
Which of the following compounds will not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction easily?
(A) Cumene
(B) Xylene
(C) Nitrobenzene
(D) Toluene
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: An atom that is attached to an aromatic ring is replaced with an electrophile in a reaction is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. Aromatic nitration, aromatic sulfonation, and Friedel-Crafts reactions are examples of this type of reaction. The aromaticity of aromatic compounds play an important role in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
Complete step by step solution:
Benzene ring involved in substitution reactions is two types based on the type of substituent that the ring carries, which are activated rings and deactivated rings.
If the substituent on the ring in which groups are donating electrons is an activated ring and which group withdraws electrons from a benzene ring is a deactivated ring.
Examples of activating groups in decreasing order,
$-N{{H}_{2}}>-N{{R}_{2}}-OH>-OR>-NHCOR>-C{{H}_{3}}$
Examples of deactivating groups with relative order from highest to lowest deactivating groups,
$-N{{O}_{2}}>-C{{F}_{3}}>-COR>-CN>-COOR>-S{{O}_{3}}H$
The activating group in the benzene ring directs the reaction to the Ortho or Para position and the deactivating group in the benzene ring directs the reaction to the Meta position.
Friedel-Crafts reaction: an organic coupling reaction involving an electrophilic aromatic substitution is used to attach a substituent to aromatic rings is Friedel-Crafts reaction, which reactions are two types- alkylation and acylation. In this reaction, aluminium chloride is used as a catalyst and involves the replacement of hydrogen atom with electrophile in an aromatic ring.
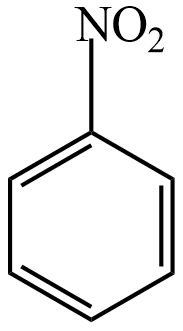
Nitrobenzene does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction, because the nitro group in nitrobenzene is a strong withdrawal group and this group repels the electrophile from it.
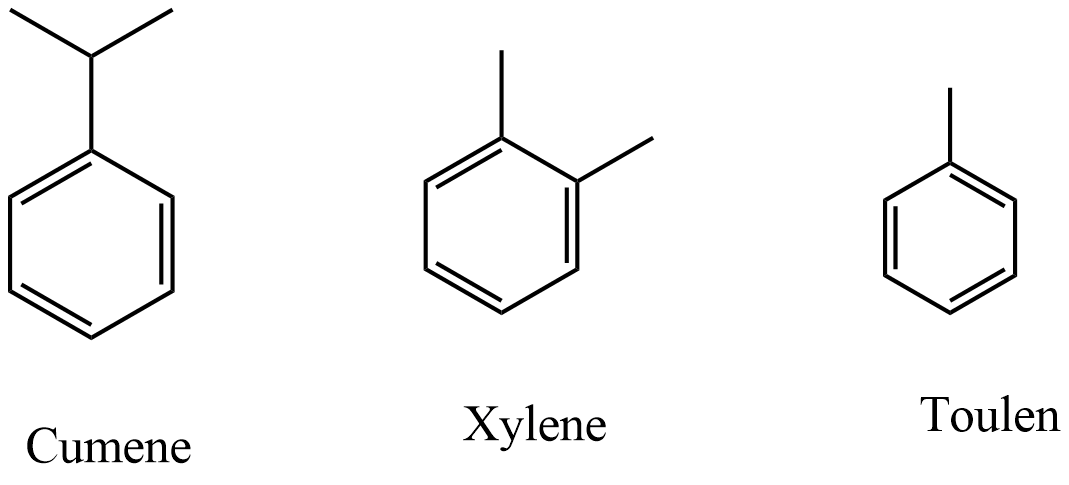
The remaining organic compounds given are containing electron-donating groups, which are undergoing Friedel-Crafts reactions easily. Hence, nitrobenzene will not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction easily.
So, the correct answer is option C.
Note: In electrophilic substitution reactions, the functional group is replaced by a hydrogen atom and is substituted in a chemical compound. Organic compounds involve two types of primary electrophilic substitution reactions which are electrophilic aromatic substitution and electrophilic aliphatic substitution reactions.
Complete step by step solution:
Benzene ring involved in substitution reactions is two types based on the type of substituent that the ring carries, which are activated rings and deactivated rings.
If the substituent on the ring in which groups are donating electrons is an activated ring and which group withdraws electrons from a benzene ring is a deactivated ring.
Examples of activating groups in decreasing order,
$-N{{H}_{2}}>-N{{R}_{2}}-OH>-OR>-NHCOR>-C{{H}_{3}}$
Examples of deactivating groups with relative order from highest to lowest deactivating groups,
$-N{{O}_{2}}>-C{{F}_{3}}>-COR>-CN>-COOR>-S{{O}_{3}}H$
The activating group in the benzene ring directs the reaction to the Ortho or Para position and the deactivating group in the benzene ring directs the reaction to the Meta position.
Friedel-Crafts reaction: an organic coupling reaction involving an electrophilic aromatic substitution is used to attach a substituent to aromatic rings is Friedel-Crafts reaction, which reactions are two types- alkylation and acylation. In this reaction, aluminium chloride is used as a catalyst and involves the replacement of hydrogen atom with electrophile in an aromatic ring.

Nitrobenzene does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction, because the nitro group in nitrobenzene is a strong withdrawal group and this group repels the electrophile from it.

The remaining organic compounds given are containing electron-donating groups, which are undergoing Friedel-Crafts reactions easily. Hence, nitrobenzene will not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction easily.
So, the correct answer is option C.
Note: In electrophilic substitution reactions, the functional group is replaced by a hydrogen atom and is substituted in a chemical compound. Organic compounds involve two types of primary electrophilic substitution reactions which are electrophilic aromatic substitution and electrophilic aliphatic substitution reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




