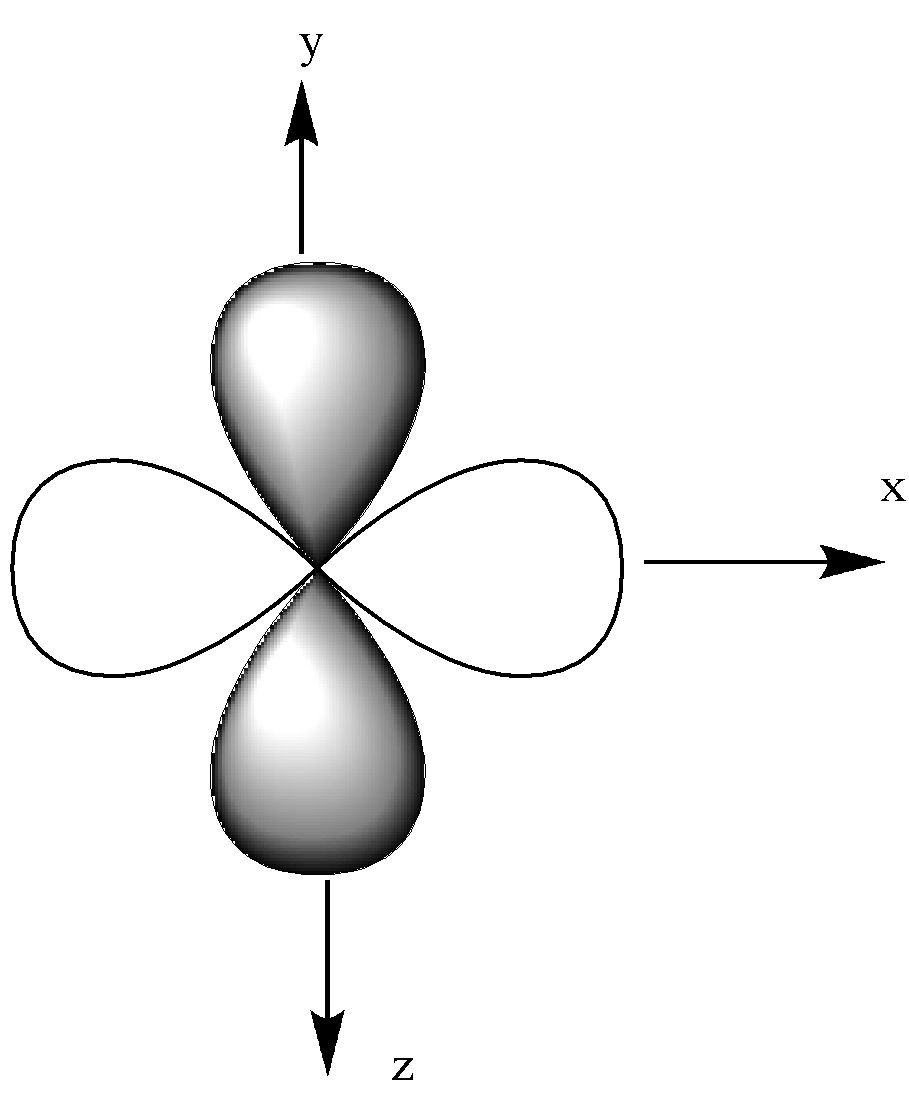
We could see that all other orbitals except the ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ orbital have a double dumbbell shape, 4 lobes.
${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ have single dumbbell-shaped and 2 number lobes.
Thus the correct answer is ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$
Therefore, the correct option is (B) .
Note: The shapes of these orbitals help us to find the d orbital splitting on the approach of octahedral as well as tetrahedral ligands. The Crystal Field theory can be understood well with the knowledge of the structure of the orbitals and their orientation. Transition metals show special properties because of the d orbitals.

The d shell has 5 orbitals in which except 1 orbital, all others have 4 lobes.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us look at all the orbitals of d.
We know that there are 5 lobes in the d orbital. They are ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xy}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xz}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{yz}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ - }}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$
First, let us have a look at the orientation of the ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xy}}}}$ orbital. It is in the x-y plane.

The ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{xz}}}}$ orbital is in the x-z plane, which means the lobe lies between the x and y-axis.

The ${{\text{d}}_{{\text{yz}}}}$ orbital lies in the y-z plane, which is between the z and y-axis.

The ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{x}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{ - }}{{\text{y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ orbital lies on the x and y-axis.

The ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ orbital is like a single dumbbell along the z-axis and a ring around the nucleus on the XY plane. It has only 2 lobes and 1 ring.

We could see that all other orbitals except the ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ orbital have a double dumbbell shape, 4 lobes.
${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$ have single dumbbell-shaped and 2 number lobes.
Thus the correct answer is ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$
Therefore, the correct option is (B) .
Note: The shapes of these orbitals help us to find the d orbital splitting on the approach of octahedral as well as tetrahedral ligands. The Crystal Field theory can be understood well with the knowledge of the structure of the orbitals and their orientation. Transition metals show special properties because of the d orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




