
Which monosaccharide forms cellulose?
A. Beta D Glucose
B. Alpha D Galactose
C. Beta D Fructose
D. Alpha D Fructose
Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: Carbohydrates are an important part of our diet; natural sources of carbohydrates include grains, fruits, and vegetables. Carbohydrates supply energy to the body, particularly glucose, a simple sugar found in starch and found in a variety of everyday foods. Carbohydrates play a variety of roles in humans, animals, and plants.
Complete answer:
Glucose is made up of two isomers of the aldohexose sugars, one of which (D-glucose) is physiologically active. L-glucose, the mirror counterpart of D-glucose, cannot be utilised by cells. The open-chain form of glucose (either 'D-' or 'L-') is in equilibrium in solutions with many cyclic isomers, each of which contains a ring of carbons closed by one oxygen atom.
There are two types of D-glucose: alpha-D-glucose and beta-D-glucose. Only the direction in which the -H and -OH groups point to carbon 1 differs. Starch is generated when alpha-glucose molecules are chemically bonded to create a polymer. When beta-glucose molecules are linked together to create a polymer, the result is cellulose.
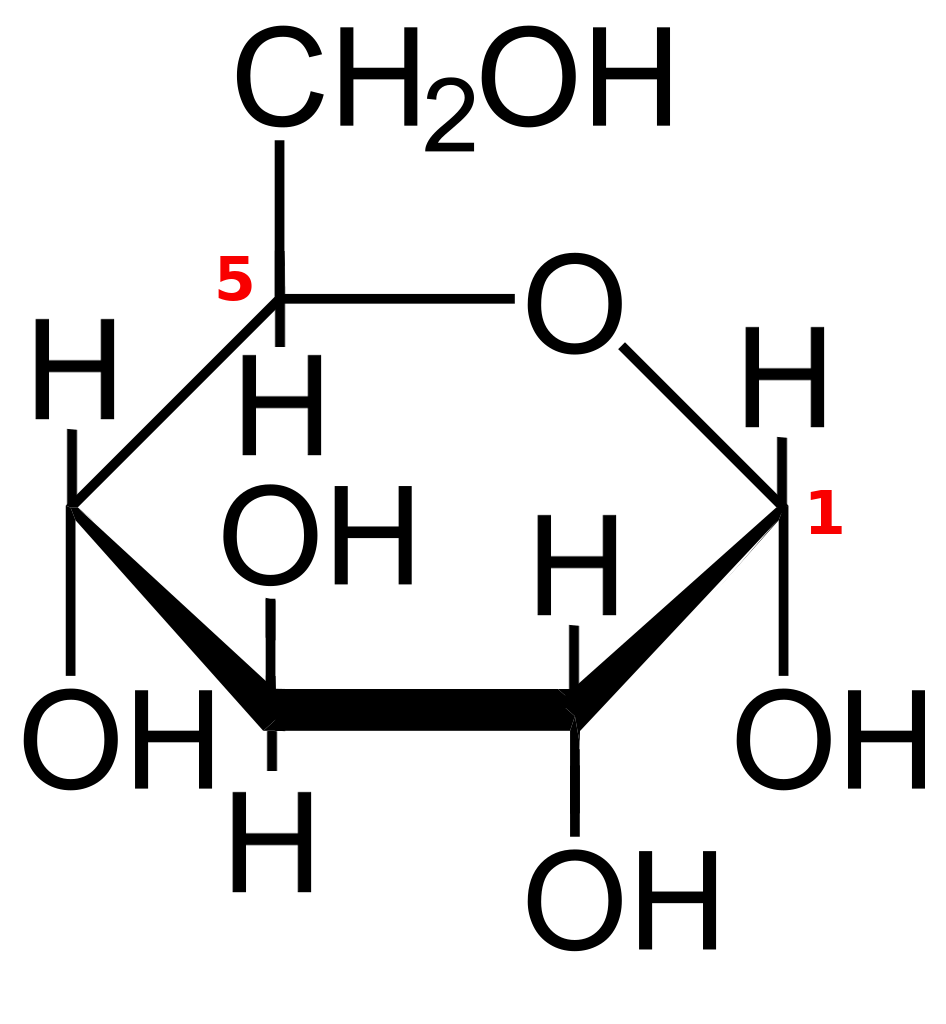
Sucrose is made up of two monomers α-D-Glucose and β-D-Fructose.
