
Which of the following causes malaria?
(a) Plasmodium
(b) Hookworm
(c) Ascaris
(d) Filarial worm
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: It is a disease caused by a parasite. Each year, approximately 210 million people are infected with these diseases, and about 440,000 people die from the disease. Its symptoms usually start with shivering and chills, followed by a high fever, followed by sweating, and a return to normal temperature.
Complete answer:
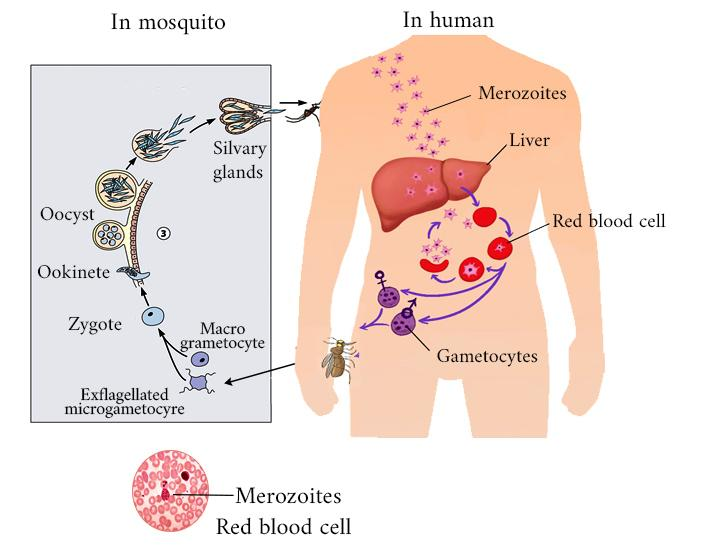
-Malaria is a life-threatening mosquito-borne blood disease.
-The female Anopheles mosquito transmits it to humans.
-Plasmodium genus, the parasite in mosquitoes, is responsible for spreading malaria. Different types of Plasmodium are:
Plasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium malariae
Plasmodium vivax
Plasmodium ovale
Hence, Plasmodium causes malaria.
Additional Information: Mosquito transmission cycle
-Uninfected mosquito. A mosquito becomes infected by feeding on an individual who has malaria.
-Transmission of the parasite. If this mosquito bites you within the future, it can transmit malaria parasites to you.
-In the liver. Once the parasites enter your body, they visit your liver — where some types can lie dormant for as long as a year.
-Into the bloodstream. They leave the liver and infect your red blood cells when the parasites mature. This is when people typically develop malaria symptoms.
-On to the next person. If an uninfected mosquito bites you now within the cycle, it'll become infected together with your malaria parasites and may spread them to the opposite people it bites.
So the correct answer is ‘Plasmodium’.
Note: Because the parasites that cause malaria affect red blood cells, people also can catch malaria from exposure to infected blood, including:
-From mother to unborn child
-Through blood transfusions
-By sharing needles used to inject drugs
Complete answer:
-Malaria is a life-threatening mosquito-borne blood disease.
-The female Anopheles mosquito transmits it to humans.
-Plasmodium genus, the parasite in mosquitoes, is responsible for spreading malaria. Different types of Plasmodium are:
Plasmodium falciparum
Plasmodium malariae
Plasmodium vivax
Plasmodium ovale
Hence, Plasmodium causes malaria.
Additional Information: Mosquito transmission cycle
-Uninfected mosquito. A mosquito becomes infected by feeding on an individual who has malaria.
-Transmission of the parasite. If this mosquito bites you within the future, it can transmit malaria parasites to you.
-In the liver. Once the parasites enter your body, they visit your liver — where some types can lie dormant for as long as a year.
-Into the bloodstream. They leave the liver and infect your red blood cells when the parasites mature. This is when people typically develop malaria symptoms.
-On to the next person. If an uninfected mosquito bites you now within the cycle, it'll become infected together with your malaria parasites and may spread them to the opposite people it bites.
So the correct answer is ‘Plasmodium’.
Note: Because the parasites that cause malaria affect red blood cells, people also can catch malaria from exposure to infected blood, including:
-From mother to unborn child
-Through blood transfusions
-By sharing needles used to inject drugs

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




