
Which of the following compounds does not undergo Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction?
${\text{A}}{\text{.}}$ Ethanoic acid
${\text{B}}{\text{.}}$ Propionic acid
${\text{C}}{\text{.}}$ Iso-butyric acid
${\text{D}}{\text{.}}$ Trichloroacetic acid
Answer
607.5k+ views
Hint- Here, we will proceed by discussing the Vell Volhard Zelinsky reaction mechanism. Then, we will draw the structures of all the acids given in the options. Those which will be having alpha hydrogen will undergo the reaction.
Complete answer:
An aldehyde or ketone in possession of α hydrogen and its enol tautomer will be in equilibrium. This aldehyde and ketone component allows electrophilic addition to occur at the hydrogen α. However, carboxylic acids usually do not form stable enols, so adding alpha is easier to do with carboxylic acids than with aldehydes and ketones. The reaction from Hell Volhard Zelinsky reveals a process for incorporating alpha with a carboxylic acid. The purpose of the process is to transform the carboxylic acid into a derivative that is subjected to tautomerization and then to apply alpha to it. For this reaction to happen, the given carboxylic acid must have at least one alpha hydrogen present.
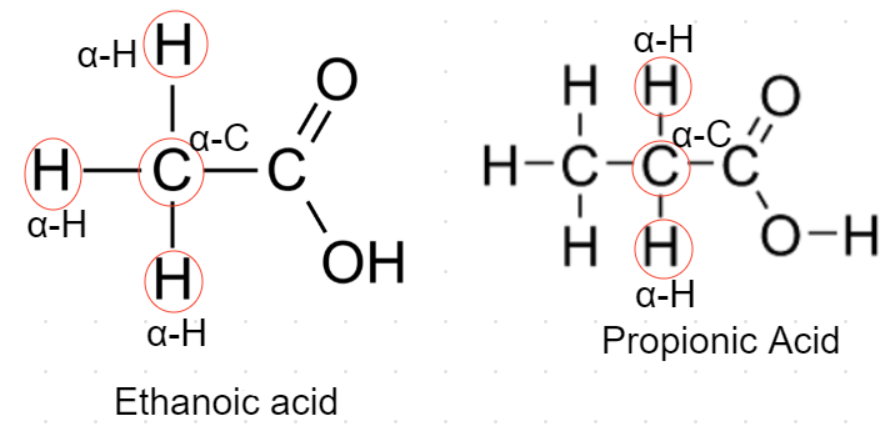
${\text{A}}{\text{.}}$ Ethanoic acid- This acid contains 3 alpha hydrogens as shown in the figure in which its structure is drawn.
So, ethanoic acid will undergo Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction.
${\text{B}}{\text{.}}$ Propionic acid- This acid contains 2 alpha hydrogens as shown in the figure in which its structure is drawn.
So, propionic acid will undergo Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction.
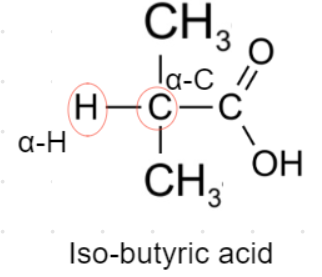
${\text{C}}{\text{.}}$ Iso-butyric acid- This acid contains 1 alpha hydrogens as shown in the figure in which its structure is drawn.
So, Iso-butyric acid will undergo Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction.
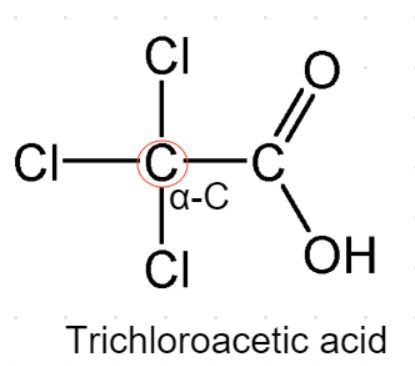
${\text{D}}{\text{.}}$ Trichloroacetic acid- This acid contains no alpha hydrogens as shown in the figure in which its structure is drawn.
So, Trichloroacetic acid will not undergo Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction due to the absence of any alpha hydrogen.
Therefore, option D is correct.
Note- For organic molecules, the alpha carbon refers to the first carbon atom that binds to a functional group, such as carbonyl. The atom of hydrogen bound to an alpha atom of carbon is considered an alpha-hydrogen molecule. The Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction mechanism is somewhat distinct from other reactions to halogenation, because it occurs in the absence of a halogen carrier.



Complete answer:
An aldehyde or ketone in possession of α hydrogen and its enol tautomer will be in equilibrium. This aldehyde and ketone component allows electrophilic addition to occur at the hydrogen α. However, carboxylic acids usually do not form stable enols, so adding alpha is easier to do with carboxylic acids than with aldehydes and ketones. The reaction from Hell Volhard Zelinsky reveals a process for incorporating alpha with a carboxylic acid. The purpose of the process is to transform the carboxylic acid into a derivative that is subjected to tautomerization and then to apply alpha to it. For this reaction to happen, the given carboxylic acid must have at least one alpha hydrogen present.
${\text{A}}{\text{.}}$ Ethanoic acid- This acid contains 3 alpha hydrogens as shown in the figure in which its structure is drawn.
So, ethanoic acid will undergo Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction.
${\text{B}}{\text{.}}$ Propionic acid- This acid contains 2 alpha hydrogens as shown in the figure in which its structure is drawn.
So, propionic acid will undergo Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction.
${\text{C}}{\text{.}}$ Iso-butyric acid- This acid contains 1 alpha hydrogens as shown in the figure in which its structure is drawn.
So, Iso-butyric acid will undergo Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction.
${\text{D}}{\text{.}}$ Trichloroacetic acid- This acid contains no alpha hydrogens as shown in the figure in which its structure is drawn.
So, Trichloroacetic acid will not undergo Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction due to the absence of any alpha hydrogen.
Therefore, option D is correct.
Note- For organic molecules, the alpha carbon refers to the first carbon atom that binds to a functional group, such as carbonyl. The atom of hydrogen bound to an alpha atom of carbon is considered an alpha-hydrogen molecule. The Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction mechanism is somewhat distinct from other reactions to halogenation, because it occurs in the absence of a halogen carrier.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




