
Which is the primary $CO_2$ acceptor for C3 plants & C4 plants?
Answer
525.5k+ views
Hint: The primary acceptor in C3 plants is a five-carbon ketose sugar and in C4 plants, it is a three-carbon molecule.
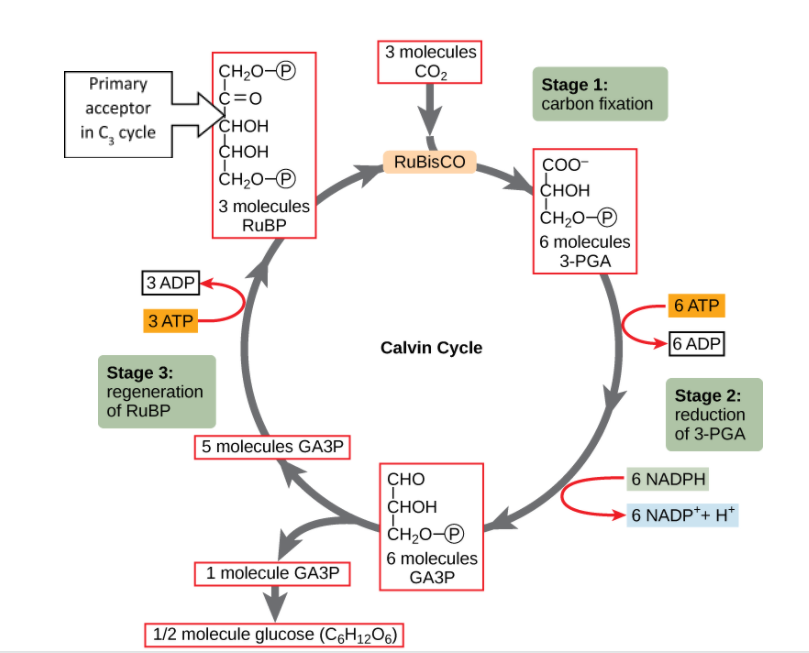
Complete answer: In the C3 cycle, carbon dioxide is reduced to form a first three carbon stable compound, 3-phosphoglyceric acid 3-PGA.
1. The initial carbon dioxide acceptor is a five-carbon molecule which is RUBP or Ribulose-1,5-biphosphate and RuBP carboxylase catalyzes this reaction.
2. The plants in which carbon dioxide is fixed in this way are known as C3 plants.
3. One molecule of glucose is formed by the fixation of six molecules of carbon dioxide in six turns.
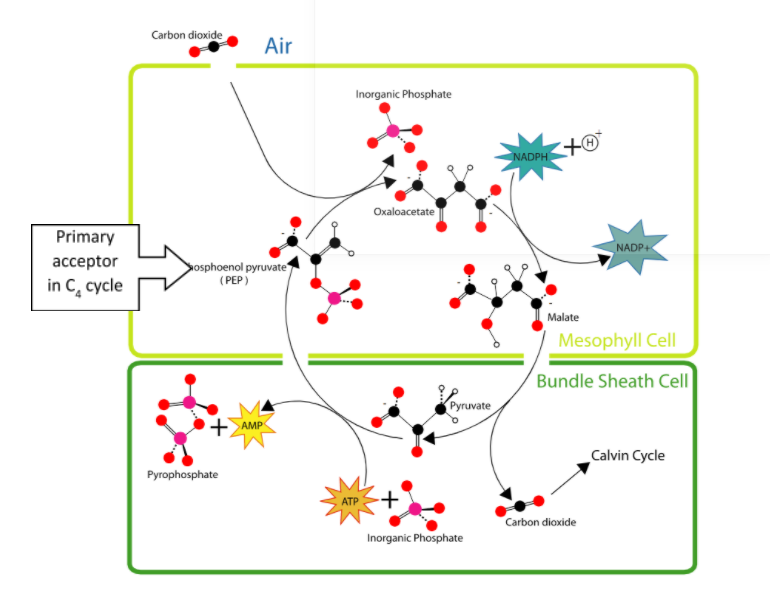
In the C4 cycle, phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) which is a three-carbon molecule act as a primary acceptor of carbon dioxide and is present in the mesophyll cells.
1. The carbon dioxide fixation is catalyzed by PEP carboxylase or PEPcase.
2. As a result of fixation, oxaloacetic acid (OAA) is formed which then converts into other four-carbon compounds such as malic acid or aspartic acid in the mesophyll cells.
3. In bundle sheath cells, C4 acids are broken down and carbon dioxide is released.
4. Then, the PEP is transported to the mesophyll cells therefore completing the cycle.
Note: Initially it was believed that since the first product was a C3 acid, the primary acceptor would be a two-carbon compound then, it was discovered that it was a five-carbon compound-RuBP.
Complete answer: In the C3 cycle, carbon dioxide is reduced to form a first three carbon stable compound, 3-phosphoglyceric acid 3-PGA.
1. The initial carbon dioxide acceptor is a five-carbon molecule which is RUBP or Ribulose-1,5-biphosphate and RuBP carboxylase catalyzes this reaction.
2. The plants in which carbon dioxide is fixed in this way are known as C3 plants.
3. One molecule of glucose is formed by the fixation of six molecules of carbon dioxide in six turns.

In the C4 cycle, phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) which is a three-carbon molecule act as a primary acceptor of carbon dioxide and is present in the mesophyll cells.
1. The carbon dioxide fixation is catalyzed by PEP carboxylase or PEPcase.
2. As a result of fixation, oxaloacetic acid (OAA) is formed which then converts into other four-carbon compounds such as malic acid or aspartic acid in the mesophyll cells.
3. In bundle sheath cells, C4 acids are broken down and carbon dioxide is released.
4. Then, the PEP is transported to the mesophyll cells therefore completing the cycle.

Note: Initially it was believed that since the first product was a C3 acid, the primary acceptor would be a two-carbon compound then, it was discovered that it was a five-carbon compound-RuBP.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




