
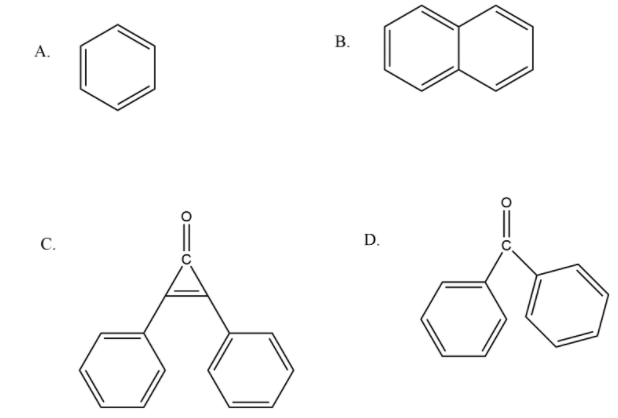
Which has maximum dipole moment?

Answer
553.8k+ views
Hint: For calculating the dipole moment we have to consider the magnitude and distance between the charges, but for estimating the highest and lowest dipole moment we can easily find them. If the bonds of carbon are symmetrical that is attached with the same atom it has zero dipole moment but when there is substitution then there is change in dipole moment.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that bonds can be classified as polar and nonpolar because of the electronegativity difference so that polarity is measured in terms of which we call dipole moment. It is defined as the product of magnitude of charge and distance between the charges, mathematically we can write it as- \[Dipole\,moment\,(\mu ) = \,q \times d\].
Here, \[\,q\] is the charge and \[d\] is the distance between the charges. Now in the above example we have some organic compounds so try to understand their structure as a sphere. So our first option is benzene which is symmetrical therefore no dipole moment is there. In the second option we have naphthalene which can be considered as two benzene rings are attached so that’s why we can also see it as spherical and symmetrical. Now a question arises that in option C and D there is benzophenone and another compound called $ 2,3 - \,diphenyl cycloprop - 2 - enone $ having a three membered ring.
In option D we have benzophenone so in that case, the dipole moment is in the above direction where there is a carbonyl group present. Now in terms of numerical value dipole moment of benzophenone is equal to $ 2.98\,D $ . While in other case of $ 2,3 - \,diphenyl cycloprop - 2 - enone $ we have a small three membered ring by which its dipole moment becomes $ 5.08\,D $
Note: Dipole moment has unit of Debye, which is represented by capital (D). Now there are many examples in which we have to compare between the examples by the only difference we see. See as in options C and D we have a benzophenone type of system but in option C there is little bit difference in the structure by introduction of three membered rings that’s why its dipole moment is greater than benzophenone.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that bonds can be classified as polar and nonpolar because of the electronegativity difference so that polarity is measured in terms of which we call dipole moment. It is defined as the product of magnitude of charge and distance between the charges, mathematically we can write it as- \[Dipole\,moment\,(\mu ) = \,q \times d\].
Here, \[\,q\] is the charge and \[d\] is the distance between the charges. Now in the above example we have some organic compounds so try to understand their structure as a sphere. So our first option is benzene which is symmetrical therefore no dipole moment is there. In the second option we have naphthalene which can be considered as two benzene rings are attached so that’s why we can also see it as spherical and symmetrical. Now a question arises that in option C and D there is benzophenone and another compound called $ 2,3 - \,diphenyl cycloprop - 2 - enone $ having a three membered ring.
In option D we have benzophenone so in that case, the dipole moment is in the above direction where there is a carbonyl group present. Now in terms of numerical value dipole moment of benzophenone is equal to $ 2.98\,D $ . While in other case of $ 2,3 - \,diphenyl cycloprop - 2 - enone $ we have a small three membered ring by which its dipole moment becomes $ 5.08\,D $
Note: Dipole moment has unit of Debye, which is represented by capital (D). Now there are many examples in which we have to compare between the examples by the only difference we see. See as in options C and D we have a benzophenone type of system but in option C there is little bit difference in the structure by introduction of three membered rings that’s why its dipole moment is greater than benzophenone.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




