
Which of the following acids on decarboxylation gives Isobutane?
A)2,2-Dimethyl butanoic acid
B)2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid
C)3-Methyl pentanoic acid
D)2-Methyl butanoic acid
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: Decarboxylation is the removal of a carboxyl group from the compound which results in the formation of an alkane and carbon dioxide. If the given acid has no branches, then the resultant alkane will be a straight chain and if the acid has one or two branches of methyl group it will form a branched-chain alkane. The resultant alkane can be secondary or tertiary alkane.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here, we have to find a compound that undergoes decarboxylation to form an Isobutane. Isobutane is a secondary alkane.
Usually, decarboxylation of the alkyl acid is the reaction for the preparation of Isobutane.
Now we have to find the compound which will lose a carboxyl group to form Isobutane.
The carbon and oxygen in the carboxyl group are preferred from the carboxyl group of the compound. The carbon leaving the compound is from the –COOH of the parent compound, which is the first carbon chain.
To form an Isobutane, the compound to undergo decarboxylation should have only 5 carbon atoms. Since 4 carbon atoms will form the Isobutane and one carbon will leave as carbon-di-oxide.
Now, Option A: 2,2-Dimethyl butanoic acid and Option C: 3-Methyl pentanoic acid will be discarded because they have 6 carbons in the compound.
So, we are left with Option B and Option D.
Let’s have a look at the decarboxylation of 2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid in the presence of NaOH and CaO.
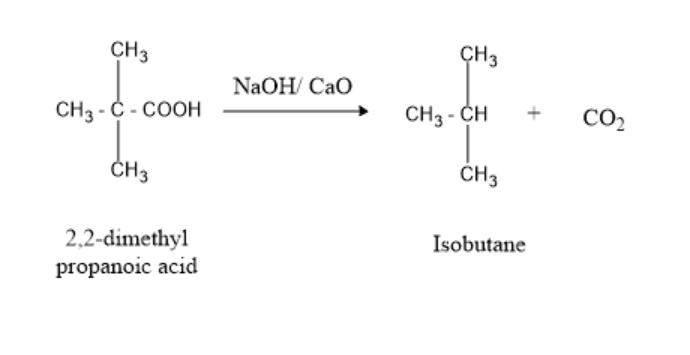
The decarboxylation of 2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid in the presence of NaOH and CaO forms Isobutane and carbon-di-oxide.
Similarly, the decarboxylation of 2-Methyl butanoic acid forms n-butane.
Therefore, 2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid forms Isobutane.
Final answer: The correct answer is Option B: 2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid.
Note:
Isobutane can also be formed by the decarboxylation of 3-methylbutanoic acid. Also, n-butane can be formed by Wurtz synthesis of an Ethyl bromide or hydrolysis of n-butyl magnesium bromide. However, reduction of alcohol results in the formation of the same parent compound.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here, we have to find a compound that undergoes decarboxylation to form an Isobutane. Isobutane is a secondary alkane.
Usually, decarboxylation of the alkyl acid is the reaction for the preparation of Isobutane.
Now we have to find the compound which will lose a carboxyl group to form Isobutane.
The carbon and oxygen in the carboxyl group are preferred from the carboxyl group of the compound. The carbon leaving the compound is from the –COOH of the parent compound, which is the first carbon chain.
To form an Isobutane, the compound to undergo decarboxylation should have only 5 carbon atoms. Since 4 carbon atoms will form the Isobutane and one carbon will leave as carbon-di-oxide.
Now, Option A: 2,2-Dimethyl butanoic acid and Option C: 3-Methyl pentanoic acid will be discarded because they have 6 carbons in the compound.
So, we are left with Option B and Option D.
Let’s have a look at the decarboxylation of 2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid in the presence of NaOH and CaO.

The decarboxylation of 2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid in the presence of NaOH and CaO forms Isobutane and carbon-di-oxide.
Similarly, the decarboxylation of 2-Methyl butanoic acid forms n-butane.
Therefore, 2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid forms Isobutane.
Final answer: The correct answer is Option B: 2,2-dimethyl propanoic acid.
Note:
Isobutane can also be formed by the decarboxylation of 3-methylbutanoic acid. Also, n-butane can be formed by Wurtz synthesis of an Ethyl bromide or hydrolysis of n-butyl magnesium bromide. However, reduction of alcohol results in the formation of the same parent compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




