
Which is the key intermediate compound linking glycolysis to the Krebs cycle?
(a)Malic acid
(b)Acetyl CoA
(c)NADH
(d)ATP
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: This is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate, and lipid metabolism. They deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle for the oxidation to generate energy.
Complete answer:
Acetyl-CoA is a molecule that takes part in many biochemical reactions. It is generated through the breakdown of both carbohydrates (by glycolysis) and lipids (by β-oxidation). It then enters the citric acid cycle within the mitochondrion by combining with oxaloacetate to make citrate, which is the initiative of the citric acid cycle or Krebs’s cycle. Its main function is to provide the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for energy production.
Additional Information
-In the Krebs cycle, all aerobic organisms release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
-Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a compound and hydrotrope. They give energy to drive many processes in living cells, e.g. contraction, and chemical synthesis.
-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) may be a cofactor that's central to metabolism. Found altogether in living cells, NAD has been named a dinucleotide as it is made up of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups.
-Malic acid is a dicarboxylic acid that is produced by all living organisms. It is donated to the sour taste of fruits and is used as a food additive.
So, the correct answer is ‘Acetyl-CoA’.
Note:
Konrad Bloch and Feodor Lynen were awarded the 1964 Nobel Prize for discoveries linking acetyl-CoA and fatty acid metabolism. At high glucose levels, the acetyl-CoA is produced through glycolysis. At low glucose levels, the assembly of acetyl-CoA is linked to β-oxidation of fatty acids.
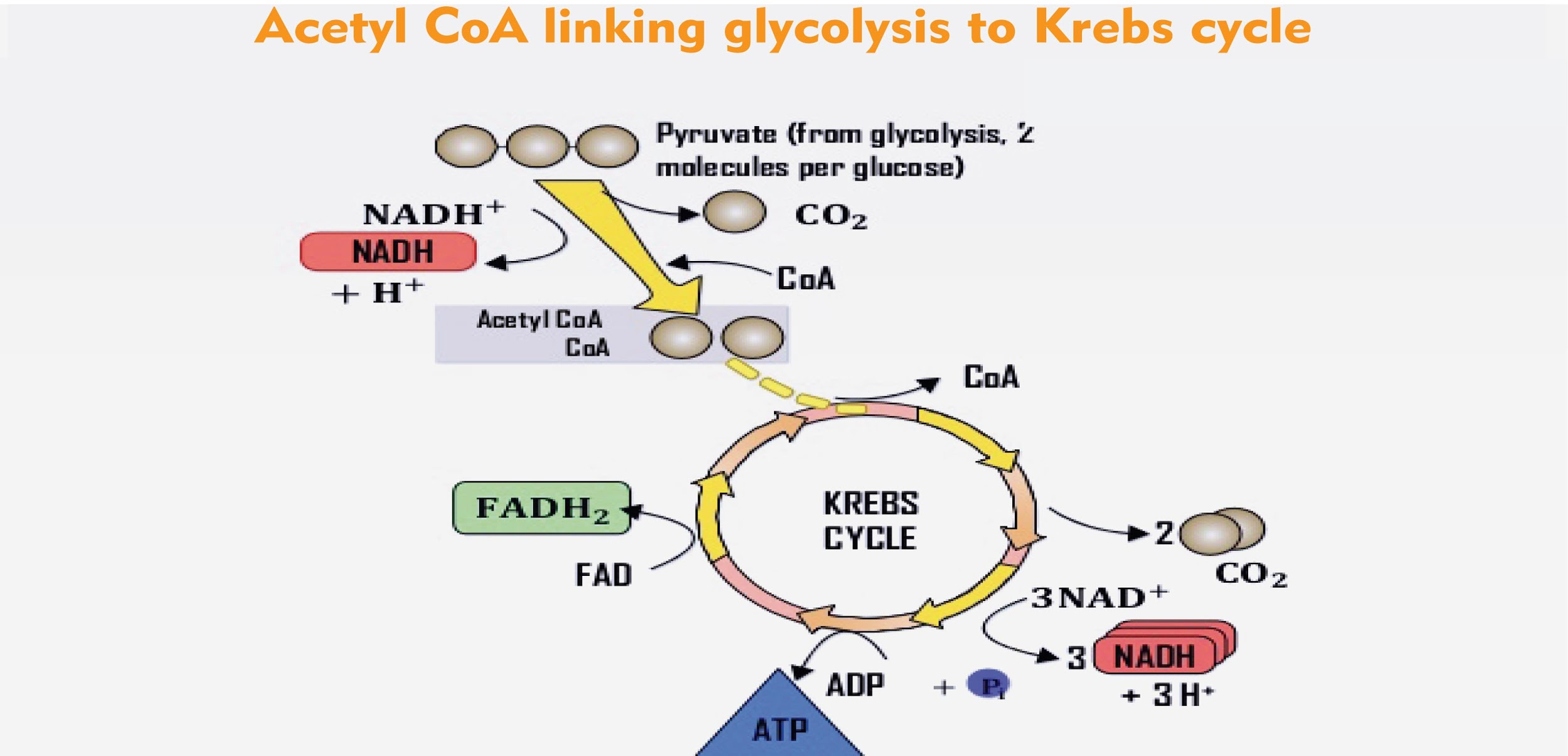
Complete answer:
Acetyl-CoA is a molecule that takes part in many biochemical reactions. It is generated through the breakdown of both carbohydrates (by glycolysis) and lipids (by β-oxidation). It then enters the citric acid cycle within the mitochondrion by combining with oxaloacetate to make citrate, which is the initiative of the citric acid cycle or Krebs’s cycle. Its main function is to provide the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for energy production.
Additional Information
-In the Krebs cycle, all aerobic organisms release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
-Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a compound and hydrotrope. They give energy to drive many processes in living cells, e.g. contraction, and chemical synthesis.
-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) may be a cofactor that's central to metabolism. Found altogether in living cells, NAD has been named a dinucleotide as it is made up of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups.
-Malic acid is a dicarboxylic acid that is produced by all living organisms. It is donated to the sour taste of fruits and is used as a food additive.
So, the correct answer is ‘Acetyl-CoA’.
Note:
Konrad Bloch and Feodor Lynen were awarded the 1964 Nobel Prize for discoveries linking acetyl-CoA and fatty acid metabolism. At high glucose levels, the acetyl-CoA is produced through glycolysis. At low glucose levels, the assembly of acetyl-CoA is linked to β-oxidation of fatty acids.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




