
Which d-orbitals have a different shape from the rest of all d-orbitals?
A. ${d_{{x^2} - {y^2}}}$
B. ${d_{{z^2}}}$
C. ${d_{xz}}$
D. ${d_{xy}}$
E. ${d_{xy}}$
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint:An orbital is the quantum mechanical refinement of Bohr’s orbit. In contrast to his concept of a circular orbit with a fixed radius, orbitals are mathematically derived regions of space with different probabilities of containing an electron. The d orbital contains 10 electrons. The d orbital is a clover shape because the electron is pushed out four times during the rotation.
Complete step by step answer:
The d orbital has ten protons to complete a fourth level of tetrahedral structure. With three spin aligned protons, it would have a spherical shape, yet four times during the rotation will have gluons that align with protons of the opposite spin to force an electron.
Now, we see the figure of all d-orbitals except ${d_{{z^2}}}$ because it has four lobes and has only two lobes.
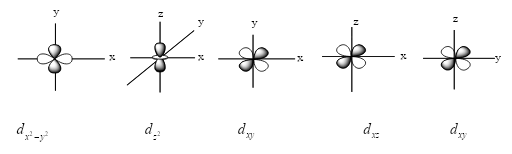
From the above figure, we see that the d-orbitals are in different shapes. ${d_{{z^2}}}$orbital has a different shape from rest of all d-orbitals.
${d_{{z^2}}}$ degenerate with other d orbitals, it has no nodal planes, instead it has 2 nodal cones. Instead of having 4 lobes, it has 2 lobes and 1 ring. That’s why this orbital is so different from the rest.
Hence, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:The standard procedure in differential calculus is to use a linear combination of two functions to produce one independent one. So ${d_{{z^2}}}$ looks different because it is a linear combination of two functions. In this orbital, 2 lobes lie on the z-axis as we see.
Complete step by step answer:
The d orbital has ten protons to complete a fourth level of tetrahedral structure. With three spin aligned protons, it would have a spherical shape, yet four times during the rotation will have gluons that align with protons of the opposite spin to force an electron.
Now, we see the figure of all d-orbitals except ${d_{{z^2}}}$ because it has four lobes and has only two lobes.

From the above figure, we see that the d-orbitals are in different shapes. ${d_{{z^2}}}$orbital has a different shape from rest of all d-orbitals.
${d_{{z^2}}}$ degenerate with other d orbitals, it has no nodal planes, instead it has 2 nodal cones. Instead of having 4 lobes, it has 2 lobes and 1 ring. That’s why this orbital is so different from the rest.
Hence, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note:The standard procedure in differential calculus is to use a linear combination of two functions to produce one independent one. So ${d_{{z^2}}}$ looks different because it is a linear combination of two functions. In this orbital, 2 lobes lie on the z-axis as we see.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




