
Which of the following contains an olefinic bond?
A. Citric acid
B. Malic acid
C. Fumaric acid
D. Ethylene chloride
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Think about what an olefinic bond consists of based on the fact that another name for alkenes is olefins. Visualize the structures of the molecules given in the options and determine which one of them has an olefinic bond.
Complete answer:
An olefinic bond is an unsaturated double bond between two carbon atoms. Alkenes are also known by the name of olefins and the bond that gives them their olefinic characters is the olefinic, unsaturated double bonds. So, the molecule that has the carbon-carbon double bond will be considered to have an olefinic bond. We will look at the structures of each of the molecules mentioned here and determine which one of them has an olefinic bond.
- Citric acid
The molecular formula of citric acid is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{8}}{{O}_{7}}$, and its IUPAC name is 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid. The structure is:
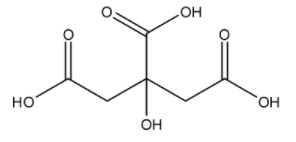
Here, we can see that none of the carbons have double bonds with each other. The only double bonds that carbon forms are with the oxygen atoms.
- Malic acid
The molecular formula of malic acid is ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{6}}{{O}_{5}}$, and its IUPAC name is 2-hydroxybutanedioic acid. The structure is:
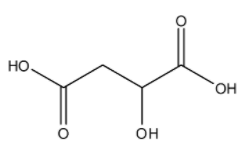
Here, we can see there are no carbon-carbon double bonds. The only double bonds that exist are between carbon and oxygen.
- Fumaric acid
The molecular formula of fumaric acid is ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{4}}{{O}_{4}}$, and its IUPAC name is (E)-but-2-enedioic acid. The structure is:
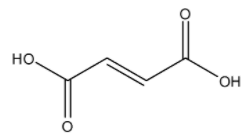
Here, we can see that there is one carbon-carbon bond present in the parent carbon chain. The carbon-carbon unsaturated double bond indicates that this is an olefinic compound and includes an olefinic bond. The IUPAC name for fumaric acid does not get confused due to the ‘E’ present. The ‘E’ in the IUPAC name signifies that the molecule has trans geometrical structure and not cis.
- Ethylene chloride
The molecular formula of ethylene chloride is ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}C{{l}_{2}}$, and its IUPAC name is 1,2-dichloroethane. The structure is:
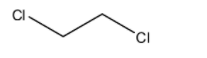
Here, we can see that there are no double bonds present in the molecule. So, it does not have an olefinic bond
Hence, the answer to this question is C. Fumaric acid
Note:
While considering the names for the given compounds, consider the common name for dichloroethane. Usually, the suffix ‘-ene’ is used to indicate that there is a carbon-carbon double bond present in the compound. But, here, the suffix ‘-ylene’ is used to indicate that the chloride is a vicinal dihalide, and not a geminal one. A geminal dihalide will have the name ethylidene chloride.
Complete answer:
An olefinic bond is an unsaturated double bond between two carbon atoms. Alkenes are also known by the name of olefins and the bond that gives them their olefinic characters is the olefinic, unsaturated double bonds. So, the molecule that has the carbon-carbon double bond will be considered to have an olefinic bond. We will look at the structures of each of the molecules mentioned here and determine which one of them has an olefinic bond.
- Citric acid
The molecular formula of citric acid is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{8}}{{O}_{7}}$, and its IUPAC name is 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid. The structure is:

Here, we can see that none of the carbons have double bonds with each other. The only double bonds that carbon forms are with the oxygen atoms.
- Malic acid
The molecular formula of malic acid is ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{6}}{{O}_{5}}$, and its IUPAC name is 2-hydroxybutanedioic acid. The structure is:

Here, we can see there are no carbon-carbon double bonds. The only double bonds that exist are between carbon and oxygen.
- Fumaric acid
The molecular formula of fumaric acid is ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{4}}{{O}_{4}}$, and its IUPAC name is (E)-but-2-enedioic acid. The structure is:

Here, we can see that there is one carbon-carbon bond present in the parent carbon chain. The carbon-carbon unsaturated double bond indicates that this is an olefinic compound and includes an olefinic bond. The IUPAC name for fumaric acid does not get confused due to the ‘E’ present. The ‘E’ in the IUPAC name signifies that the molecule has trans geometrical structure and not cis.
- Ethylene chloride
The molecular formula of ethylene chloride is ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}C{{l}_{2}}$, and its IUPAC name is 1,2-dichloroethane. The structure is:

Here, we can see that there are no double bonds present in the molecule. So, it does not have an olefinic bond
Hence, the answer to this question is C. Fumaric acid
Note:
While considering the names for the given compounds, consider the common name for dichloroethane. Usually, the suffix ‘-ene’ is used to indicate that there is a carbon-carbon double bond present in the compound. But, here, the suffix ‘-ylene’ is used to indicate that the chloride is a vicinal dihalide, and not a geminal one. A geminal dihalide will have the name ethylidene chloride.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




