
Which is true for recessive disease in families A and B?
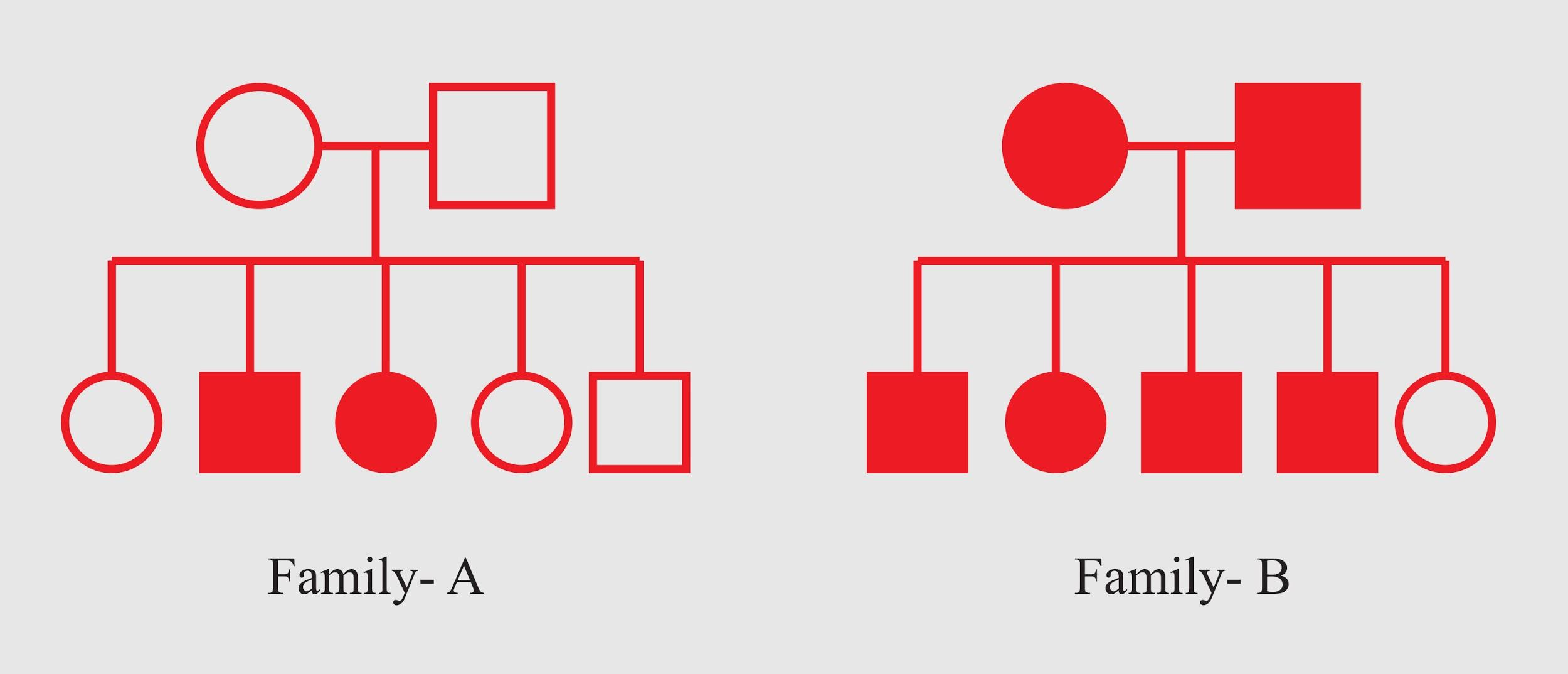
(A)In family A, both parents are homozygous recessive
(B)In family B, both the parents are homozygous dominant
(C)In family B both parents are heterozygous recessive
(D)In family A, both the parents are heterozygous recessive

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: Homozygous and heterozygous represents the zygosity in an individual and in the case of multigenerational conditions, it determines whether the parents and their offsprings will be affected by it or not.
Complete answer:
In family A, both of the parents are heterozygous recessive.
In the case of family A, we can see that the parents are not affected by the disease but two of their offspring are affected. Therefore, they are heterozygous recessive for the disease.
In the case of family B, both the parents as well as most of their children are affected by the disease. This concludes that they are homozygous recessive for the disease.
Additional Information: Test cross represents the breeding of an individual with a phenotypically recessive individual to determine the zygosity of the former one by looking into the proportions of phenotypes in offsprings. Zygosity is defined as the degree to which both copies of a gene have the same genetic sequence. This can be of two types- heterozygous and homozygous.
In the case of heterozygous, there is one dominant and one recessive allele whereas, homozygous individuals have further two types namely homozygous recessive and homozygous dominant. In homozygous dominant, there are two dominant alleles whereas the recessive one has two recessive alleles.
So, the correct answer is “In family A, both parents are heterozygous recessive”.
