
Which minimum requirements do you require to check if the given figures are congruent:
Two rhombuses.
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: First we need to know the definition of congruence. We say the figures are congruent if all the sides and angles of the two figures are equal. Here we are given with two rhombuses. A rhombus has four sides in which opposite sides are parallel and all the sides are equal in length. For two different rhombuses you need to check for the requirements that are needed to say that two rhombuses are congruent. Since sides are equal we need to say side lengths of two rhombuses are equal and angles are equal.
Complete step-by-step solution
Now let us consider that there are two rhombuses as follows
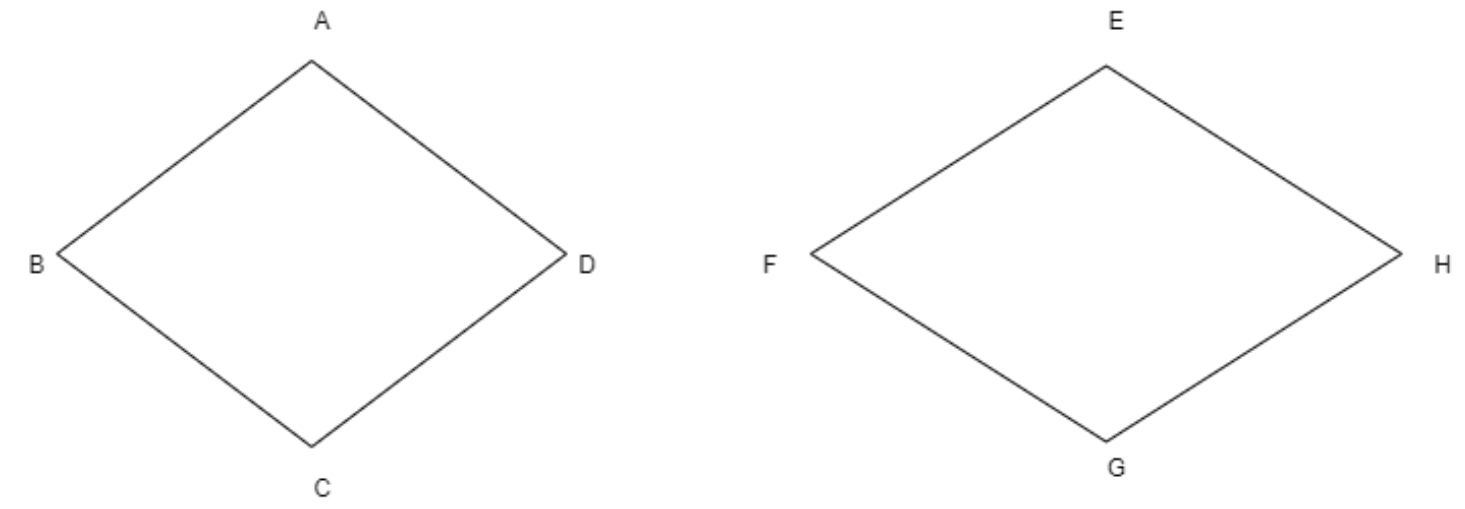
Let us consider the first rhombus ABCD
We know that the rhombus has all its sides are of equal length and opposite angles are equal we can write that
Here, \[AB=BC=CD=DA\], and \[\angle BAD =\angle BCD\], \[\angle ABC=\angle ADC\]
Now let us consider the second rhombus EFGH
By applying the definition of rhombus we can write
\[EF=FG=GH=HE\] and \[\angle FEH=\angle FGH\], \[\angle EFG=\angle EHG\]
Now we need to find the minimum required condition to say that both rhombuses are congruent.
Here, we can see that all the sides of each rhombus are equal, if one side of the first rhombus is equal to one side of the second rhombus then respectively all the sides of both rhombuses are equal.
So, if \[AB=EF\] is required to say that all sides of both rhombuses are equal.
Now let us consider the two adjacent angles of the first rhombus and two adjacent angles of the second rhombus. Let us take the angles \[\angle ABC,\angle BAD,\angle EFG,\angle FEG\].
Now if the respective adjacent angles of one rhombus are equal to respective adjacent angles of the second rhombus we can conclude that all the respective angles of two rhombuses are equal.
So, if \[\angle ABC=\angle EFG\] and \[\angle BAD=\angle FEG\] is required to say respective angles are equal in both rhombuses.
Here, as we can see all the sides and respective angles are equal we can say that two rhombuses are congruent.
Therefore the minimum requirements are one side of both rhombuses and two respective adjacent angles of both rhombuses are equal, then we can say that they are congruent.
Note: Students may make mistakes in taking the angles into consideration. That is there is no need to be the adjacent angles of one rhombus are equal. There is no need to be \[\angle ABC=\angle BAD\]. This may or may not happen. Some students will take this also into the consideration.
Complete step-by-step solution
Now let us consider that there are two rhombuses as follows

Let us consider the first rhombus ABCD
We know that the rhombus has all its sides are of equal length and opposite angles are equal we can write that
Here, \[AB=BC=CD=DA\], and \[\angle BAD =\angle BCD\], \[\angle ABC=\angle ADC\]
Now let us consider the second rhombus EFGH
By applying the definition of rhombus we can write
\[EF=FG=GH=HE\] and \[\angle FEH=\angle FGH\], \[\angle EFG=\angle EHG\]
Now we need to find the minimum required condition to say that both rhombuses are congruent.
Here, we can see that all the sides of each rhombus are equal, if one side of the first rhombus is equal to one side of the second rhombus then respectively all the sides of both rhombuses are equal.
So, if \[AB=EF\] is required to say that all sides of both rhombuses are equal.
Now let us consider the two adjacent angles of the first rhombus and two adjacent angles of the second rhombus. Let us take the angles \[\angle ABC,\angle BAD,\angle EFG,\angle FEG\].
Now if the respective adjacent angles of one rhombus are equal to respective adjacent angles of the second rhombus we can conclude that all the respective angles of two rhombuses are equal.
So, if \[\angle ABC=\angle EFG\] and \[\angle BAD=\angle FEG\] is required to say respective angles are equal in both rhombuses.
Here, as we can see all the sides and respective angles are equal we can say that two rhombuses are congruent.
Therefore the minimum requirements are one side of both rhombuses and two respective adjacent angles of both rhombuses are equal, then we can say that they are congruent.
Note: Students may make mistakes in taking the angles into consideration. That is there is no need to be the adjacent angles of one rhombus are equal. There is no need to be \[\angle ABC=\angle BAD\]. This may or may not happen. Some students will take this also into the consideration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 7 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

AIM To prepare stained temporary mount of onion peel class 7 biology CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of the national daily class 7 english CBSE

List of coprime numbers from 1 to 100 class 7 maths CBSE





