
Which of the following compounds is amphoteric in nature?
A.
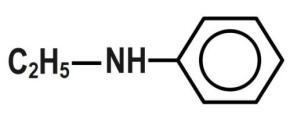
B.\[C{{H}_{3}}COOH\]
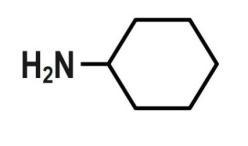
C.
D.\[C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\]


Answer
513.3k+ views
Hint: We know that an amphoteric compound is a molecule or ion that can react both as an acid and as a base. The element is from the thirteenth group of the periodic table. Now try to answer it accordingly. For example, water is amphoteric. It can be transformed into a compound that can be used as an alkali or an acid. Most amphoteric compounds are metal oxides or hydroxides.
Complete answer:
According to the Bronsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases: acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. An amphoteric molecule can either donate or accept a proton, thus acting either as an acid or a base. In the given question we have to observe that all of the options are compounds. Now we know that to have the amphoteric nature you need to have the characteristic of having both the reactions with the amphoteric in nature. So among these first we have to make the formulas for them then we can see which one also has the basic nature,
Amphoteric oxides are those metal oxides which show both the acidic and basic behavior. Amphoteric meaning, in the simplest term, can be stated as any compound that can be mixed with other compounds both as a base and an acid. Amphoteric is a popular term in the field of chemistry explaining the reactivity of a compound that shows alkaline nature when mixed with an acid and demonstrates acidic characteristics in an alkaline environment. As water is amphoteric, it is used widely for such reactions. Due to the presence of electrons over the N−atom of amide and having resonance structure, amides are amphoteric in nature.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note:
Remember that the metals such as copper, zinc, tin, lead, aluminium, and beryllium form amphoteric oxides or hydroxides. Amphoteric nature depends on the oxidation states of the oxide. The common examples of the amphoteric species are water, amino acids, hydrogen carbonate ion, and hydrogen sulfate ions.
Complete answer:
According to the Bronsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases: acids are proton donors and bases are proton acceptors. An amphoteric molecule can either donate or accept a proton, thus acting either as an acid or a base. In the given question we have to observe that all of the options are compounds. Now we know that to have the amphoteric nature you need to have the characteristic of having both the reactions with the amphoteric in nature. So among these first we have to make the formulas for them then we can see which one also has the basic nature,
Amphoteric oxides are those metal oxides which show both the acidic and basic behavior. Amphoteric meaning, in the simplest term, can be stated as any compound that can be mixed with other compounds both as a base and an acid. Amphoteric is a popular term in the field of chemistry explaining the reactivity of a compound that shows alkaline nature when mixed with an acid and demonstrates acidic characteristics in an alkaline environment. As water is amphoteric, it is used widely for such reactions. Due to the presence of electrons over the N−atom of amide and having resonance structure, amides are amphoteric in nature.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note:
Remember that the metals such as copper, zinc, tin, lead, aluminium, and beryllium form amphoteric oxides or hydroxides. Amphoteric nature depends on the oxidation states of the oxide. The common examples of the amphoteric species are water, amino acids, hydrogen carbonate ion, and hydrogen sulfate ions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




