
Which is the example of the hexadentate ligand?
A. $2,2 - $dipyridyl
B. Dimethylglyoxime
C. Iminodiacetate ion
D. Ethylene diamine tetra acetate ion (EDTA)
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint:We can determine the denticity by counting the number of donor atoms of a ligand. The prefix ‘Hexa’ in hexadentate denotes the six. The ligand which has six donor atoms is known as a hexadentate ligand.
Complete answer:
Ligand is a molecule that binds with metal to form a complex. The molecule binds with metal with some of its atoms. Denticity of a ligand is defined as the number of donor atoms of a ligand.
The ligands which bind with metal through a single atom are known as unidentate ligand such chloro ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }$ , ammonia ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ and water ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$.
The ligands which bind with metal through two atoms are known as bidentate ligand such ethylene diamine \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] and oxalate \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}_4^{2 - }\].
The ligands which bind with metal through six atoms are known as a hexadentate ligand. The ligands which bind with metal through three or more atoms are known as the polydentate ligand.
We will draw the structure of all ligand to determine their denticity as follows:
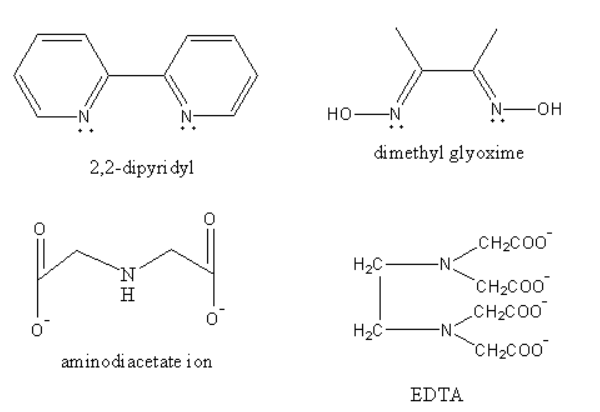
The ligand $2,2 - $dipyridyl, is a bidentate ligand as it has two donor nitrogen atoms. Dimethylglyoxime is a bidentate ligand as it has two donor nitrogen atoms. Iminodiacetate ion is a tridentate ligand as it has three donor atoms, one is nitrogen and two are oxygen. Ethylenediamine tetra acetate ion is a hexadentate ligand as it has six donor sites, two nitrogen and four oxygen atoms.
Therefore option (D) Ethylene diamine tetra acetate ion (EDTA) is correct.
Note:
The atoms which donate electrons to the metal are the donor atoms of the ligand. The donor atoms have a negative charge or lone pair of electron. The ethylene diamine has two hydroxyl groups but these oxygen atoms cannot work as donor atoms due to steric factors. Similarly, the two oxygen atoms in iminodiacetate ions also cannot work as donor atoms.
Complete answer:
Ligand is a molecule that binds with metal to form a complex. The molecule binds with metal with some of its atoms. Denticity of a ligand is defined as the number of donor atoms of a ligand.
The ligands which bind with metal through a single atom are known as unidentate ligand such chloro ${\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }$ , ammonia ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ and water ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}$.
The ligands which bind with metal through two atoms are known as bidentate ligand such ethylene diamine \[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\] and oxalate \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}_4^{2 - }\].
The ligands which bind with metal through six atoms are known as a hexadentate ligand. The ligands which bind with metal through three or more atoms are known as the polydentate ligand.
We will draw the structure of all ligand to determine their denticity as follows:

The ligand $2,2 - $dipyridyl, is a bidentate ligand as it has two donor nitrogen atoms. Dimethylglyoxime is a bidentate ligand as it has two donor nitrogen atoms. Iminodiacetate ion is a tridentate ligand as it has three donor atoms, one is nitrogen and two are oxygen. Ethylenediamine tetra acetate ion is a hexadentate ligand as it has six donor sites, two nitrogen and four oxygen atoms.
Therefore option (D) Ethylene diamine tetra acetate ion (EDTA) is correct.
Note:
The atoms which donate electrons to the metal are the donor atoms of the ligand. The donor atoms have a negative charge or lone pair of electron. The ethylene diamine has two hydroxyl groups but these oxygen atoms cannot work as donor atoms due to steric factors. Similarly, the two oxygen atoms in iminodiacetate ions also cannot work as donor atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




