
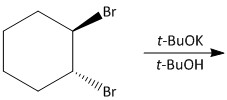
Which is the final main product of the following reaction of trans-\[1,2\]-dibromocyclohexane?
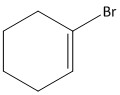
A.
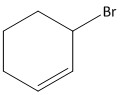
B.
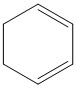
C.
D.





Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Cyclohexane exists in chair and boat conformations. The boat form is more stable conformer, but during a reaction it transforms into chair form. \[t - BuOK\] is a very strong base used for abstracting protons.
Complete step by step answer:
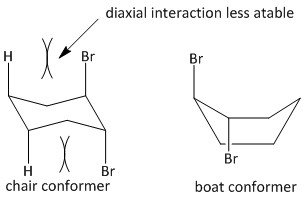
The trans-\[1,2\]-dibromocyclohexane exists in the form of chair and boat conformation. The boat conformation is of lower energy and more stable and the chair conformation is of higher energy and less stable due to diaxial interactions between the large bromine and hydrogen atoms.
For the given reaction, when trans-\[1,2\]-dibromocyclohexane was treated with potassium t-butoxide in t-butanol, an elimination reaction will occur. Potassium t-butoxide is known as a very strong base and used for abstraction of protons.
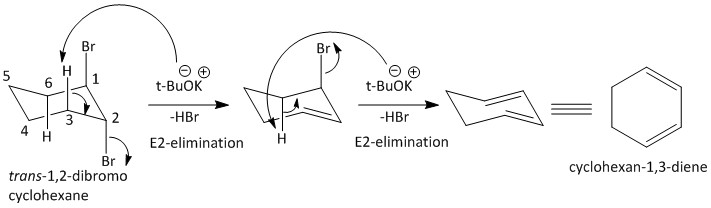
For the given compound the proton present on the carbon adjacent to the carbon attached to bromine will be abstracted by the base. This will result in two \[E2\] types of elimination reactions causing release of bromine atoms in the form of \[HBr\].
For the \[E2\] elimination an antiperiplanar orientation is required. Such orientation is only possible for a chair conformer and not a boat conformer. The hydrogen atoms at the \[C3\] and \[C6\] position of the Cyclohexane ring are antiperiplanar with the bromine atoms at \[C1\] and \[C2\].
The mechanism for the \[E2\] elimination is as follows:
Thus the option C is the correct answer, i.e. Cyclohexane-\[1,3\]-diene.
Note:
Elimination reactions are of various types like \[E1\], \[E2\] and \[E1cb\]. Unlike \[E2\] which is bimolecular with respect to substrate and the base, \[E1\] is unimolecular which includes formation of stable carbocation and \[E1cb\] which is unimolecular conjugate base elimination. The stereochemistry of the product varies according to the type of elimination.
Complete step by step answer:
The trans-\[1,2\]-dibromocyclohexane exists in the form of chair and boat conformation. The boat conformation is of lower energy and more stable and the chair conformation is of higher energy and less stable due to diaxial interactions between the large bromine and hydrogen atoms.

For the given reaction, when trans-\[1,2\]-dibromocyclohexane was treated with potassium t-butoxide in t-butanol, an elimination reaction will occur. Potassium t-butoxide is known as a very strong base and used for abstraction of protons.
For the given compound the proton present on the carbon adjacent to the carbon attached to bromine will be abstracted by the base. This will result in two \[E2\] types of elimination reactions causing release of bromine atoms in the form of \[HBr\].
For the \[E2\] elimination an antiperiplanar orientation is required. Such orientation is only possible for a chair conformer and not a boat conformer. The hydrogen atoms at the \[C3\] and \[C6\] position of the Cyclohexane ring are antiperiplanar with the bromine atoms at \[C1\] and \[C2\].
The mechanism for the \[E2\] elimination is as follows:

Thus the option C is the correct answer, i.e. Cyclohexane-\[1,3\]-diene.
Note:
Elimination reactions are of various types like \[E1\], \[E2\] and \[E1cb\]. Unlike \[E2\] which is bimolecular with respect to substrate and the base, \[E1\] is unimolecular which includes formation of stable carbocation and \[E1cb\] which is unimolecular conjugate base elimination. The stereochemistry of the product varies according to the type of elimination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




