
Which has an electronic configuration $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^1}$ ?
A. $N{a^ + }$
B. Al
C. F
D. Ti
E. B
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The electronic configuration of an element describes how electrons are distributed in its atomic orbitals. The electronic configurations of atoms follow a standard notation in which all electron-containing atomic subshells are placed in a sequence.
Complete step by step answer:
The electronic configuration of an atom is written with the help of the subshell labels. Now, these labels contain the shell number (given by the principal quantum number), the subshell name, (given by the azimuthal quantum number) and the total number of electrons in the subshell in superscript.
For example if the two electrons are filled in the' subshell of the first shell, then the resulting notation is $1{s^2}$. The three rules that dictate the manner in which electrons are filled in atomic orbitals are Aufbau principle, Pauli’s exclusion principle and Hund’s rule.
In Aufbau principle, the electrons must completely fill the atomic orbitals of a given energy level before occupying an orbital associated with a higher energy.
In Pauli’s exclusion principle, no two electrons can have equal values for all four quantum numbers and each subshell of an orbital can accommodate a maximum of two electrons and both the electrons must have opposite spins.
In Hund’s rule, all the subshells in an orbital must be singly occupied before any subshell is doubly occupied.
The order in which the electrons are filled in atomic orbitals as per the Aufbau principle is as shown:
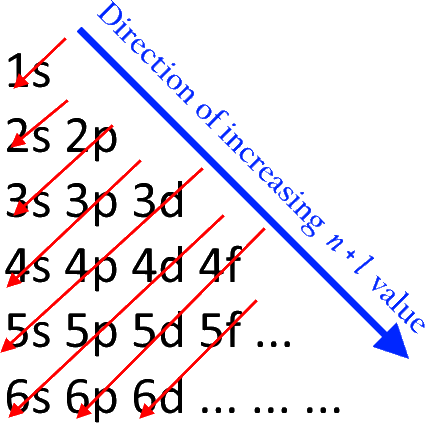
Now, among the given options Al is the correct option as, the atomic number of aluminum Is 13 and further, according the given rules, its electronic configuration is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^1}$.
Hence, option B is correct.
Note:
The electronic configuration of copper is $[Ar]3{d^{10}}4{s^1}$. This configuration disobeys the aufbau principle due to the relatively small energy gap between the $3d$ and the $4s$ orbitals and chromium is also one such exception in this case. These exceptions can sometimes be explained by the stability provided by half-filled or completely filled subshells.
Complete step by step answer:
The electronic configuration of an atom is written with the help of the subshell labels. Now, these labels contain the shell number (given by the principal quantum number), the subshell name, (given by the azimuthal quantum number) and the total number of electrons in the subshell in superscript.
For example if the two electrons are filled in the' subshell of the first shell, then the resulting notation is $1{s^2}$. The three rules that dictate the manner in which electrons are filled in atomic orbitals are Aufbau principle, Pauli’s exclusion principle and Hund’s rule.
In Aufbau principle, the electrons must completely fill the atomic orbitals of a given energy level before occupying an orbital associated with a higher energy.
In Pauli’s exclusion principle, no two electrons can have equal values for all four quantum numbers and each subshell of an orbital can accommodate a maximum of two electrons and both the electrons must have opposite spins.
In Hund’s rule, all the subshells in an orbital must be singly occupied before any subshell is doubly occupied.
The order in which the electrons are filled in atomic orbitals as per the Aufbau principle is as shown:

Now, among the given options Al is the correct option as, the atomic number of aluminum Is 13 and further, according the given rules, its electronic configuration is $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^1}$.
Hence, option B is correct.
Note:
The electronic configuration of copper is $[Ar]3{d^{10}}4{s^1}$. This configuration disobeys the aufbau principle due to the relatively small energy gap between the $3d$ and the $4s$ orbitals and chromium is also one such exception in this case. These exceptions can sometimes be explained by the stability provided by half-filled or completely filled subshells.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