Note: In the case of the disease shown in the question, family A has parents that have heterozygous alleles. Therefore, even though they are not affected by the disease, some of their offspring get affected who inherit the dominant alleles. The differentiation of heterozygous and homozygous can be understood by the following diagram-
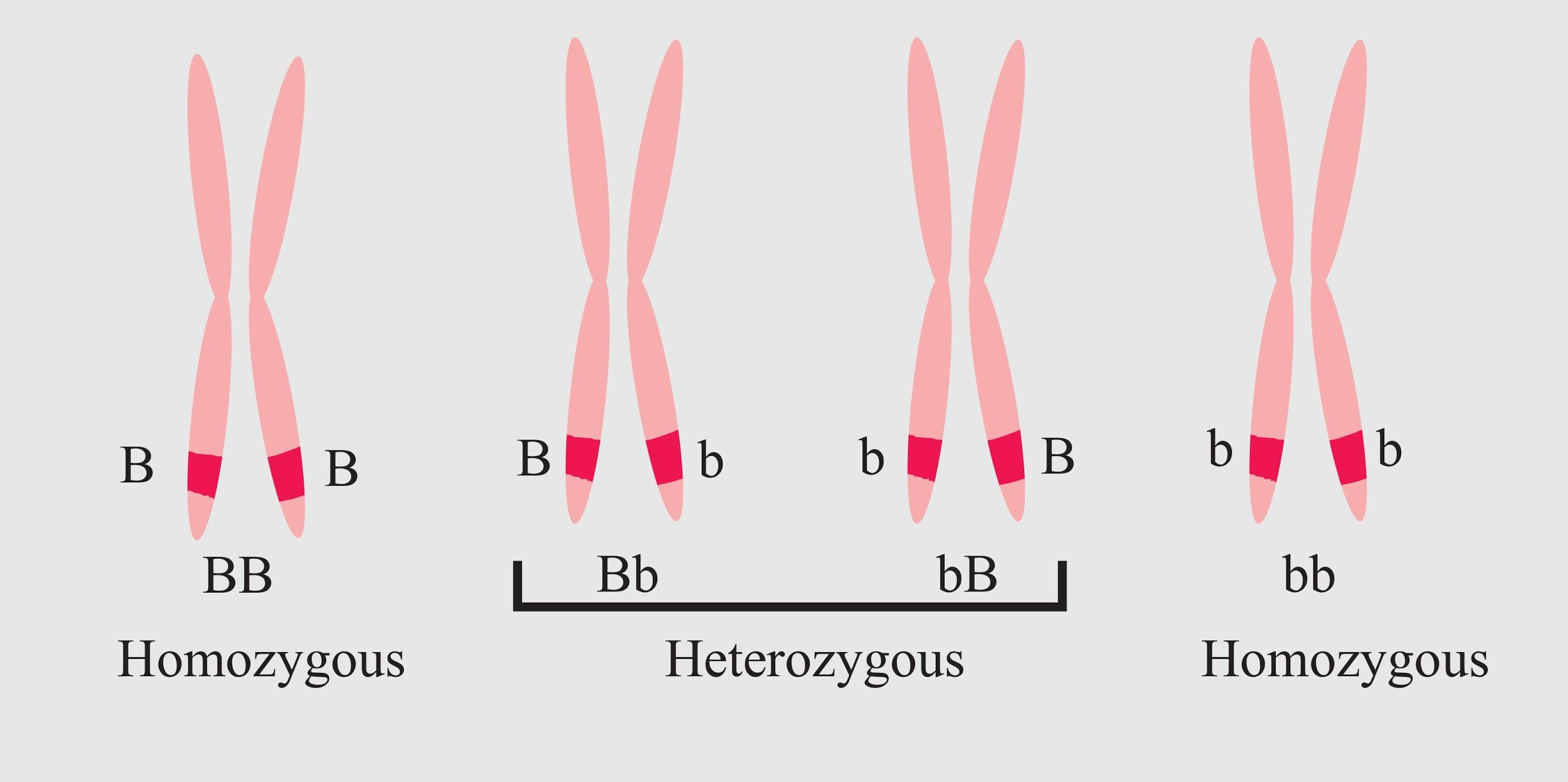
Complete answer:
In family A, both of the parents are heterozygous recessive.
In the case of family A, we can see that the parents are not affected by the disease but two of their offspring are affected. Therefore, they are heterozygous recessive for the disease.
In the case of family B, both the parents as well as most of their children are affected by the disease. This concludes that they are homozygous recessive for the disease.
Additional Information: Test cross represents the breeding of an individual with a phenotypically recessive individual to determine the zygosity of the former one by looking into the proportions of phenotypes in offsprings. Zygosity is defined as the degree to which both copies of a gene have the same genetic sequence. This can be of two types- heterozygous and homozygous.
In the case of heterozygous, there is one dominant and one recessive allele whereas, homozygous individuals have further two types namely homozygous recessive and homozygous dominant. In homozygous dominant, there are two dominant alleles whereas the recessive one has two recessive alleles.
So, the correct answer is “In family A, both parents are heterozygous recessive”.
Note: In the case of the disease shown in the question, family A has parents that have heterozygous alleles. Therefore, even though they are not affected by the disease, some of their offspring get affected who inherit the dominant alleles. The differentiation of heterozygous and homozygous can be understood by the following diagram-

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