Cellulose made up of β -D-Glucose.
Starch made up of α-D-Glucose.
Lactose is made up of two monomers β-D-Galactose and β-D-Glucose.
So, the correct answer is A. β -D-Glucose.
The stoichiometric formula for carbohydrates is ($CH_2O$)n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. In other words, the carbon-to-hydrogen-to-oxygen ratio in carbohydrate molecules is 1:2:1. This formula also explains how the term "carbohydrate" came to be: the components are carbon ("carbo") and water (thus "hydrate"). Monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides are the three forms of carbohydrates.
The notation 'a-' indicates that the hydroxyl group linked to C-1 and the -$CH_2OH$ group at C-5 are on opposing sides of the ring's plane (a trans arrangement), whereas 'ß-' indicates that they are on the same side of the plane (a cis arrangement).
Cellulose, the other primary glucose polysaccharide present in plants, has a structural rather than a nutritive function. One of the most abundant organic substances in the biosphere is cellulose. Each year, a lot of cellulose is generated and destroyed on Earth. It's a non-branched polymer made up of glucose residues linked together by -1,4 links.
Note:-
The covalent chemical links that connect ring-shaped sugar molecules to other molecules are known as glycosidic bonds. They can be O-linked or N-linked because they are formed by a condensation process between an alcohol or amine from one molecule and the anomeric carbon of the sugar.
Complete answer:
Glucose is made up of two isomers of the aldohexose sugars, one of which (D-glucose) is physiologically active. L-glucose, the mirror counterpart of D-glucose, cannot be utilised by cells. The open-chain form of glucose (either 'D-' or 'L-') is in equilibrium in solutions with many cyclic isomers, each of which contains a ring of carbons closed by one oxygen atom.
There are two types of D-glucose: alpha-D-glucose and beta-D-glucose. Only the direction in which the -H and -OH groups point to carbon 1 differs. Starch is generated when alpha-glucose molecules are chemically bonded to create a polymer. When beta-glucose molecules are linked together to create a polymer, the result is cellulose.

Sucrose is made up of two monomers α-D-Glucose and β-D-Fructose.
Cellulose made up of β -D-Glucose.
Starch made up of α-D-Glucose.
Lactose is made up of two monomers β-D-Galactose and β-D-Glucose.
So, the correct answer is A. β -D-Glucose.
The stoichiometric formula for carbohydrates is ($CH_2O$)n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. In other words, the carbon-to-hydrogen-to-oxygen ratio in carbohydrate molecules is 1:2:1. This formula also explains how the term "carbohydrate" came to be: the components are carbon ("carbo") and water (thus "hydrate"). Monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides are the three forms of carbohydrates.
The notation 'a-' indicates that the hydroxyl group linked to C-1 and the -$CH_2OH$ group at C-5 are on opposing sides of the ring's plane (a trans arrangement), whereas 'ß-' indicates that they are on the same side of the plane (a cis arrangement).
Cellulose, the other primary glucose polysaccharide present in plants, has a structural rather than a nutritive function. One of the most abundant organic substances in the biosphere is cellulose. Each year, a lot of cellulose is generated and destroyed on Earth. It's a non-branched polymer made up of glucose residues linked together by -1,4 links.
Note:-
The covalent chemical links that connect ring-shaped sugar molecules to other molecules are known as glycosidic bonds. They can be O-linked or N-linked because they are formed by a condensation process between an alcohol or amine from one molecule and the anomeric carbon of the sugar.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




